Exam Review I - UW-Madison Department of Physics
... Electric field from a uniform ring of charge. The magnitude of the electric field on the x-axis ...
... Electric field from a uniform ring of charge. The magnitude of the electric field on the x-axis ...
Lesson-36: Principle of operation of D
... actually a necessary condition for production of steady electromagnetic torque. What is the sufficient condition then? Let us look once again at figure 36.9(a) where stator and rotor number of poles are same and equal to 4. Suppose the relative position of the poles shown, is at a particular instant ...
... actually a necessary condition for production of steady electromagnetic torque. What is the sufficient condition then? Let us look once again at figure 36.9(a) where stator and rotor number of poles are same and equal to 4. Suppose the relative position of the poles shown, is at a particular instant ...
Q/1 Determine the magnitude FS of the tensile spring force in order
... OB rotates clockwise about the fixed pivot O under the action of the force P, the element S slides freely upward in its slot, releasing the flow. If an internal tensional spring exerts a moment M – 20 N.m as shown, determine the force p required to open the valve. Neglect all friction. ...
... OB rotates clockwise about the fixed pivot O under the action of the force P, the element S slides freely upward in its slot, releasing the flow. If an internal tensional spring exerts a moment M – 20 N.m as shown, determine the force p required to open the valve. Neglect all friction. ...
The theory of dipoles vortex Author: Prof. Vasile Tudor, The
... be explained by reference to the dipoles vortex in the two universes in which universal particles involved entering (or leaving) through a pole and leaving (or entering) through the other pole with motion opposing meanings. On the other hand, implies that the elementary particles and corresponding a ...
... be explained by reference to the dipoles vortex in the two universes in which universal particles involved entering (or leaving) through a pole and leaving (or entering) through the other pole with motion opposing meanings. On the other hand, implies that the elementary particles and corresponding a ...
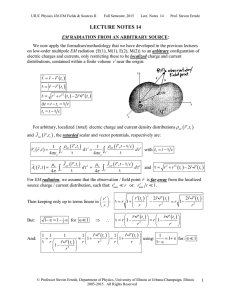
Lecture Notes 14: Electromagnetic Radiation from An Arbitrary Source, Radiation Reaction on a Moving Point Charge
... dtr dtr2 zˆ cos rˆ sin ˆ with: to t r c ...
... dtr dtr2 zˆ cos rˆ sin ˆ with: to t r c ...
Document
... Part 1) What is their acceleration, if hill was considered smooth? Part 2) What is their acceleration if hill has a coefficient of friction of 0.21? Part 3) How far down the hill will the skier travel in 33 seconds in part 2 ...
... Part 1) What is their acceleration, if hill was considered smooth? Part 2) What is their acceleration if hill has a coefficient of friction of 0.21? Part 3) How far down the hill will the skier travel in 33 seconds in part 2 ...
Deflection of a stream of liquid metal by means of an alternating
... In both these cases the jet thickness, d , increases during the interaction with the magnetic field. It is of interest to note that when h = 0 there is no equilibrium unless the magnetic pressure vanishes. When both h and p , are zero, then to lowest order in the jet thickness, any shape C gives ris ...
... In both these cases the jet thickness, d , increases during the interaction with the magnetic field. It is of interest to note that when h = 0 there is no equilibrium unless the magnetic pressure vanishes. When both h and p , are zero, then to lowest order in the jet thickness, any shape C gives ris ...
The Voltaic Origins of Helmholtz`s Physics of Ions
... phenomena to central forces acting on pairs of mass points. Laplacian physics already provided this reduction for gravitational, electrostatic, and magnetostatic phenomena. Helmholtz extended it to electrochemistry. The main facts to be explained were the contact tension of two different metals (now ...
... phenomena to central forces acting on pairs of mass points. Laplacian physics already provided this reduction for gravitational, electrostatic, and magnetostatic phenomena. Helmholtz extended it to electrochemistry. The main facts to be explained were the contact tension of two different metals (now ...
Oscillating dipole model for the X-ray standing wave enhanced
... without second member plus a source field, which is a particular solution of the propagation equation with a second source term given by the current density induced by the dipole. The propagation problem can be solved by means of the dyadic Green function formalism [13,14], but since this approach r ...
... without second member plus a source field, which is a particular solution of the propagation equation with a second source term given by the current density induced by the dipole. The propagation problem can be solved by means of the dyadic Green function formalism [13,14], but since this approach r ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.