Chapter 2: Forces
... A girl pulls a wheeled backpack with a force of 3 N. If the backpack has a mass of 6 kg, what is its acceleration? ...
... A girl pulls a wheeled backpack with a force of 3 N. If the backpack has a mass of 6 kg, what is its acceleration? ...
BE 581
... If a current of 1 A flows in a direction perpendicular to the field lines of a 1 T magnetic field, each one-meter length of moving charges will experience a magnetic force of 1 N ...
... If a current of 1 A flows in a direction perpendicular to the field lines of a 1 T magnetic field, each one-meter length of moving charges will experience a magnetic force of 1 N ...
Electrostatics
... – Electrostatic Force of ith point charge is equal to charge qi (properties of the point: intrinsic) times a function E (property related to space and properties of other point charges: extrinsic) ...
... – Electrostatic Force of ith point charge is equal to charge qi (properties of the point: intrinsic) times a function E (property related to space and properties of other point charges: extrinsic) ...
Ch16_ChargesFields_p..
... If the test charge q is removed, electric field at position A is A) zero. the left. ...
... If the test charge q is removed, electric field at position A is A) zero. the left. ...
20-4 Motional emf
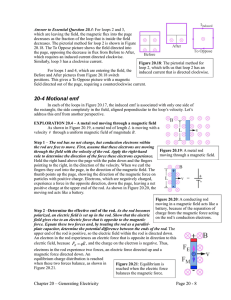
... In each of the loops in Figure 20.17, the induced emf is associated with only one side of the rectangle, the side completely in the field, aligned perpendicular to the loop’s velocity. Let’s address this emf from another perspective. EXPLORATION 20.4 – A metal rod moving through a magnetic field As ...
... In each of the loops in Figure 20.17, the induced emf is associated with only one side of the rectangle, the side completely in the field, aligned perpendicular to the loop’s velocity. Let’s address this emf from another perspective. EXPLORATION 20.4 – A metal rod moving through a magnetic field As ...
Chapter 30
... The torque has a maximum value when the field is perpendicular to the normal to the plane of the loop The torque is zero when the field is parallel to the normal to the plane of the loop IA B where A is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and has a magnitude equal to the area of the loop ...
... The torque has a maximum value when the field is perpendicular to the normal to the plane of the loop The torque is zero when the field is parallel to the normal to the plane of the loop IA B where A is perpendicular to the plane of the loop and has a magnitude equal to the area of the loop ...
If you put your cursor over a text box, it will be an arrow and WILL
... Which of the following is an example of acceleration? a) A runner moving at a constant speed of 2 m/s in a straight line. b) A car going at a constant speed around a circular track. c) An airplane taxiing at a constant speed in a straight line. d) All of the above. ...
... Which of the following is an example of acceleration? a) A runner moving at a constant speed of 2 m/s in a straight line. b) A car going at a constant speed around a circular track. c) An airplane taxiing at a constant speed in a straight line. d) All of the above. ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
... • Soft magnets are easier to magnetize than hard magnets, but they also loose their magnetism easier that hard magnets. • A magnetic pole is an area of a magnet where the magnetic force appears to be the strongest. • Two like poles of magnets repel each other; two opposite poles attract one another. ...
... • Soft magnets are easier to magnetize than hard magnets, but they also loose their magnetism easier that hard magnets. • A magnetic pole is an area of a magnet where the magnetic force appears to be the strongest. • Two like poles of magnets repel each other; two opposite poles attract one another. ...
how maglev trains operate
... coils in the system. Nonetheless, at slower speed (below 30 km/h or 19 mph), current induced in this coils and resultant magnetic flux are not large enough to levitate the train. So, wheels or other form of landing gears are installed to support the train until it reaches the take-off speed. ...
... coils in the system. Nonetheless, at slower speed (below 30 km/h or 19 mph), current induced in this coils and resultant magnetic flux are not large enough to levitate the train. So, wheels or other form of landing gears are installed to support the train until it reaches the take-off speed. ...
Origin of Inertial Mass
... Gravitational mass and inertial mass are distinct properties of matter that originate by fundamentally different mechanisms and relate to different forces. The force of gravity is an attraction of two bodies for each other. This article is concerned with inertial mass only and does not deal with gr ...
... Gravitational mass and inertial mass are distinct properties of matter that originate by fundamentally different mechanisms and relate to different forces. The force of gravity is an attraction of two bodies for each other. This article is concerned with inertial mass only and does not deal with gr ...
Modern Physics 342
... The following equation can be used to calculate any energy released from allowed transitions. DE (EOd EOp ) DmBB The difference Eod –Eop is constant, while Dml has 3 different values, therefore, DE has only three different values. ...
... The following equation can be used to calculate any energy released from allowed transitions. DE (EOd EOp ) DmBB The difference Eod –Eop is constant, while Dml has 3 different values, therefore, DE has only three different values. ...
Presentation2 Equilibrium Conditions
... mounted on small rollers so that it is free to move along the inclined ramp. Two cables are attached to the cart-one for each hand. If the hands are together so that the cables are parallel and if each cable lies essentially in a vertical plane, determine the force P which each hand must exert on it ...
... mounted on small rollers so that it is free to move along the inclined ramp. Two cables are attached to the cart-one for each hand. If the hands are together so that the cables are parallel and if each cable lies essentially in a vertical plane, determine the force P which each hand must exert on it ...
Back
... A 1 g bullet is fired into a 2kg block of wood with a initial velocity of 100m/s sitting on a frictionless surface? What is the final velocity of the bullet and the block of wood? Back ...
... A 1 g bullet is fired into a 2kg block of wood with a initial velocity of 100m/s sitting on a frictionless surface? What is the final velocity of the bullet and the block of wood? Back ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.