CHAPTER 23: Electric Potential Responses to Questions
... have to be roughly circular. 12. The potential at point P would be unchanged. Each bit of positive charge will contribute an amount to the potential based on its charge and its distance from point P. Moving charges to different locations on the ring does not change their distance from P, and hence d ...
... have to be roughly circular. 12. The potential at point P would be unchanged. Each bit of positive charge will contribute an amount to the potential based on its charge and its distance from point P. Moving charges to different locations on the ring does not change their distance from P, and hence d ...
physics syllabus
... Physics is a science that deals with matter and energy and their interactions. It is concerned with systems, laws, models, principles and theories that explain the physical behaviour of our world and the universe. Physics is regarded as a fundamental scientific discipline since all advances in techn ...
... Physics is a science that deals with matter and energy and their interactions. It is concerned with systems, laws, models, principles and theories that explain the physical behaviour of our world and the universe. Physics is regarded as a fundamental scientific discipline since all advances in techn ...
IGCSE Physics Scheme of Work supplied by Cambridge
... Likewise, teachers who wish to devise other courses conducted in different orders will not find their learners disadvantaged provided their courses also cover the syllabus. An attempt has been made to place syllabus items within the unit structure in an order that is both logical and consistent. Whe ...
... Likewise, teachers who wish to devise other courses conducted in different orders will not find their learners disadvantaged provided their courses also cover the syllabus. An attempt has been made to place syllabus items within the unit structure in an order that is both logical and consistent. Whe ...
The Free High School Science Texts
... textbooks you probably own or use. • We know people copy textbooks illegally but we would LOVE it if you copied our’s - go ahead copy to your hearts content, legally! • Publishers’ revenue is generated by controlling the market, we don’t want any money, go ahead, distribute our books far and wide - ...
... textbooks you probably own or use. • We know people copy textbooks illegally but we would LOVE it if you copied our’s - go ahead copy to your hearts content, legally! • Publishers’ revenue is generated by controlling the market, we don’t want any money, go ahead, distribute our books far and wide - ...
electric charges and fields
... A metal rod held in hand and rubbed with wool will not show any sign of being charged. However, if a metal rod with a wooden or plastic handle is rubbed without touching its metal part, it shows signs of charging. Suppose we connect one end of a copper wire to a neutral pith ball and the other end t ...
... A metal rod held in hand and rubbed with wool will not show any sign of being charged. However, if a metal rod with a wooden or plastic handle is rubbed without touching its metal part, it shows signs of charging. Suppose we connect one end of a copper wire to a neutral pith ball and the other end t ...
Recommended Websites for Animation/Demonstration
... Recommended Websites for Animation/Demonstration Almost all website animations depend on one or more web technologies. Shockwave and Flash are available free from macromedia.com. Java is available from java.com. 1) Flash Animations for Physics – This site contains 89 animations with a description of ...
... Recommended Websites for Animation/Demonstration Almost all website animations depend on one or more web technologies. Shockwave and Flash are available free from macromedia.com. Java is available from java.com. 1) Flash Animations for Physics – This site contains 89 animations with a description of ...
New topological excitations and melting transitions in quantum Hall systems
... excitations causes the crystalline bubbles to elongate, change symmetry, and form topological textures. While such behavior is known to occur in bilayer electron systems [16], this phenomena is unique and unanticipated in single-layer 2D systems. The textures have vortex or hedgehog symmetry, depend ...
... excitations causes the crystalline bubbles to elongate, change symmetry, and form topological textures. While such behavior is known to occur in bilayer electron systems [16], this phenomena is unique and unanticipated in single-layer 2D systems. The textures have vortex or hedgehog symmetry, depend ...
Physics
... Physics is a science that deals with matter and energy and their interactions. It is concerned with systems, laws, models, principles and theories that explain the physical behaviour of our world and the universe. Physics is regarded as a fundamental scientific discipline since all advances in techn ...
... Physics is a science that deals with matter and energy and their interactions. It is concerned with systems, laws, models, principles and theories that explain the physical behaviour of our world and the universe. Physics is regarded as a fundamental scientific discipline since all advances in techn ...
Electricity and Magnetism
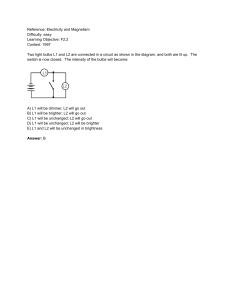
... A neutral plastic comb feels no force from a large horseshoe magnet, when it is brought close. Suppose the comb were charged electrostatically. Under what conditions will it feel an electromagnetic force due to the magnet? A) The comb will never feel an electromagnetic force from the magnet. B) If t ...
... A neutral plastic comb feels no force from a large horseshoe magnet, when it is brought close. Suppose the comb were charged electrostatically. Under what conditions will it feel an electromagnetic force due to the magnet? A) The comb will never feel an electromagnetic force from the magnet. B) If t ...
THIRD ORDER OPTICAL NONLINEARITIES Mansoor Sheik-Bahae Michael P. Hasselbeck
... for example, this assumption is excellent because the response is exceedingly fast. The response is not infinitely fast, however. Response times can vary by orders of magnitude depending on the physical mechanism and resonance conditions involved. Furthermore, Eq.(1) assumes locality, which implies ...
... for example, this assumption is excellent because the response is exceedingly fast. The response is not infinitely fast, however. Response times can vary by orders of magnitude depending on the physical mechanism and resonance conditions involved. Furthermore, Eq.(1) assumes locality, which implies ...
H Graphene Field-Effect Transistors on Undoped Semiconductor Substrates for Radiation Detection
... II. GRAPHENE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS Graphene is a monolayer of graphite with unique electronic properties [1]. Graphene has a high carrier mobility, reaching 10 times or greater than that of Si at room temperature [2]. Graphene is a low-noise electronic material and has a resistance, which is very ...
... II. GRAPHENE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS Graphene is a monolayer of graphite with unique electronic properties [1]. Graphene has a high carrier mobility, reaching 10 times or greater than that of Si at room temperature [2]. Graphene is a low-noise electronic material and has a resistance, which is very ...
Modeling Linear and Nonlinear Soft Ferromagnetic Materials Thesis project from Sebasti`
... i a la memòria dels meus iaios, Justo i José. ...
... i a la memòria dels meus iaios, Justo i José. ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.