PDF - University of California, Berkeley
... exchange to crystal field is larger or smaller than a critical value, the crystal will or will not order at the lowest temperatures. ' The Tb,Y, ,Sb system is of particular interest since the exchange interaction between the Tb ions varies with c whereas the crystal field is virtually unaffected, th ...
... exchange to crystal field is larger or smaller than a critical value, the crystal will or will not order at the lowest temperatures. ' The Tb,Y, ,Sb system is of particular interest since the exchange interaction between the Tb ions varies with c whereas the crystal field is virtually unaffected, th ...
STRUCTURAL AND PHASE COMPOSITION MODIFICATION OF
... From the magnetic point of view, changes It can be that the measured values were of phase composition during the TM, first of below the expected value, probably because all, decrease of the amount of hard magnetic the maximum magnetic field of 50 kOe is not Nd Fe B phase (up to 75 mass%), increase ...
... From the magnetic point of view, changes It can be that the measured values were of phase composition during the TM, first of below the expected value, probably because all, decrease of the amount of hard magnetic the maximum magnetic field of 50 kOe is not Nd Fe B phase (up to 75 mass%), increase ...
PowerPoint
... “This stuff is really neat... It is fun to actually see the calculations for magnetism. However, since this is the first time I’ve really seen it, it is still a bit confusing. If you could go through different examples and go over the actual concepts more, that would be great.” “Magnets. How do they ...
... “This stuff is really neat... It is fun to actually see the calculations for magnetism. However, since this is the first time I’ve really seen it, it is still a bit confusing. If you could go through different examples and go over the actual concepts more, that would be great.” “Magnets. How do they ...
Magnetic Effects of Electric current
... Answer: (c) and (d) When a proton enters in a region of magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force. As a result of the force, the path of the proton becomes circular. Hence, its velocity and momentum change. Question 11: State Fleming’s left-hand rule. Answer: Fleming’s left hand rule states th ...
... Answer: (c) and (d) When a proton enters in a region of magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force. As a result of the force, the path of the proton becomes circular. Hence, its velocity and momentum change. Question 11: State Fleming’s left-hand rule. Answer: Fleming’s left hand rule states th ...
1 AC Losses in High Temperature Superconductors under non –Sinusoidal Conditions
... AC losses in superconductors characterize their physical properties (the microscopic motion of the Abrikosov vortices, phase state of the vortex lattice, etc) as well as determining ranges of the rated currents and magnetic fields for superconducting devices that are required for the optimal operati ...
... AC losses in superconductors characterize their physical properties (the microscopic motion of the Abrikosov vortices, phase state of the vortex lattice, etc) as well as determining ranges of the rated currents and magnetic fields for superconducting devices that are required for the optimal operati ...
Self-Inductance
... • Consider an isolated circuit consisting of a switch, a resistor, and a source of EMF. • When the switch is closed, the current doesn’t immediately jump from zero to its maximum value, ...
... • Consider an isolated circuit consisting of a switch, a resistor, and a source of EMF. • When the switch is closed, the current doesn’t immediately jump from zero to its maximum value, ...
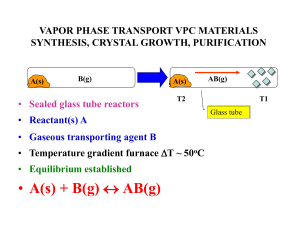
vapor phase transport vpc materials synthesis, crystal growth
... In the effect, there is an exclusion of magnetic flux brought about by “electrical screening currents" that flow at the surface of the superconductor and which generate a magnetic field that exactly cancels (repels) the externally applied field inside the superconductor (Lenz’s law). ...
... In the effect, there is an exclusion of magnetic flux brought about by “electrical screening currents" that flow at the surface of the superconductor and which generate a magnetic field that exactly cancels (repels) the externally applied field inside the superconductor (Lenz’s law). ...
Sample Electric Field Questions
... Draw the electric field produce by the following: Indicate where E = 0. For every unit of charge use 2 field lines. ...
... Draw the electric field produce by the following: Indicate where E = 0. For every unit of charge use 2 field lines. ...
Electronic Circuits
... peak in the emission spectrum in the near infrared, but also a substantial amount of light in the visible part of the spectrum. The high intensity causes the light to appear nearly white to the eye. Running a lamp at temperatures much higher than this results in a lifetime which decreases exponentia ...
... peak in the emission spectrum in the near infrared, but also a substantial amount of light in the visible part of the spectrum. The high intensity causes the light to appear nearly white to the eye. Running a lamp at temperatures much higher than this results in a lifetime which decreases exponentia ...
The Electromagnetic Radiation Mechanism
... finally ended when Einstein presented the theory of light quanta in 1905, in which he combined electromagnetic wave and particle photon to explain photoelectrons ejection (De Broglie, 1929), Einstein based his arguments for his light quanta hypotheis upon Boltzmann’s statistical interpretation ...
... finally ended when Einstein presented the theory of light quanta in 1905, in which he combined electromagnetic wave and particle photon to explain photoelectrons ejection (De Broglie, 1929), Einstein based his arguments for his light quanta hypotheis upon Boltzmann’s statistical interpretation ...
Name: Activity – Induced EMF in a Coil of Wire Objectives: • Observe
... that is either positive or negative. As the coil continues to move past the magnet, the voltage should reverse. If you stop the coil, the voltage will disappear. This potential difference is the result of a current in the wire created by the motion of the electrons in the wire through the magnetic f ...
... that is either positive or negative. As the coil continues to move past the magnet, the voltage should reverse. If you stop the coil, the voltage will disappear. This potential difference is the result of a current in the wire created by the motion of the electrons in the wire through the magnetic f ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.