Document
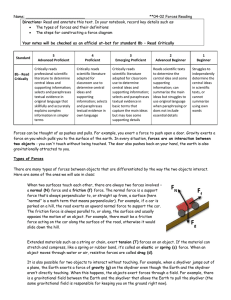
... force on you which pulls you to the surface of the earth. In every situation, forces are an interaction between two objects - you can't touch without being touched. The door also pushes back on your hand, the earth is also gravitationally attracted to you. Types of Forces There are many types of for ...
... force on you which pulls you to the surface of the earth. In every situation, forces are an interaction between two objects - you can't touch without being touched. The door also pushes back on your hand, the earth is also gravitationally attracted to you. Types of Forces There are many types of for ...
Why is there Magnetism?
... Conclusion • An example was given to show that, at least in one case, the effects of a magnetic field on a moving charge may be completely described as the effects of an electric field on that same charge in its rest frame • This is a general truth: magnetic effects are merely electric effects in a ...
... Conclusion • An example was given to show that, at least in one case, the effects of a magnetic field on a moving charge may be completely described as the effects of an electric field on that same charge in its rest frame • This is a general truth: magnetic effects are merely electric effects in a ...
Physics 2102 Spring 2002 Lecture 8
... Magnetic Force on a Wire of Arbitrary Shape Placed in a Nonuniform Magnetic Field In this case we divide the wire into elements of length dL, which can be considered as straight. The magnetic force on each element is dFB = idL B. The net magnetic force on the wire is given by the integral FB i ...
... Magnetic Force on a Wire of Arbitrary Shape Placed in a Nonuniform Magnetic Field In this case we divide the wire into elements of length dL, which can be considered as straight. The magnetic force on each element is dFB = idL B. The net magnetic force on the wire is given by the integral FB i ...
Physics MCAS Study Guide Motion and Forces Distance
... Radiation-heat that is transferred by electromagnetic radiation (infrared rays). Only heat transfer that can travel through a vacuum. Travels at speed of light. Phase changes occur when substances are at their melting/freezing or boiling/condensing temperatures and energy is absorbed or released. No ...
... Radiation-heat that is transferred by electromagnetic radiation (infrared rays). Only heat transfer that can travel through a vacuum. Travels at speed of light. Phase changes occur when substances are at their melting/freezing or boiling/condensing temperatures and energy is absorbed or released. No ...
Chapter 3
... stick together, are the source of friction. – Static friction=two surfaces not moving past each other – Sliding friction= opposes the motion of 2 surfaces sliding past each other – Rolling friction=between the rolling object and the surface it rolls on (tire on ...
... stick together, are the source of friction. – Static friction=two surfaces not moving past each other – Sliding friction= opposes the motion of 2 surfaces sliding past each other – Rolling friction=between the rolling object and the surface it rolls on (tire on ...
Displacement Current 2.
... The Transverse Electromagnetic (TEM) Wave. First we close the switch in the top conductor near the battery. Traditionally , when the resulting TEM step (i.e. logic transition from low to high) travels through a vacuum from left to right, guided by two conductors (the signal line and the 0v line), th ...
... The Transverse Electromagnetic (TEM) Wave. First we close the switch in the top conductor near the battery. Traditionally , when the resulting TEM step (i.e. logic transition from low to high) travels through a vacuum from left to right, guided by two conductors (the signal line and the 0v line), th ...
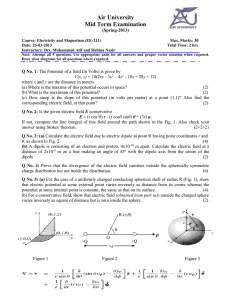
Q No - Air University
... (b) A dipole is consisting of an electron and proton, 4x10-10 m apart. Calculate the electric field at a distance of 2x10-8 m on a line making an angle of 45o with the dipole axis from the centre of the dipole. ...
... (b) A dipole is consisting of an electron and proton, 4x10-10 m apart. Calculate the electric field at a distance of 2x10-8 m on a line making an angle of 45o with the dipole axis from the centre of the dipole. ...
File
... • Bringing a charged object near (but not touching) a neutral object polarizes (temporarily separates) the charge of the neutral object. – Like charges in the neutral object are repelled by the charged object. – Unlike charges in the neutral object are attracted by the neutral object. ...
... • Bringing a charged object near (but not touching) a neutral object polarizes (temporarily separates) the charge of the neutral object. – Like charges in the neutral object are repelled by the charged object. – Unlike charges in the neutral object are attracted by the neutral object. ...
Magnetism - Electrical and Computer Engineering Department
... Classification of Materials according to magnetism Non-magnetic r=1 Ex. air, free space, many materials in their natural state. ...
... Classification of Materials according to magnetism Non-magnetic r=1 Ex. air, free space, many materials in their natural state. ...
1-Electromagnetic Forces - MrD-Home
... What happens then….. If we have a whole bunch of current carrying ...
... What happens then….. If we have a whole bunch of current carrying ...
magnetic field - Rosehill
... end of a magnet and enter the South end of a magnet. If you take a bar magnet and break it into two pieces, each piece will again have a North pole and a South pole. If you take one of those pieces and break it into two, each of the smaller pieces will have a North pole and a South pole. No matter h ...
... end of a magnet and enter the South end of a magnet. If you take a bar magnet and break it into two pieces, each piece will again have a North pole and a South pole. If you take one of those pieces and break it into two, each of the smaller pieces will have a North pole and a South pole. No matter h ...
PS2MotionForces
... When one object exerts a force on a second object, that second object exerts a force that is equal in strength, and opposite in direction or For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force ...
... When one object exerts a force on a second object, that second object exerts a force that is equal in strength, and opposite in direction or For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force ...
ECE 571 ()
... b. Prerequisite by Topic Students must also be familiar with transmission line circuits, transient and steady state solutions, phasors, reflection coefficient, Smith chart, matching circuits, wave propagation in materials, vector analysis, electrostatics, magnetostatics, steady electric currents, qu ...
... b. Prerequisite by Topic Students must also be familiar with transmission line circuits, transient and steady state solutions, phasors, reflection coefficient, Smith chart, matching circuits, wave propagation in materials, vector analysis, electrostatics, magnetostatics, steady electric currents, qu ...
Slide 1
... o It only really means something by defining what happens o It cannot really be ‘explained’ in terms of anything else o When drawing diagrams of objects with charge usually positive is RED negative BLUE (or black) but many other colours used, so be careful! ...
... o It only really means something by defining what happens o It cannot really be ‘explained’ in terms of anything else o When drawing diagrams of objects with charge usually positive is RED negative BLUE (or black) but many other colours used, so be careful! ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.