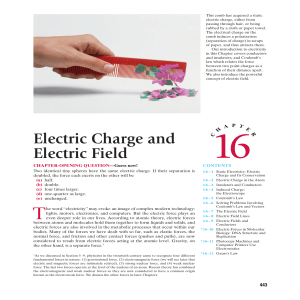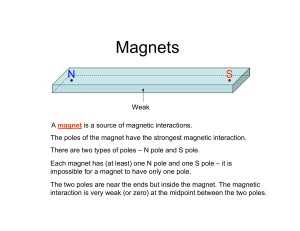
Magnets
... Each magnet has (at least) one N pole and one S pole – it is impossible for a magnet to have only one pole. The two poles are near the ends but inside the magnet. The magnetic interaction is very weak (or zero) at the midpoint between the two poles. ...
... Each magnet has (at least) one N pole and one S pole – it is impossible for a magnet to have only one pole. The two poles are near the ends but inside the magnet. The magnetic interaction is very weak (or zero) at the midpoint between the two poles. ...
Ch 16) Electric Charge and Electric Field
... even deeper role in our lives. According to atomic theory, electric forces between atoms and molecules hold them together to form liquids and solids, and electric forces are also involved in the metabolic processes that occur within our bodies. Many of the forces we have dealt with so far, such as e ...
... even deeper role in our lives. According to atomic theory, electric forces between atoms and molecules hold them together to form liquids and solids, and electric forces are also involved in the metabolic processes that occur within our bodies. Many of the forces we have dealt with so far, such as e ...
Quarks, Gluons, QCD
... are calculated and measured to be independent of Q2 at constant Bjorken x • Inelastic structure functions are independent on Q2 -> constituents are pointlike and quasi-free (inside the proton) • One experimental example • Structure function = Fourier Transform of charge distribution→ Structure Funct ...
... are calculated and measured to be independent of Q2 at constant Bjorken x • Inelastic structure functions are independent on Q2 -> constituents are pointlike and quasi-free (inside the proton) • One experimental example • Structure function = Fourier Transform of charge distribution→ Structure Funct ...
Velocity shear instability and plasma billows at the Earth`s magnetic
... different conditions of geomagnetic configuration, solar wind, and solar cycle. Because of the frequent observation in situ of the CDPS during periods of northward IMF the subject engages the attention of the magnetospheric community. During periods of northward IMF the KH instability is an importan ...
... different conditions of geomagnetic configuration, solar wind, and solar cycle. Because of the frequent observation in situ of the CDPS during periods of northward IMF the subject engages the attention of the magnetospheric community. During periods of northward IMF the KH instability is an importan ...
The Earth`s Magnetic Field
... environment from dangerous radiation and high energy plasma from the Sun by partially blocking it out. However, there is always some part of the plasma and radiation that is able to penetrate through the magnetic field barrier, and this often leads to magnetic disturbances around the Earth. Before h ...
... environment from dangerous radiation and high energy plasma from the Sun by partially blocking it out. However, there is always some part of the plasma and radiation that is able to penetrate through the magnetic field barrier, and this often leads to magnetic disturbances around the Earth. Before h ...
battery. - SCHOOLinSITES
... • The earliest and best known person for having studied the nature of gravitational force is (38) Isaac Newton. • The force of attraction between two bodies is (39) gravitational force. • It is directly proportional to the mass of an object – the greater the mass, the greater the gravitational force ...
... • The earliest and best known person for having studied the nature of gravitational force is (38) Isaac Newton. • The force of attraction between two bodies is (39) gravitational force. • It is directly proportional to the mass of an object – the greater the mass, the greater the gravitational force ...
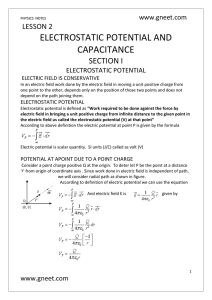
electrostatic potential and capacitance
... Thus in the case of metallic conductor, placed in an external electric field (1) A steady electric charge distribution is induced on the surface of the conductor (2) The net electric field inside the conductor is zero (3) The net electric charge inside the conductor is zero (4) On the outer surface ...
... Thus in the case of metallic conductor, placed in an external electric field (1) A steady electric charge distribution is induced on the surface of the conductor (2) The net electric field inside the conductor is zero (3) The net electric charge inside the conductor is zero (4) On the outer surface ...
Memristor-The Missing Circuit Element
... shown in Fig. 3.4 Using this tracer, the p-q curves of three memristors realized by the type-l M-R mutator circuit of Fig. 2 are shown in Fig. 4(b), (d), and (f) corresponding to the nonlinear resistor V-Z curve shown in Fig. 4(c), (e), and (g), respectively. To demonstrate the rather “peculiar” vol ...
... shown in Fig. 3.4 Using this tracer, the p-q curves of three memristors realized by the type-l M-R mutator circuit of Fig. 2 are shown in Fig. 4(b), (d), and (f) corresponding to the nonlinear resistor V-Z curve shown in Fig. 4(c), (e), and (g), respectively. To demonstrate the rather “peculiar” vol ...
Proceedings - TRANSCOM 2017, 12th international
... currents. Type of excitation coil and its spatial orientation influence the selection. For example for the plate with a thickness of 5mm the optimum excitation frequency is 20kHz for both the considered coils. When the plate with a thickness of 30mm is used in conjunction with a circular coil the op ...
... currents. Type of excitation coil and its spatial orientation influence the selection. For example for the plate with a thickness of 5mm the optimum excitation frequency is 20kHz for both the considered coils. When the plate with a thickness of 30mm is used in conjunction with a circular coil the op ...
Quantum Physics
... Active Figure 27.4 is a schematic diagram of a photoelectric effect apparatus. An evacuated glass tube known as a photocell contains a metal plate E (the emitter) connected to the negative terminal of a variable power supply. Another metal plate, C (the collector), is maintained at a positive potent ...
... Active Figure 27.4 is a schematic diagram of a photoelectric effect apparatus. An evacuated glass tube known as a photocell contains a metal plate E (the emitter) connected to the negative terminal of a variable power supply. Another metal plate, C (the collector), is maintained at a positive potent ...
Wadhwa_uta_2502M_10153
... moments contribute to its overall response; the magnetic induction is given by: B=µo (H+M) where µo is the permeability of free space, and the magnetization M is the magnetic moment per unit volume. All materials are magnetic to some extent, with their response depending upon their atomic structure ...
... moments contribute to its overall response; the magnetic induction is given by: B=µo (H+M) where µo is the permeability of free space, and the magnetization M is the magnetic moment per unit volume. All materials are magnetic to some extent, with their response depending upon their atomic structure ...
MODELING THE BEHAVIOR OF A HOMOPOLAR MOTOR
... this thesis using both physical experimentation and simulation software. This type of motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy using the Lorentz force. The torque from this force is used to propel the homopolar motor forward. The nickel-metal hydride batteries used in this study store ...
... this thesis using both physical experimentation and simulation software. This type of motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy using the Lorentz force. The torque from this force is used to propel the homopolar motor forward. The nickel-metal hydride batteries used in this study store ...
Electric field of due to a point charge.
... Example: calculate the electric field at the electron’s distance away from the proton in a hydrogen atom (5.3x10-11 m). To be worked at the blackboard. ...
... Example: calculate the electric field at the electron’s distance away from the proton in a hydrogen atom (5.3x10-11 m). To be worked at the blackboard. ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.