MasteringPhysics: Assignment Print View
... Learning Goal: To understand the electric force between charged and uncharged conductors and insulators. When a test charge is brought near a charged object, we know from Coulomb's law that it will experience a net force (either attractive or repulsive, depending on the nature of the object's charge ...
... Learning Goal: To understand the electric force between charged and uncharged conductors and insulators. When a test charge is brought near a charged object, we know from Coulomb's law that it will experience a net force (either attractive or repulsive, depending on the nature of the object's charge ...
2.3 Mechanical Advantage
... class lever that converts a small input force into a much larger output force. When a machine turns a small input force into a larger output force, we say that the machine gives us a mechanical advantage. Mechanical advantage (MA) is the ratio of the output force to the input force (for example, the ...
... class lever that converts a small input force into a much larger output force. When a machine turns a small input force into a larger output force, we say that the machine gives us a mechanical advantage. Mechanical advantage (MA) is the ratio of the output force to the input force (for example, the ...
Updated Tutor HS Physics Content - legacy
... water as shown in the photo. There are simple laws of physics that govern motion. These laws are universal; that is, they apply to every object in the universe. Much of the work done in describing motion was done by Sir Isaac Newton. This chapter is about motion, the causes of motion, and the univer ...
... water as shown in the photo. There are simple laws of physics that govern motion. These laws are universal; that is, they apply to every object in the universe. Much of the work done in describing motion was done by Sir Isaac Newton. This chapter is about motion, the causes of motion, and the univer ...
The Magnetic Field of the Earth
... that Gilbert postulated that the Earth is, in fact, a gigantic magnet. The origin of the Earth’s field has, however, remained enigmatic for another 300 years after Gilbert’s manifesto ’De Magnete’. It was also known early on that the field was not constant in time, and the secular variation is well ...
... that Gilbert postulated that the Earth is, in fact, a gigantic magnet. The origin of the Earth’s field has, however, remained enigmatic for another 300 years after Gilbert’s manifesto ’De Magnete’. It was also known early on that the field was not constant in time, and the secular variation is well ...
Chapter 21 The Electric Field I: Discrete Charge Distributions
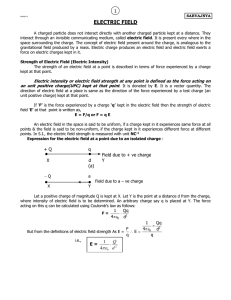
... (c) False. Electric field lines intersect any point in space occupied by a point charge. (d) True. An electric field partially polarizes the molecules; resulting in the separation of their charges and the creation of electric dipole moments. 17 ••• [SSM] Two molecules have dipole moments of equal ma ...
... (c) False. Electric field lines intersect any point in space occupied by a point charge. (d) True. An electric field partially polarizes the molecules; resulting in the separation of their charges and the creation of electric dipole moments. 17 ••• [SSM] Two molecules have dipole moments of equal ma ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... This document is a work in progress. An issue under consideration is whether inductance shortfall due to field inhomogeneity should be represented as an operator acting on the number of turns, or as a finite reluctance on the external magnetic path. The turns operator approach has been used in this ...
... This document is a work in progress. An issue under consideration is whether inductance shortfall due to field inhomogeneity should be represented as an operator acting on the number of turns, or as a finite reluctance on the external magnetic path. The turns operator approach has been used in this ...
Section 9.6: Work done on a many
... • When the work done by an external force on a system is positive, the change in energy is positive, and when work is negative, the energy change is negative. • External force adds or subtracts energy from system • Examples of negative and positive work are illustrated in the figure • The work done ...
... • When the work done by an external force on a system is positive, the change in energy is positive, and when work is negative, the energy change is negative. • External force adds or subtracts energy from system • Examples of negative and positive work are illustrated in the figure • The work done ...
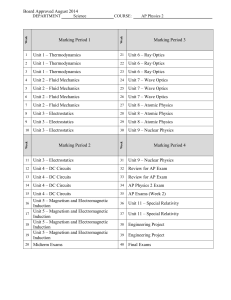
Marking Period 1 Marking Period 3 Unit 1 – Thermodynamics 21
... The AP Physics 1: Algebra-based and AP Physics 2: Algebra-based concepts are articulated together in one concept outline, providing the full scope of conceptual understandings a student should acquire by the end of an introductory sequence in college-level algebra-based physics. The key concepts and ...
... The AP Physics 1: Algebra-based and AP Physics 2: Algebra-based concepts are articulated together in one concept outline, providing the full scope of conceptual understandings a student should acquire by the end of an introductory sequence in college-level algebra-based physics. The key concepts and ...
The nature of Petschek-type reconnection T. G. Forbes
... and thickness, no detailed matching is possible between the flows in the diffusion region and the flows in the external region outside. This lack of detailed matching is sometimes misunderstood to mean that there is no matching at all, but in fact the average properties of the diffusion region are r ...
... and thickness, no detailed matching is possible between the flows in the diffusion region and the flows in the external region outside. This lack of detailed matching is sometimes misunderstood to mean that there is no matching at all, but in fact the average properties of the diffusion region are r ...
How to Succeed in Physics (and reduce your workload)
... Founded by two Harvard graduates in 2005, Veritas Tutors (www. veritutors.com) is the premiere provider of educational services and products in the Boston area. Offering subject tutoring, standardized test preparation, and admissions consulting, Veritas Tutors is dedicated to providing the best poss ...
... Founded by two Harvard graduates in 2005, Veritas Tutors (www. veritutors.com) is the premiere provider of educational services and products in the Boston area. Offering subject tutoring, standardized test preparation, and admissions consulting, Veritas Tutors is dedicated to providing the best poss ...
Interaction and confinement in nanostructures: Spin
... dots [7] has been achieved. These oscillations – the back and forth flopping between two states in a quantum mechanical superposition – directly show quantum mechanics at work. The observation of coherent oscillations in solid-state systems represents the frontier in our ability to control nature at ...
... dots [7] has been achieved. These oscillations – the back and forth flopping between two states in a quantum mechanical superposition – directly show quantum mechanics at work. The observation of coherent oscillations in solid-state systems represents the frontier in our ability to control nature at ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.