Uniform Electric Fields
... The electric field is uniform? Yes. The lines are equally spaced and parallel between the plates. At the ends of the plates, you will get some bowing, like in the diagram on the first page. But in between the plates, the field is constant. Don’t loose sight that we are talking about the area bet ...
... The electric field is uniform? Yes. The lines are equally spaced and parallel between the plates. At the ends of the plates, you will get some bowing, like in the diagram on the first page. But in between the plates, the field is constant. Don’t loose sight that we are talking about the area bet ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy conclusion
... THE PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Energy can neither be created not destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of molecul ...
... THE PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Energy can neither be created not destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another. The result of a non-conservative force is often to remove mechanical energy and transform it into heat. Heat energy is the kinetic or vibrational energy of molecul ...
chapter25.4 - Colorado Mesa University
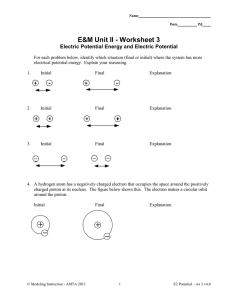
... I only. II only. I and II. II and III. None of these. ...
... I only. II only. I and II. II and III. None of these. ...
Millikan`s Idea Robert Millikan was a scientist who studied electricity
... charged plates at the top and bottom ...
... charged plates at the top and bottom ...
[ ] ( )
... The positive charge at point P is being moved into a more positive region of space (closer to the lower left corner) and, therefore, against an increasingly stronger electric field. Thus, the movement of this charge will require an applied force (that will need to increase against the increasing ele ...
... The positive charge at point P is being moved into a more positive region of space (closer to the lower left corner) and, therefore, against an increasingly stronger electric field. Thus, the movement of this charge will require an applied force (that will need to increase against the increasing ele ...
Chapter 4 - Equilibrium of Particle
... - Tension always acts in the direction of the cable - Tension force in a continuous cable must have a constant magnitude for equilibrium ...
... - Tension always acts in the direction of the cable - Tension force in a continuous cable must have a constant magnitude for equilibrium ...
MU08-CHAPTER4.doc
... electric current consists of a lot of free charges carrying the electric current charge, put forwarded by an external voltage source connected to the end points of the wire loop. In aim of demonstrating this arrangement, we make use of the adjoining figure (see above). The wire is placed out in a x, ...
... electric current consists of a lot of free charges carrying the electric current charge, put forwarded by an external voltage source connected to the end points of the wire loop. In aim of demonstrating this arrangement, we make use of the adjoining figure (see above). The wire is placed out in a x, ...
Motor Effect - Seattle Central
... north pole of the magnets by using a compass; the south end of a compass will point toward the north pole of a magnet.) Your palm will then naturally "push" in the direction of the magnetic force on the wire. The deflecting force that a magnet exerts on a current-carrying wire is the mechanism behi ...
... north pole of the magnets by using a compass; the south end of a compass will point toward the north pole of a magnet.) Your palm will then naturally "push" in the direction of the magnetic force on the wire. The deflecting force that a magnet exerts on a current-carrying wire is the mechanism behi ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.












![[ ] ( )](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008772670_1-1114645c0ba57101fceae49a66333251-300x300.png)