PHYS150-Ch19
... Ferromagnetic materials have domains, regions in which its atomic dipoles are aligned, giving the region a strong dipole moment. ...
... Ferromagnetic materials have domains, regions in which its atomic dipoles are aligned, giving the region a strong dipole moment. ...
Section 15: Magnetic properties of materials
... more or less exactly for sufficiently high T. Here C and TC are positive constants independent of temperature and different for each material. It was found that in some materials TC=0 and this equation is obeyed down to the lowest temperatures at which measurements have been made. This class of mate ...
... more or less exactly for sufficiently high T. Here C and TC are positive constants independent of temperature and different for each material. It was found that in some materials TC=0 and this equation is obeyed down to the lowest temperatures at which measurements have been made. This class of mate ...
EMF Brochure 2013
... The American Cancer Society reviewed a January 2000 study that found no association between EMFs and childhood cancer: “This was a nice, large, population-based study. It found no evidence of an association of EMF and acute lymphoclastic leukemia, all leukemias, central nervous system tumors, and al ...
... The American Cancer Society reviewed a January 2000 study that found no association between EMFs and childhood cancer: “This was a nice, large, population-based study. It found no evidence of an association of EMF and acute lymphoclastic leukemia, all leukemias, central nervous system tumors, and al ...
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES
... not appear to be inherent in the phenomena. Take, for example, the reciprocal electrodynamic action of a magnet and a conductor. The observable phenomenon here depends only on the relative motion of the conductor and the magnet, whereas the customary view draws a sharp distinction between the two ca ...
... not appear to be inherent in the phenomena. Take, for example, the reciprocal electrodynamic action of a magnet and a conductor. The observable phenomenon here depends only on the relative motion of the conductor and the magnet, whereas the customary view draws a sharp distinction between the two ca ...
on the electrodynamics of moving bodies
... not appear to be inherent in the phenomena. Take, for example, the reciprocal electrodynamic action of a magnet and a conductor. The observable phenomenon here depends only on the relative motion of the conductor and the magnet, whereas the customary view draws a sharp distinction between the two ca ...
... not appear to be inherent in the phenomena. Take, for example, the reciprocal electrodynamic action of a magnet and a conductor. The observable phenomenon here depends only on the relative motion of the conductor and the magnet, whereas the customary view draws a sharp distinction between the two ca ...
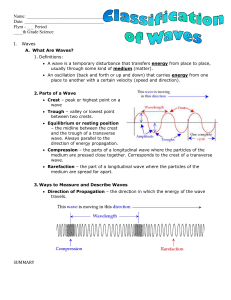
Waves What Are Waves? Definitions: A wave is a temporary
... gives rise to the electric force, which causes static electricity and drives the flow of electric current in electrical conductors. The magnetic field can be produced by the motion of electric charges, such as an electric current flowing along a wire, and gives rise to the magnetic force one assoc ...
... gives rise to the electric force, which causes static electricity and drives the flow of electric current in electrical conductors. The magnetic field can be produced by the motion of electric charges, such as an electric current flowing along a wire, and gives rise to the magnetic force one assoc ...
16-1 and 16-2 Electric Charge
... 5. Explain the concept of electric field and determine the resultant electric field at a point some distance from two or more point charges. 6. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric force on a charged particle placed in an electric field. 7. Sketch the electric field pattern in the r ...
... 5. Explain the concept of electric field and determine the resultant electric field at a point some distance from two or more point charges. 6. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric force on a charged particle placed in an electric field. 7. Sketch the electric field pattern in the r ...
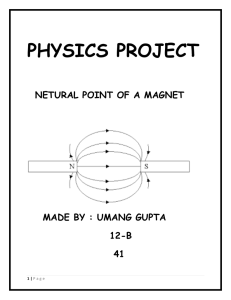
Neutral point of a Magnet
... around the magnet. It is determined which direction a current is flowing by using a series of left-hand rules. Each magnet has its own flux shape, and rule. 8|Page ...
... around the magnet. It is determined which direction a current is flowing by using a series of left-hand rules. Each magnet has its own flux shape, and rule. 8|Page ...
Wednesday, Jan. 25, 2006
... Motion of a Charged Particle in an Electric Field • If an object with an electric charge q is at a point in space where electric field is E, the force exerting on the object is F qE. • What do you think will happen to the charge? – Let’s think about the cases like these on the right. – The object ...
... Motion of a Charged Particle in an Electric Field • If an object with an electric charge q is at a point in space where electric field is E, the force exerting on the object is F qE. • What do you think will happen to the charge? – Let’s think about the cases like these on the right. – The object ...
Problem 1. (5 points) A number of point charges with values Qi are
... Problem 1. (5 points) A number of point charges with values Qi are fixed at positions ri. If we double the value of each and every charge, but keep the positions the same, the following quantities also double (list all that apply): (A) the total potential energy of system, (B) the force between part ...
... Problem 1. (5 points) A number of point charges with values Qi are fixed at positions ri. If we double the value of each and every charge, but keep the positions the same, the following quantities also double (list all that apply): (A) the total potential energy of system, (B) the force between part ...
Google DeepMind Neural Networks
... Duality and the electron’s spin also, building the Bridge between the Classical and Quantum Theories. The Planck Distribution Law of the electromagnetic oscillators explains the electron/proton mass rate and the Weak and Strong Interactions by the diffraction patterns. The Weak Interaction changes t ...
... Duality and the electron’s spin also, building the Bridge between the Classical and Quantum Theories. The Planck Distribution Law of the electromagnetic oscillators explains the electron/proton mass rate and the Weak and Strong Interactions by the diffraction patterns. The Weak Interaction changes t ...
Document
... without friction at constant speed. What is I? In what direction does it flow? • The component of the weight down the plane must be equal to the component of the magnetic force up the plane... Wednesday, February 6, 2008 ...
... without friction at constant speed. What is I? In what direction does it flow? • The component of the weight down the plane must be equal to the component of the magnetic force up the plane... Wednesday, February 6, 2008 ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.