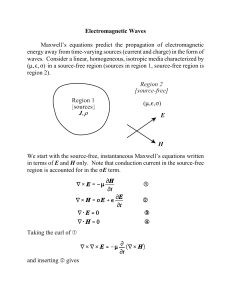
Large-Scale Bose-Einstein Condensation in a Vapor of Cesium
... Einstein first noticed that Bose gas would condense to the lowest energy state. However, the result of the condensation doesn't produce crystals, this fact shows that BEC doesn't occur in the position space but occurs in the momentum space. “The term ‘condensation’ often implies a condensation in sp ...
... Einstein first noticed that Bose gas would condense to the lowest energy state. However, the result of the condensation doesn't produce crystals, this fact shows that BEC doesn't occur in the position space but occurs in the momentum space. “The term ‘condensation’ often implies a condensation in sp ...
UNIT 6
... is brought near a steel paper clip, magnetic domains that attract the magnet grow and domains that repel the magnet shrink. The paper clip quickly builds a magnetic field that attracts the magnet, no matter which pole is used (Figure 16.10). When the magnet is pulled away the domains tend to go back ...
... is brought near a steel paper clip, magnetic domains that attract the magnet grow and domains that repel the magnet shrink. The paper clip quickly builds a magnetic field that attracts the magnet, no matter which pole is used (Figure 16.10). When the magnet is pulled away the domains tend to go back ...
On the computational complexity of Ising spin glass models
... In this section we summarise some basic definitions from graph theory, referring the reader to Berge (1970) and Harary (1969) for a more complete discussion. A graph G = (V, E) consists of a set of vertices V, and a set E of unordered pairs of different vertices called edges. In our case vertices ar ...
... In this section we summarise some basic definitions from graph theory, referring the reader to Berge (1970) and Harary (1969) for a more complete discussion. A graph G = (V, E) consists of a set of vertices V, and a set E of unordered pairs of different vertices called edges. In our case vertices ar ...
Manual.
... Even the tiny magnets inside the matter are derived from charges movement. The charges which move in the matter are called electrons. The electron has two types of circular movement. One movement it rotates around the nucleus and the second movement it rotates around itself. The rotation around itse ...
... Even the tiny magnets inside the matter are derived from charges movement. The charges which move in the matter are called electrons. The electron has two types of circular movement. One movement it rotates around the nucleus and the second movement it rotates around itself. The rotation around itse ...
Electric Current - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... So if between B and C, another resistance is placed, then no current flows through that resistance. d) Potentiometer :It is a device used to measure potential difference with high accuracy, without drawing any current from the unknown source. [* Basic Figure of a potentiometer : ??] Principle of Pot ...
... So if between B and C, another resistance is placed, then no current flows through that resistance. d) Potentiometer :It is a device used to measure potential difference with high accuracy, without drawing any current from the unknown source. [* Basic Figure of a potentiometer : ??] Principle of Pot ...
29_InstructorSolutionsWin
... EXECUTE: (a) The field is into the page and is increasing so the flux is increasing. The field of the induced current is out of the page. To produce field out of the page the induced current is counterclockwise. (b) The field is into the page and is decreasing so the flux is decreasing. The field of ...
... EXECUTE: (a) The field is into the page and is increasing so the flux is increasing. The field of the induced current is out of the page. To produce field out of the page the induced current is counterclockwise. (b) The field is into the page and is decreasing so the flux is decreasing. The field of ...
3-2- Theory
... number of magnetization curves for different speeds be plotted on the same base and to the same scale, then the ordinates of the various curves for any particular value of the excitation will vary in direct proportion to the speed, i.e. the critical resistance varies directly with speed. If the resi ...
... number of magnetization curves for different speeds be plotted on the same base and to the same scale, then the ordinates of the various curves for any particular value of the excitation will vary in direct proportion to the speed, i.e. the critical resistance varies directly with speed. If the resi ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.