Lab22_MagneticMenageriefillin
... PART 2: The Bottom Power Supply: A Function Generator 1. Hook the bottom power supply to the outer solenoid with alligator clips. Hook the negative (black) clip first, then the red (which has a rubber guard), but it doesn’t matter to which terminal. This power supply (already turned on) should be s ...
... PART 2: The Bottom Power Supply: A Function Generator 1. Hook the bottom power supply to the outer solenoid with alligator clips. Hook the negative (black) clip first, then the red (which has a rubber guard), but it doesn’t matter to which terminal. This power supply (already turned on) should be s ...
Physics 21
... to west parallel to the surface of Earth. What is the magnitude and direction of the force resulting from Earth’s magnetic field acting on each meter of the wire? ...
... to west parallel to the surface of Earth. What is the magnitude and direction of the force resulting from Earth’s magnetic field acting on each meter of the wire? ...
Schumann Resonance Frequencies Found Within
... assumed to be related to the physicochemical restraints for protein synthesis. However it may also involve the latency required to represent information within a component of the space within the resonance cavity [25]. The classic current decay within the electric field between the earth’s surface a ...
... assumed to be related to the physicochemical restraints for protein synthesis. However it may also involve the latency required to represent information within a component of the space within the resonance cavity [25]. The classic current decay within the electric field between the earth’s surface a ...
What is the relationship between electric force and electric field
... depending on their signs. 2. Both Fg and Fe are forces that act at a distance. The g is always an attractive force, while E can attract or repel, depending on the charges. 3. Fe and E are the electrical analogs to Fg and g. Both forces are proportional to some constant ( a charge or mass, respective ...
... depending on their signs. 2. Both Fg and Fe are forces that act at a distance. The g is always an attractive force, while E can attract or repel, depending on the charges. 3. Fe and E are the electrical analogs to Fg and g. Both forces are proportional to some constant ( a charge or mass, respective ...
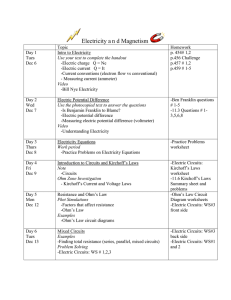
Electricity and Magnetism Task List
... -Make sure all homework is complete -Ohm’s Law Lab activity should be handed in -For extra circuit practice complete worksheets Electric Circuits WS#4 Resistors in Series and Parallel – More Practice -For extra magnetism practice try p. 542 # 5-14, 28 ...
... -Make sure all homework is complete -Ohm’s Law Lab activity should be handed in -For extra circuit practice complete worksheets Electric Circuits WS#4 Resistors in Series and Parallel – More Practice -For extra magnetism practice try p. 542 # 5-14, 28 ...
Chapter 29 Slides - MSU Denver Sites
... • To determine the direction of an induced emf • To calculate the emf induced by a moving conductor • To learn how a changing magnetic flux generates an electric field • To study the four fundamental equations that describe electricity and magnetism Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... • To determine the direction of an induced emf • To calculate the emf induced by a moving conductor • To learn how a changing magnetic flux generates an electric field • To study the four fundamental equations that describe electricity and magnetism Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. ...
Nirma University Chemical Engineering Department Handouts for AI
... devices that measure temperature because of the physical principle of the positive temperature coefficient of electrical resistance of metals. The hotter they become, the larger or higher the value of their electrical resistance. The Advantages of RTDs The advantages of RTDs include stable output fo ...
... devices that measure temperature because of the physical principle of the positive temperature coefficient of electrical resistance of metals. The hotter they become, the larger or higher the value of their electrical resistance. The Advantages of RTDs The advantages of RTDs include stable output fo ...
up11_educue_ch29
... magnetic field inside a long, straight solenoid. The field is directed into the plane of the drawing, and is increasing. What is the direction of the electric force on a positive point charge placed at point a, point b, or point c (the center of the solenoid)? 1. a: to the left; b: straight up; c: d ...
... magnetic field inside a long, straight solenoid. The field is directed into the plane of the drawing, and is increasing. What is the direction of the electric force on a positive point charge placed at point a, point b, or point c (the center of the solenoid)? 1. a: to the left; b: straight up; c: d ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.