News
... current loop, Moving coil galvanometer, Ammeter, Voltmeter, Hall effect, Circulating charge, Thompson’s experiment. 9. Ampere’s Law and Biot-Savart Law: Ampere’s law and application such as calculation of magnetic induction near a long wire, inside a current carrying cylindrical wire, inside a solen ...
... current loop, Moving coil galvanometer, Ammeter, Voltmeter, Hall effect, Circulating charge, Thompson’s experiment. 9. Ampere’s Law and Biot-Savart Law: Ampere’s law and application such as calculation of magnetic induction near a long wire, inside a current carrying cylindrical wire, inside a solen ...
2016 - thephysicsteacher.ie
... The restoring force is the force acting in towards equilibrium position. There doesn’t seem to be any force acting in this direction, but there is a component of the weight acting inwards. To find out the size of this inward component we resolve the 3.5 N into 2 components; one acting in the directi ...
... The restoring force is the force acting in towards equilibrium position. There doesn’t seem to be any force acting in this direction, but there is a component of the weight acting inwards. To find out the size of this inward component we resolve the 3.5 N into 2 components; one acting in the directi ...
PowerPoint - GeoWeb
... • If the dispersion is small, then the packet maintains its shape by propagates with a velocity given by dw/dk as opposed to individual frequencies that propagate with velocity w/k ...
... • If the dispersion is small, then the packet maintains its shape by propagates with a velocity given by dw/dk as opposed to individual frequencies that propagate with velocity w/k ...
Forces Practice Questions 1. A push or pull is called a. motion b
... a. The forces are unbalanced. b. The forces are balanced. c. A positive net force is acting on the bike. d. A negative net force is acting on the bike. 23. The motion of an object can be changed by a(n) a. unbalanced force b. balanced force c. net force equal to zero d. large velocity 24. Newton’s f ...
... a. The forces are unbalanced. b. The forces are balanced. c. A positive net force is acting on the bike. d. A negative net force is acting on the bike. 23. The motion of an object can be changed by a(n) a. unbalanced force b. balanced force c. net force equal to zero d. large velocity 24. Newton’s f ...
What Is a Force?
... • Both gravity and air resistance affect the motion of a falling object. • As objects fall to the ground, they accelerate and gain speed. • Terminal velocity is the constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity. ...
... • Both gravity and air resistance affect the motion of a falling object. • As objects fall to the ground, they accelerate and gain speed. • Terminal velocity is the constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity. ...
Lecture slides with notes - University of Toronto Physics
... Magnet: An object consisting of two poles called North and South Poles of a magnet are the ends where objects are most strongly attracted ...
... Magnet: An object consisting of two poles called North and South Poles of a magnet are the ends where objects are most strongly attracted ...
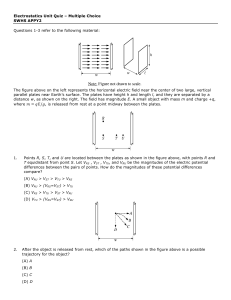
1. Which point, J or K, has a higher electric potential
... The work is the same along both paths, for this reason: Along path 2, you fight the field head on (from F to D), which means your force is directly against the field; but that force acts over a short distance. Along path 1 you fight the field at an angle, not head-on, which means you’re exerting a s ...
... The work is the same along both paths, for this reason: Along path 2, you fight the field head on (from F to D), which means your force is directly against the field; but that force acts over a short distance. Along path 1 you fight the field at an angle, not head-on, which means you’re exerting a s ...
Momentum - Cloudfront.net
... The rational is that if you are going to collide with something at a high speed, it is better to allow the kinetic energy to crumple the bumper in an inelastic collision than let the bumper shake you around as your car bounces in an elastic collision. Making their bumpers this way benefits the car c ...
... The rational is that if you are going to collide with something at a high speed, it is better to allow the kinetic energy to crumple the bumper in an inelastic collision than let the bumper shake you around as your car bounces in an elastic collision. Making their bumpers this way benefits the car c ...
inelastic collision
... Ex. 6 - Starting from rest, two skaters “push off” against each other on smooth level ice. One is a woman (m1 = 54 kg), and one is a man (m2 = 88 kg). The woman recoils with a velocity of vf1 = +2.5 m/s. Find the recoil velocity vf2 of the man. ...
... Ex. 6 - Starting from rest, two skaters “push off” against each other on smooth level ice. One is a woman (m1 = 54 kg), and one is a man (m2 = 88 kg). The woman recoils with a velocity of vf1 = +2.5 m/s. Find the recoil velocity vf2 of the man. ...
electromagnetic induction
... This expression shows that the inducted emf and consequently the current in the coil change their direction in sinusoidal way. So, an alternating sinusoidal emf (fig.7) (and current) is induced in coil. In a real AC generator the current goes out of coil into the external circuit by use of a set of ...
... This expression shows that the inducted emf and consequently the current in the coil change their direction in sinusoidal way. So, an alternating sinusoidal emf (fig.7) (and current) is induced in coil. In a real AC generator the current goes out of coil into the external circuit by use of a set of ...
Magnetic Field B is
... • The source of the Earth’s magnetic field is likely convection currents in the Earth’s core. • There is strong evidence that the magnitude of a planet’s magnetic field is related to its rate of rotation. • The direction of the Earth’s magnetic field reverses Periodically (over thousands of years!). ...
... • The source of the Earth’s magnetic field is likely convection currents in the Earth’s core. • There is strong evidence that the magnitude of a planet’s magnetic field is related to its rate of rotation. • The direction of the Earth’s magnetic field reverses Periodically (over thousands of years!). ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.