maxwell.lab
... The approach we’ll use starts with a key observation: we have expressions for curlB in terms of E (actually, one of its derivatives) and for curlE in terms of B. Look at the second equation in the table. If we take the curl of both sides, we’ll have an expression for the curl of curlE (on the left) ...
... The approach we’ll use starts with a key observation: we have expressions for curlB in terms of E (actually, one of its derivatives) and for curlE in terms of B. Look at the second equation in the table. If we take the curl of both sides, we’ll have an expression for the curl of curlE (on the left) ...
AP Sample Questions
... An object at rest will stay at rest, an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force greater than zero Ex. A car rider continues forward when the driver suddenly applies the brakes ...
... An object at rest will stay at rest, an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force greater than zero Ex. A car rider continues forward when the driver suddenly applies the brakes ...
Lect13
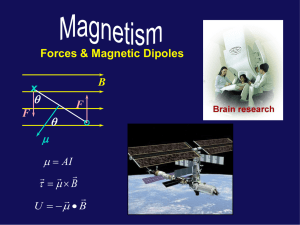
... • There will be a force on each of the charges moving in the wire. What will be the total force dF on a length dl of the wire? • Suppose current is made up of n charges/volume each carrying charge q and moving with velocity v through a wire of cross-section A. ...
... • There will be a force on each of the charges moving in the wire. What will be the total force dF on a length dl of the wire? • Suppose current is made up of n charges/volume each carrying charge q and moving with velocity v through a wire of cross-section A. ...
Purdue University PHYS221 EXAM I September 24,2002
... (15) The picture below shows the trajectories of particles produced in a particle physics experiment. The particles are moving from the center of the picture outward to the edges of the picture. There is a magnetic field present directed into the page. What are the signs on the charges of particles ...
... (15) The picture below shows the trajectories of particles produced in a particle physics experiment. The particles are moving from the center of the picture outward to the edges of the picture. There is a magnetic field present directed into the page. What are the signs on the charges of particles ...
PPT
... problem called the two dimensional Ising model in a magnetic field. It is built around a 16qubit superconducting adiabatic quantum computer processor. The system is designed to be used in concert with a conventional front end for any application that requires the solution of an NP-complete problem. ...
... problem called the two dimensional Ising model in a magnetic field. It is built around a 16qubit superconducting adiabatic quantum computer processor. The system is designed to be used in concert with a conventional front end for any application that requires the solution of an NP-complete problem. ...
Interactions Between Electric and Magnetic Fields.
... • What do you suppose would happen if the current in one of the wires changes direction? • Applying the cross product below and the right hand rule, we find that the force generated by the magnetic fields cause the wires to move away from each other. • In summary, if the current in both wires moves ...
... • What do you suppose would happen if the current in one of the wires changes direction? • Applying the cross product below and the right hand rule, we find that the force generated by the magnetic fields cause the wires to move away from each other. • In summary, if the current in both wires moves ...
fallagu2007posterv02
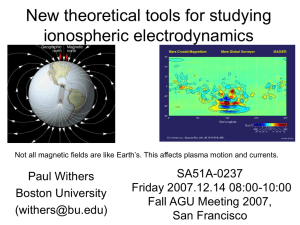
... ionospheric plasma motion. Dynamo theory and the conductivity equation is used to study currents caused by plasma motion. Ambipolar diffusion models are used to study changes in plasma density caused by vertical plasma motion. The conductivity equation, which states that the current density vector e ...
... ionospheric plasma motion. Dynamo theory and the conductivity equation is used to study currents caused by plasma motion. Ambipolar diffusion models are used to study changes in plasma density caused by vertical plasma motion. The conductivity equation, which states that the current density vector e ...
Document
... 2. Introduce the concepts and formalism for dealing with the coupling between rf fields and beams. 3. Then we will look at linear collider hardware to see how it works and how the concepts from sections 1 and 2 are implemented. 4. Study wakefields – these are beam/structure interactions which can le ...
... 2. Introduce the concepts and formalism for dealing with the coupling between rf fields and beams. 3. Then we will look at linear collider hardware to see how it works and how the concepts from sections 1 and 2 are implemented. 4. Study wakefields – these are beam/structure interactions which can le ...
Total Angular Momentum
... A magnesium atom excited to the 3s3p triplet state has no lower triplet state to which it can decay. It is called metastable, because it lives for such a long time on the atomic scale. ...
... A magnesium atom excited to the 3s3p triplet state has no lower triplet state to which it can decay. It is called metastable, because it lives for such a long time on the atomic scale. ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.