Chapter 6 Momentum and Impulse
... • It will also absorb some of the energy from the body • It will spread out the area of contact – Decreases the pressure – Helps prevent penetration wounds ...
... • It will also absorb some of the energy from the body • It will spread out the area of contact – Decreases the pressure – Helps prevent penetration wounds ...
Introduction
... These strategies are beneficial for a couple of reasons. First of all, they are student-centred with the result that they can engage the students. Students become consciously aware of not only their own ideas but those of other students. Meaningful discussions of different ideas can occur when the i ...
... These strategies are beneficial for a couple of reasons. First of all, they are student-centred with the result that they can engage the students. Students become consciously aware of not only their own ideas but those of other students. Meaningful discussions of different ideas can occur when the i ...
Friction, Inclines and Multi
... Check Mr.Walsh’s awesome simulation of any 2 object system (http://ophysics.com/f3.html); it will really help you check your FDBs and you will get a better understanding of what is happening. Remember, you can solve these problems with multiple objects in two ways: a) Draw FDBs and apply Newton’s 2n ...
... Check Mr.Walsh’s awesome simulation of any 2 object system (http://ophysics.com/f3.html); it will really help you check your FDBs and you will get a better understanding of what is happening. Remember, you can solve these problems with multiple objects in two ways: a) Draw FDBs and apply Newton’s 2n ...
Edge theory of ferromagnetic quantum Hall states
... The bulk properties of the quantum Hall systems at filling fraction 1/m, m5odd, in the presence of low magnetic fields, have been subject of many theoretical and experimental investigations in recent years. The spin degree of freedom plays an important role in these systems. Here we focus on propert ...
... The bulk properties of the quantum Hall systems at filling fraction 1/m, m5odd, in the presence of low magnetic fields, have been subject of many theoretical and experimental investigations in recent years. The spin degree of freedom plays an important role in these systems. Here we focus on propert ...
Lab 5.2 – Magnetic Fields Getting Started: Open the PhET
... D. Generator (Note: This is the FIFTH Tab) 1. Here you will find a water faucet, a compass, a bar magnet on a wheel (turbine), and a coil of wire connected to an incandescent bulb. Move the compass around a little and determine what it is reacting to at this time. ...
... D. Generator (Note: This is the FIFTH Tab) 1. Here you will find a water faucet, a compass, a bar magnet on a wheel (turbine), and a coil of wire connected to an incandescent bulb. Move the compass around a little and determine what it is reacting to at this time. ...
Chapter 6 - UniMAP Portal
... (a) What is the magnitude of the repulsive electrostatic force between two protons in a nucleus? Taking the distance from center to center of these protons to be 3 x 10-15m. b) If the protons were released from rest, how would the magnitude of their initial acceleration compare with that of the acce ...
... (a) What is the magnitude of the repulsive electrostatic force between two protons in a nucleus? Taking the distance from center to center of these protons to be 3 x 10-15m. b) If the protons were released from rest, how would the magnitude of their initial acceleration compare with that of the acce ...
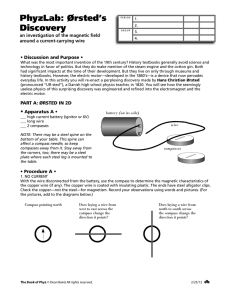
CVX - Canvas™ : L 2 Oersteds Discovery
... h. Again draw the compasses on the compass platform, but do not draw the direction of the needles yet. Label the diagram in accordance with the direction of the current (TOWARD or AWAY). Show the direction of the current with an "arrow" at the center of the compass arrangement (where the wire passes ...
... h. Again draw the compasses on the compass platform, but do not draw the direction of the needles yet. Label the diagram in accordance with the direction of the current (TOWARD or AWAY). Show the direction of the current with an "arrow" at the center of the compass arrangement (where the wire passes ...
Paper
... [18]. At zero magnetic field, it may be possible to observe multiply charged vortices in a spinor condensate ‘‘unwind’’ themselves as predicted in Ref. [6]. The unwinding process is precisely the position-dependent spin rotation demonstrated in previous work [18], with the spin texture investigated ...
... [18]. At zero magnetic field, it may be possible to observe multiply charged vortices in a spinor condensate ‘‘unwind’’ themselves as predicted in Ref. [6]. The unwinding process is precisely the position-dependent spin rotation demonstrated in previous work [18], with the spin texture investigated ...
Problems for the Course F5170 – Introduction to
... separation of electric charge. Plasma frequencies of other particles can be defined in a similar way. However, the electron plasma frequency is the most important because of high mobility of electrons (the proton/electron mass ratio mp /me is 1.8 × 103 ). Note that plasma oscillations will only be o ...
... separation of electric charge. Plasma frequencies of other particles can be defined in a similar way. However, the electron plasma frequency is the most important because of high mobility of electrons (the proton/electron mass ratio mp /me is 1.8 × 103 ). Note that plasma oscillations will only be o ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.