J J Thompson Lab - ahs-sph4u
... • is an elementary particle: smallest speck of matter • is normally found in the immediate vicinity of a nucleus, forming an atom • Mass (me): 9.11 x 10-31 kg • Charge (e): 1.6 x 10-19 C (C = Coulombs) • Charge is found by Millikan’s Oil Drop experiment • So, if we can find e/me, we can determine me ...
... • is an elementary particle: smallest speck of matter • is normally found in the immediate vicinity of a nucleus, forming an atom • Mass (me): 9.11 x 10-31 kg • Charge (e): 1.6 x 10-19 C (C = Coulombs) • Charge is found by Millikan’s Oil Drop experiment • So, if we can find e/me, we can determine me ...
Summary of equations chapters 7.
... We call this Ohm’s law also it is not a real law much more a rule of thumb. We derived a relation between current density and electric field using a microscopic model, calculating first the acceleration from the applied electric field, turning that into an acceleration of the electrons. We furthermo ...
... We call this Ohm’s law also it is not a real law much more a rule of thumb. We derived a relation between current density and electric field using a microscopic model, calculating first the acceleration from the applied electric field, turning that into an acceleration of the electrons. We furthermo ...
Science 2 Syllabus - Mueller at Brighton
... This outline is subject to change. Based on class time and students’ interests, topics may be added or eliminated. 1. The Foundation of Physics: Famous physicists, measuring, and what physics is all about 2. Matter: Composition of matter, atomic physics, molecules and mass, solids and liquids, gases ...
... This outline is subject to change. Based on class time and students’ interests, topics may be added or eliminated. 1. The Foundation of Physics: Famous physicists, measuring, and what physics is all about 2. Matter: Composition of matter, atomic physics, molecules and mass, solids and liquids, gases ...
Name
... 1. Which statement is not true? ___ 1. The electric field obeys the principle of superposition. ___ 2. The tangent to an electric field line at a point gives the direction of the field at that point. ___ 3. The density of electric field lines is directly proportional to the strength of the field. __ ...
... 1. Which statement is not true? ___ 1. The electric field obeys the principle of superposition. ___ 2. The tangent to an electric field line at a point gives the direction of the field at that point. ___ 3. The density of electric field lines is directly proportional to the strength of the field. __ ...
Physics Fall Midterm Review
... Differentiate between conductors and insulators Distinguish between charging by contact, charging by induction, charging by polarization Calculate electric force using Coulomb’s Law Apply the superposition principle to find the resultant force on a charge Describe the basic properties of e ...
... Differentiate between conductors and insulators Distinguish between charging by contact, charging by induction, charging by polarization Calculate electric force using Coulomb’s Law Apply the superposition principle to find the resultant force on a charge Describe the basic properties of e ...
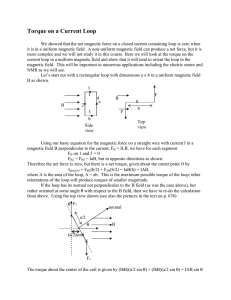
Torque on a Current Loop
... of the nucleus may depend on its local environment, since the other atoms nearby may produce small B fields themselves due to their circulating currents. NMR is so sensitive to this that it can measure a signal that tells the numbers of nuclei from atoms in different local environments. The signal l ...
... of the nucleus may depend on its local environment, since the other atoms nearby may produce small B fields themselves due to their circulating currents. NMR is so sensitive to this that it can measure a signal that tells the numbers of nuclei from atoms in different local environments. The signal l ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... Hang a bar magnet by a thread. It will line-up in a north-south direction. The end pointing north is the “north pole” The other end is the “south pole” ...
... Hang a bar magnet by a thread. It will line-up in a north-south direction. The end pointing north is the “north pole” The other end is the “south pole” ...
chapter32.4 - Colorado Mesa University
... After the discovery that electric current produces a magnetic field, Ampère set up two parallel wires that could carry large currents either in the same or opposite direction. ...
... After the discovery that electric current produces a magnetic field, Ampère set up two parallel wires that could carry large currents either in the same or opposite direction. ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.