PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... •To compute magnetic fields produced by currents, use BiotSavart’s law for each element of current, and then integrate. • Straight currents produce circular magnetic field lines, with amplitude B=0i/2r (use right hand rule for direction). • Circular currents produce a magnetic field at the center ...
... •To compute magnetic fields produced by currents, use BiotSavart’s law for each element of current, and then integrate. • Straight currents produce circular magnetic field lines, with amplitude B=0i/2r (use right hand rule for direction). • Circular currents produce a magnetic field at the center ...
Snímek 1 - Cesta k vědě - Gymnázium Jaroslava Seiferta
... Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon based upon the quantum mechanical magnetic properties of an atom's nucleus. All nuclei that contain odd numbers of protons or neutrons have an intrinsic magnetic moment and angular momentum. The most commonly measured nuclei are 1H (the most ...
... Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon based upon the quantum mechanical magnetic properties of an atom's nucleus. All nuclei that contain odd numbers of protons or neutrons have an intrinsic magnetic moment and angular momentum. The most commonly measured nuclei are 1H (the most ...
Pre-class test FISI-3171
... (Write your answers on the answer sheets.) 1. When two parallel wires have current flowing in the same direction, the mutual force they experience will be? (5 points) a) attractive. b) repulsive. c) zero. 2. A static electric field is conservative, but an electric field produced by a changing magnet ...
... (Write your answers on the answer sheets.) 1. When two parallel wires have current flowing in the same direction, the mutual force they experience will be? (5 points) a) attractive. b) repulsive. c) zero. 2. A static electric field is conservative, but an electric field produced by a changing magnet ...
9. Charges in motion in a magnetic field
... magnetic and electric fields whose magnitude are 0.10 T and 1000 N/C, respectively. Suddenly, the electric field is turned off and the ion is moving on a circular path of radius 1.2 cm, due to the action of the magnetic field, only. Find the mass of the ion. This is a spectrometer device able to ide ...
... magnetic and electric fields whose magnitude are 0.10 T and 1000 N/C, respectively. Suddenly, the electric field is turned off and the ion is moving on a circular path of radius 1.2 cm, due to the action of the magnetic field, only. Find the mass of the ion. This is a spectrometer device able to ide ...
Lesson Sheet
... pointing changed. This indicated that the electricity flowing through the wire had created a magnetic field. When he stopped the flow of electricity, the compass needle returned to its original position. Although most scientists are pleased by these unexpected discoveries, Hans Oersted was not. His ...
... pointing changed. This indicated that the electricity flowing through the wire had created a magnetic field. When he stopped the flow of electricity, the compass needle returned to its original position. Although most scientists are pleased by these unexpected discoveries, Hans Oersted was not. His ...
2015 Q10 - Loreto Balbriggan
... In a cloud chamber an electron travels perpendicular to the direction of a magnetic field of flux density 90 mT and it follows a circular path. Calculate the radius of the circle when the electron has a speed of 1.45 × 108 m s–1. Describe the path of a neutrino in the same magnetic field. ...
... In a cloud chamber an electron travels perpendicular to the direction of a magnetic field of flux density 90 mT and it follows a circular path. Calculate the radius of the circle when the electron has a speed of 1.45 × 108 m s–1. Describe the path of a neutrino in the same magnetic field. ...
Homework #1 Solutions
... E VALUATE : The force the electron exerts on the proton is equal in magnitude to the force the proton exerts on the electron, but the accelerations of the two particles are very different because their masses are very different. 21.10. IDENTIFY: We need to determine the number of protons in each box ...
... E VALUATE : The force the electron exerts on the proton is equal in magnitude to the force the proton exerts on the electron, but the accelerations of the two particles are very different because their masses are very different. 21.10. IDENTIFY: We need to determine the number of protons in each box ...
EXPLANATORY NOTE «Investigation of the effects of
... electrical form of energy to magnetic form and vice versa. As it is running at any other wave process for instance in the mechanics of continuum where kinetic energy of molecules movement of continuum is converted into the potential energy of interacting molecules and vice versa. Exactly this effect ...
... electrical form of energy to magnetic form and vice versa. As it is running at any other wave process for instance in the mechanics of continuum where kinetic energy of molecules movement of continuum is converted into the potential energy of interacting molecules and vice versa. Exactly this effect ...
Chapter 15 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN VACUUM
... propagating in the z direction, is uniform, that is, there is no oscillatory E field pointing in the direction of propagation. A uniform E field in the direction of propagation means that the component in the direction of propagation is not a travelling wave. That is, the oscillating electric f ...
... propagating in the z direction, is uniform, that is, there is no oscillatory E field pointing in the direction of propagation. A uniform E field in the direction of propagation means that the component in the direction of propagation is not a travelling wave. That is, the oscillating electric f ...
Chapter 18 - Electric Forces and Electric Fields • Atomic nature of
... • This is the electric force or the electrostatic force - force due to electric ...
... • This is the electric force or the electrostatic force - force due to electric ...
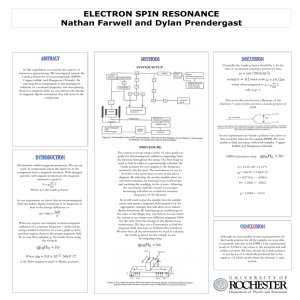
Poster: ESR
... This is not the case however. Because of the electrons ½ spin system, we have a Lande g-factor of ...
... This is not the case however. Because of the electrons ½ spin system, we have a Lande g-factor of ...
Physics 202 Exam 1.doc
... Ignore the sign of the answer. Answer ‘e’ is to be used as ‘none of the above’, ‘cannot be answered’, etc You may not have a cell phone or any electronic device (other than a non-programmable calculator with one memory and two pencils. You may not have any paper even blank or notes at your seat. You ...
... Ignore the sign of the answer. Answer ‘e’ is to be used as ‘none of the above’, ‘cannot be answered’, etc You may not have a cell phone or any electronic device (other than a non-programmable calculator with one memory and two pencils. You may not have any paper even blank or notes at your seat. You ...
Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion - Garnet Valley School District
... His friend sees him struggling so he helps push the box by applying a 25 Newton force in the same direction. What is the net force on the box? ...
... His friend sees him struggling so he helps push the box by applying a 25 Newton force in the same direction. What is the net force on the box? ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.