Hydrodynamic theory of thermoelectric transport
... So far, the theories of this negative magnetoresistance assume two facts about the dynamics of the quasiparticles of the Weyl semimetal. Firstly, it is assumed that the quasiparticles are long lived, and that a kinetic description of their dynamics is valid. Secondly, it is assumed that the dominant ...
... So far, the theories of this negative magnetoresistance assume two facts about the dynamics of the quasiparticles of the Weyl semimetal. Firstly, it is assumed that the quasiparticles are long lived, and that a kinetic description of their dynamics is valid. Secondly, it is assumed that the dominant ...
chapter 3 - UniMAP Portal
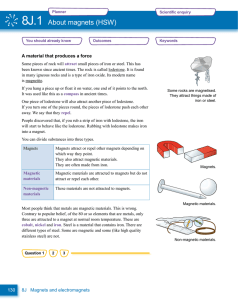
... INTRODUCTION (Cont’d) He used compass to show that current produces magnetic fields that loop around the conductor. The field grows weaker as it moves away from the source of current. A represents current coming out of paper. ...
... INTRODUCTION (Cont’d) He used compass to show that current produces magnetic fields that loop around the conductor. The field grows weaker as it moves away from the source of current. A represents current coming out of paper. ...
Properties Of Conductors
... The above properties of a conductor influence the behaviour of a conductor placed in an electric field. Consider, for instance, what happens when a charge is brought near an uncharged conductor. The conductor is placed in the electric field of the point charge. The field inside the conductor should, ...
... The above properties of a conductor influence the behaviour of a conductor placed in an electric field. Consider, for instance, what happens when a charge is brought near an uncharged conductor. The conductor is placed in the electric field of the point charge. The field inside the conductor should, ...
Chapter 25
... charge-field system gains or loses when a charge of magnitude e (an electron or a proton) is moved through a potential difference of 1 volt ...
... charge-field system gains or loses when a charge of magnitude e (an electron or a proton) is moved through a potential difference of 1 volt ...
college physics
... Doug rubs a piece of fur on a hard rubber rod, giving the rod a negative charge. What happens? Protons are removed from the rod. D. The fur is left neutral. Electrons are added to the rod. E. Negative ions added to the fur. The fur is also charged negatively. ...
... Doug rubs a piece of fur on a hard rubber rod, giving the rod a negative charge. What happens? Protons are removed from the rod. D. The fur is left neutral. Electrons are added to the rod. E. Negative ions added to the fur. The fur is also charged negatively. ...
P - UniMAP Portal
... The parallelogram law is used; the diagonal (resultant) is known to be equal 25kN and to be directed to the right. This sides are drawn paralled to the ropes.If the drawing is done to scale, we measure ...
... The parallelogram law is used; the diagonal (resultant) is known to be equal 25kN and to be directed to the right. This sides are drawn paralled to the ropes.If the drawing is done to scale, we measure ...
Inequivalence of direct and converse magnetoelectric coupling at electromechanical resonance
... between stress and strain, as well as electric field and magnetic field, new expressions for frequency response of ME effects have been derived by adopting different sets of constitutive equations of the materials for DME and CME effects. The theoretical results are in good agreement with the experi ...
... between stress and strain, as well as electric field and magnetic field, new expressions for frequency response of ME effects have been derived by adopting different sets of constitutive equations of the materials for DME and CME effects. The theoretical results are in good agreement with the experi ...
Brief Introduction to Superconductivity
... we would need more parameters. Ounce the lattice is known, a potential with the same symmetry can be defined. This is all that is needed as input to the Schrödinger equation. The problem of solving it is not at all trivial. There are several methods known nowadays to solve this equation. Ready-to-us ...
... we would need more parameters. Ounce the lattice is known, a potential with the same symmetry can be defined. This is all that is needed as input to the Schrödinger equation. The problem of solving it is not at all trivial. There are several methods known nowadays to solve this equation. Ready-to-us ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
... Q.79 – A horizontal telephone wire 103 m long is lying along east in earth’s magnetic field. It falls freely to the ground from a height of 10 m. Calculate the emf induced in the wire when the wire strikes the ground assuming that the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field has flux density ...
... Q.79 – A horizontal telephone wire 103 m long is lying along east in earth’s magnetic field. It falls freely to the ground from a height of 10 m. Calculate the emf induced in the wire when the wire strikes the ground assuming that the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field has flux density ...
James Clerk Maxwell - Math Tutorials and More by George
... In the history of physics there are three individuals who stand out above all others. They are Isaac Newton, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Each of these men dramatically changed the way we look at the physical world — Isaac Newton with his laws of motion, James Clerk Maxwell with his ele ...
... In the history of physics there are three individuals who stand out above all others. They are Isaac Newton, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Each of these men dramatically changed the way we look at the physical world — Isaac Newton with his laws of motion, James Clerk Maxwell with his ele ...
Unit 7 Part 2---Electric Field Notes
... The electric field is a storehouse of energy that can be transported over long distances and the energy contained in it can be used to do work for us (for example, it can power our toaster or light a light bulb). The electric field is responsible for pushing charge and energy through electrical circ ...
... The electric field is a storehouse of energy that can be transported over long distances and the energy contained in it can be used to do work for us (for example, it can power our toaster or light a light bulb). The electric field is responsible for pushing charge and energy through electrical circ ...
Thermodynamics of Electric and Magnetic Systems
... The systems which contain electric or magnetic media have besides the electric (respectively magnetic) properties also the common properties of a thermodynamic systems (that is thermal, volumic, chemical); moreover, there are correlations between the electric (magnetic) properties and the thermal or ...
... The systems which contain electric or magnetic media have besides the electric (respectively magnetic) properties also the common properties of a thermodynamic systems (that is thermal, volumic, chemical); moreover, there are correlations between the electric (magnetic) properties and the thermal or ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.