Particle acceleration in an active medium - Technion
... are accelerated by the resonant space charge wave which develops in the system @2#. ~ii! Wake-field acceleration ~WFA!, suggested by Sprangle et al. @3#, is based on a large wake field left after a very intense but short laser impulse which propagates in plasma. ~iii! Inverse Čerenkov @4# relies on ...
... are accelerated by the resonant space charge wave which develops in the system @2#. ~ii! Wake-field acceleration ~WFA!, suggested by Sprangle et al. @3#, is based on a large wake field left after a very intense but short laser impulse which propagates in plasma. ~iii! Inverse Čerenkov @4# relies on ...
File
... always moving in random directions. When an object’s atoms or particles move faster, its thermal energy increases, because when heated, the particles are moving incredibly fast. So as the atoms gets faster and faster the object starts to emit a glow of light. This glow is shown by the image on the r ...
... always moving in random directions. When an object’s atoms or particles move faster, its thermal energy increases, because when heated, the particles are moving incredibly fast. So as the atoms gets faster and faster the object starts to emit a glow of light. This glow is shown by the image on the r ...
Potential
... Example 1. What is the potential energy if a +2 nC charge moves from to point A, 8 cm away from a +6 mC charge? The P.E. will be positive at point A, because the field can do + work if q is released. Potential ...
... Example 1. What is the potential energy if a +2 nC charge moves from to point A, 8 cm away from a +6 mC charge? The P.E. will be positive at point A, because the field can do + work if q is released. Potential ...
Unit 03 Lab - TTU Physics
... cup. Would the number of holes you cut and the size of the holes matter? Explain your reasoning. c. Perform the experiment in part b. d. Consider the large space enclosed by chicken wire (ask an instructor to show it to you). Predict the magnitude of the electric field inside the space enclosed by ...
... cup. Would the number of holes you cut and the size of the holes matter? Explain your reasoning. c. Perform the experiment in part b. d. Consider the large space enclosed by chicken wire (ask an instructor to show it to you). Predict the magnitude of the electric field inside the space enclosed by ...
A Magnetotelluric Investigation of Geoelectrical Dimensionality and Study of the
... The skin depth permits the characterisation of the investigation depth, which, as can be seen, increases according to the square root of the product of medium resistivity and period. Although it has been defined for homogeneous media, its use can be extended to heterogeneous cases as well (e.g. geol ...
... The skin depth permits the characterisation of the investigation depth, which, as can be seen, increases according to the square root of the product of medium resistivity and period. Although it has been defined for homogeneous media, its use can be extended to heterogeneous cases as well (e.g. geol ...
Edmund Taylor Whittaker. 1873-1956
... 'Report on the progress of the solution of the problem of three bodies' (B.1) which covers the period 1868-1898, and which provides a complete summary of the development of the 'new dynamical astronomy'. While Whittaker was Astronomer Royal of Ireland he wrote a few papers on various astronomical su ...
... 'Report on the progress of the solution of the problem of three bodies' (B.1) which covers the period 1868-1898, and which provides a complete summary of the development of the 'new dynamical astronomy'. While Whittaker was Astronomer Royal of Ireland he wrote a few papers on various astronomical su ...
Unit 27
... In the last unit you observed that permanent magnets can exert forces both on freely moving charges and on electrical currents in conductors. We have postulated the existence of a mathematical entity called the magnetic field in order to introduce the Lorentz force law as a way of mathematically des ...
... In the last unit you observed that permanent magnets can exert forces both on freely moving charges and on electrical currents in conductors. We have postulated the existence of a mathematical entity called the magnetic field in order to introduce the Lorentz force law as a way of mathematically des ...
ZAMPONI Part B2 AQUAMAN
... For the sake of concreteness, we will initially focus on some specific problems that have recently emerged in the first two fields mentioned above (namely, quantum computing and condensed matter), on which we believe that progress can be made in the short term using the quantum cavity method. These ...
... For the sake of concreteness, we will initially focus on some specific problems that have recently emerged in the first two fields mentioned above (namely, quantum computing and condensed matter), on which we believe that progress can be made in the short term using the quantum cavity method. These ...
Document
... A region of fluid upwelling interacts with the field line. Because of the Coriolis force the fluid exhibits helicity (rotating as it moves upwards). The magnetic field line is carried along and twisted to produce a poloidal loop. ...
... A region of fluid upwelling interacts with the field line. Because of the Coriolis force the fluid exhibits helicity (rotating as it moves upwards). The magnetic field line is carried along and twisted to produce a poloidal loop. ...
Solar cycle dependence of quiet-time magnetospheric currents
... In addition, all the magnetic effects due to induction in the Earth have been considered. Presently this kind of parameterization is widely accepted in the main field modeling community, and it is employed, for example, in model families such as CHAOS (CHAMP, Ørsted, SAC-C) (e.g., Olsen et al., 2006 ...
... In addition, all the magnetic effects due to induction in the Earth have been considered. Presently this kind of parameterization is widely accepted in the main field modeling community, and it is employed, for example, in model families such as CHAOS (CHAMP, Ørsted, SAC-C) (e.g., Olsen et al., 2006 ...
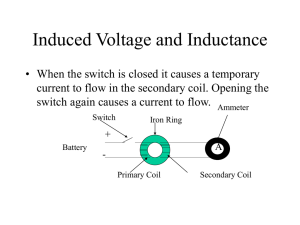
Induced Voltage and Inductance
... Lenz’s Law • Lenz’s law states that the direction of the induced emf is such that if an induced current were able to flow, it oppose the change that causes it. • In the above diagram as the bar moves to the right the flux is increased into the page. To offset this the induced current must flow coun ...
... Lenz’s Law • Lenz’s law states that the direction of the induced emf is such that if an induced current were able to flow, it oppose the change that causes it. • In the above diagram as the bar moves to the right the flux is increased into the page. To offset this the induced current must flow coun ...
Lectures in physics Part 2: Electricity, magnetism and quantum mechanics Przemysław Borys 20.05.2014
... 1. Provide the interpretation to the divergence and describe the Gauss-Ostrogradski theorem. 2. Provide the interpretation to the curl and describe the Stokes theorem. 3. Provide the interpretation of a gradient. 14. The Electric Field 14.1 The Coulomb's law The Coulomb's law describes the force tha ...
... 1. Provide the interpretation to the divergence and describe the Gauss-Ostrogradski theorem. 2. Provide the interpretation to the curl and describe the Stokes theorem. 3. Provide the interpretation of a gradient. 14. The Electric Field 14.1 The Coulomb's law The Coulomb's law describes the force tha ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.