3 5-1 Kinematics of Uniform Circular Motion
... Modern physics currently recognizes four fundamental ...
... Modern physics currently recognizes four fundamental ...
Powerpoint template for scientific posters
... Materials and Methods We will solve Maxwell’s equations for the magnetic field of the system and the RF noise through the use of finite element analysis (see Figure 1). The system to be modeled is broken into multiple linked simplified regions of the original object, i.e. finite elements. Physic ...
... Materials and Methods We will solve Maxwell’s equations for the magnetic field of the system and the RF noise through the use of finite element analysis (see Figure 1). The system to be modeled is broken into multiple linked simplified regions of the original object, i.e. finite elements. Physic ...
Maxwell Eguations and Electromagnetic Waves
... We must underline the fact that the displacement current is not a real current, it is a timevarying electric field. The only reason for calling it displacement current density is that the dimension of this quantity coincides with that of current density. This phenomenon and equation is the symmetric ...
... We must underline the fact that the displacement current is not a real current, it is a timevarying electric field. The only reason for calling it displacement current density is that the dimension of this quantity coincides with that of current density. This phenomenon and equation is the symmetric ...
Document
... Energy may be transferred three ways: conduction, convection, and radiation. a) Energy may be conducted directly from one object to another as when a pan is in direct physical contact with a hot burner. b) The Sun heats the Earth’s surface with radiant energy causing the air near the ground to incre ...
... Energy may be transferred three ways: conduction, convection, and radiation. a) Energy may be conducted directly from one object to another as when a pan is in direct physical contact with a hot burner. b) The Sun heats the Earth’s surface with radiant energy causing the air near the ground to incre ...
Lesson 15 - Magnetic Fields II
... generators, stronger magnets (electromagnets), and electrical power. It was the development of the battery in the late 1700's that would begin the age of electricity. Thus, many of the conventions concerning magnets (using N/S instead of +/-) are historical in nature. ...
... generators, stronger magnets (electromagnets), and electrical power. It was the development of the battery in the late 1700's that would begin the age of electricity. Thus, many of the conventions concerning magnets (using N/S instead of +/-) are historical in nature. ...
Exam II - Physics
... A transformer utilizes two coils of wire, each connected to its own circuit. They are close enough to one another so that the magnetic field of the primary coil is detected as a flux within the secondary coil. If a constant, direct current (DC) is flowing through the primary coil, then the secondary ...
... A transformer utilizes two coils of wire, each connected to its own circuit. They are close enough to one another so that the magnetic field of the primary coil is detected as a flux within the secondary coil. If a constant, direct current (DC) is flowing through the primary coil, then the secondary ...
8Jsumm
... You can find the shape of the magnetic field using iron filings or using a plotting compass. The Earth has a magnetic field. A compass is a small magnet that always points north. But magnetic materials placed near a compass can change the direction that it points. Magnets can be used to sort iron an ...
... You can find the shape of the magnetic field using iron filings or using a plotting compass. The Earth has a magnetic field. A compass is a small magnet that always points north. But magnetic materials placed near a compass can change the direction that it points. Magnets can be used to sort iron an ...
PURDUE UNIVERSITY PHYS221 FINAL EXAM
... The resistance is not changed. The resistance increases by a factor of four. The resistance decreases by a factor of four. ...
... The resistance is not changed. The resistance increases by a factor of four. The resistance decreases by a factor of four. ...
1.3, 1.4
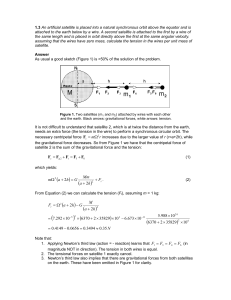
... magnitude NOT in direction). The tension in both wires is equal. 2. The tensional forces on satellite 1 exactly cancel. 3. Newton’s third law also implies that there are gravitational forces from both satellites on the earth. These have been omitted in Figure 1 for clarity. ...
... magnitude NOT in direction). The tension in both wires is equal. 2. The tensional forces on satellite 1 exactly cancel. 3. Newton’s third law also implies that there are gravitational forces from both satellites on the earth. These have been omitted in Figure 1 for clarity. ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.