PHYSICS – Motor and Generators Section I
... current. The main features of a galvanometer, depicted on the right, are a carrying coil, magnets and a restoring spring. When current flows through the circuit and through the galvanometer, the motor effect is induced, producing a force that rotates the needle to one direction. However instead of r ...
... current. The main features of a galvanometer, depicted on the right, are a carrying coil, magnets and a restoring spring. When current flows through the circuit and through the galvanometer, the motor effect is induced, producing a force that rotates the needle to one direction. However instead of r ...
Document
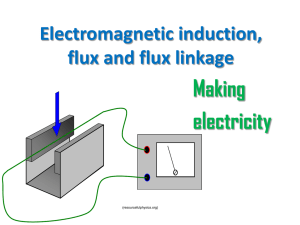
... If the loop moves from one region of magnetic field to another region of differing magnetic field ...
... If the loop moves from one region of magnetic field to another region of differing magnetic field ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion Reading Guide
... skate wheels on a road, sliding across tile, etc. (any situation where two surfaces are in contact and one is trying to slow the other down) 2. What makes force a vector? It has both size and direction. 3. What is a net force? The overall force acting on an object when all of the forces acting on it ...
... skate wheels on a road, sliding across tile, etc. (any situation where two surfaces are in contact and one is trying to slow the other down) 2. What makes force a vector? It has both size and direction. 3. What is a net force? The overall force acting on an object when all of the forces acting on it ...
Chapter 22 Electrostatics Exercise Answers
... a charge of the same sign as the ion. The side of the atom closer to the ion is then attracted more strongly to the ion than the farther side is repelled, making for a net attraction. (By Newton’s third law, the ion, in turn, is attracted to the atom.) 41. The forces on the electron and proton will ...
... a charge of the same sign as the ion. The side of the atom closer to the ion is then attracted more strongly to the ion than the farther side is repelled, making for a net attraction. (By Newton’s third law, the ion, in turn, is attracted to the atom.) 41. The forces on the electron and proton will ...
force
... (Direct Proportion – as one variable goes up or down the other variable also goes up or down) The force of gravity increases as the distance between two objects __________. The force of gravity decreases as the distance between two objects __________. ...
... (Direct Proportion – as one variable goes up or down the other variable also goes up or down) The force of gravity increases as the distance between two objects __________. The force of gravity decreases as the distance between two objects __________. ...
Assignment for the Course `Ferroelectric materials and Applications`
... - If the elastic energy in purely harmonic (has a quadratic dependence on P), is ferroelectricity possible? - What other condition the harmonic term of the elastic energy should fulfil? ...
... - If the elastic energy in purely harmonic (has a quadratic dependence on P), is ferroelectricity possible? - What other condition the harmonic term of the elastic energy should fulfil? ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... 2) Speed stays the same, but direction constantly changes 3) Cut the string a) Force = 0 b) Ball would fly out maintaining its velocity ...
... 2) Speed stays the same, but direction constantly changes 3) Cut the string a) Force = 0 b) Ball would fly out maintaining its velocity ...
ELECTRIC POTENTIAL-ENERGY (U)
... How much work does an external force Fext have to do to bring qo from infinity to a place located at a distance r from Q , at constant velocity? ...
... How much work does an external force Fext have to do to bring qo from infinity to a place located at a distance r from Q , at constant velocity? ...
12 Outline Small
... Balanced Forces: when the forces on an object are balanced, the net force is zero and there is no change in the object’s ...
... Balanced Forces: when the forces on an object are balanced, the net force is zero and there is no change in the object’s ...
Solutions1
... Picture the Problem Choose the coordinate system shown in the diagram and let Ug = 0 where y = 0. We’ll let our system include the ball and the earth. Then the work done on the ball by the electric field will change the energy of the system. The diagram summarizes what we know about the motion of th ...
... Picture the Problem Choose the coordinate system shown in the diagram and let Ug = 0 where y = 0. We’ll let our system include the ball and the earth. Then the work done on the ball by the electric field will change the energy of the system. The diagram summarizes what we know about the motion of th ...
6.013 Electromagnetics and Applications, Chapter 2
... where εo = 8.8542×10-12 [farads m-1] is the permittivity of vacuum, μo = 4π×10-7 [henries m-1] is the permeability of vacuum3, v is the velocity of the local net charge density ρ, and σ is the conductivity of a medium [Siemens m-1]. If we regard the electrical sources ρ and J as given, then the equa ...
... where εo = 8.8542×10-12 [farads m-1] is the permittivity of vacuum, μo = 4π×10-7 [henries m-1] is the permeability of vacuum3, v is the velocity of the local net charge density ρ, and σ is the conductivity of a medium [Siemens m-1]. If we regard the electrical sources ρ and J as given, then the equa ...
Lecture Notes and Solved Problems
... period during which the field can be allowed to vanish if the magnitude of the average induced emf is to be kept less than 0.010 V. Solution: Use Faraday's law of induction. ...
... period during which the field can be allowed to vanish if the magnitude of the average induced emf is to be kept less than 0.010 V. Solution: Use Faraday's law of induction. ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.