Introduction I. Waves on a String
... A hand steadily wiggles the left end of the string up and down. The figure below shows snapshots of the wave on the string at three instants in time (t1, t2, t3) as the wave travels to the right. The dot painted on the string is indicated at point 1. The pictures below show two possible physical sit ...
... A hand steadily wiggles the left end of the string up and down. The figure below shows snapshots of the wave on the string at three instants in time (t1, t2, t3) as the wave travels to the right. The dot painted on the string is indicated at point 1. The pictures below show two possible physical sit ...
Handout - Association of Educators in Imaging and
... 1. Open the Faraday Law simulation and discover what you can about induction. Make a list of ways to cause induction. 2. What made you think that induction had occurred? 3. Open Faraday’s Electromagnet Lab. Investigate using the window called Pickup Coil. See if you can discover more things that eff ...
... 1. Open the Faraday Law simulation and discover what you can about induction. Make a list of ways to cause induction. 2. What made you think that induction had occurred? 3. Open Faraday’s Electromagnet Lab. Investigate using the window called Pickup Coil. See if you can discover more things that eff ...
Analysis of Contact Force in Eddy-current System Using the
... with other objects using the existing methods, such as Maxwell stress tensor method, magnetic charge method, or magnetizing current method. These methods are applicable for force computation only when the object is surrounded by air. The virtual air-gap concept has been proposed for calculating the ...
... with other objects using the existing methods, such as Maxwell stress tensor method, magnetic charge method, or magnetizing current method. These methods are applicable for force computation only when the object is surrounded by air. The virtual air-gap concept has been proposed for calculating the ...
MAGNETIC BRAKING
... brakes are a relatively new technology that are beginning to gain popularity due to their high degree of safety. Rather than slowing a train via friction, which can often be affected by various elements such as rain, eddy current brakes rely completely on certain magnetic properties and resistance. ...
... brakes are a relatively new technology that are beginning to gain popularity due to their high degree of safety. Rather than slowing a train via friction, which can often be affected by various elements such as rain, eddy current brakes rely completely on certain magnetic properties and resistance. ...
Graphene with adatoms: Tuning the magnetic moment with an applied...
... Dirac-like dispersion relation of its electrons is the origin of many unusual properties, which may lead to electronic or spintronic applications.1–3 For example, adatoms on graphene may develop magnetic moments which can be manipulated by an applied electric field in a manner similar to its other e ...
... Dirac-like dispersion relation of its electrons is the origin of many unusual properties, which may lead to electronic or spintronic applications.1–3 For example, adatoms on graphene may develop magnetic moments which can be manipulated by an applied electric field in a manner similar to its other e ...
Studies on post-flare loop prominence of 1981 April 27
... to be connected with the flare-like bright patches. The brightest part of the post-flare loop is on the top, which is in agreement with the work of Nolte et al. (1979). In Figure 1 are shown, schematically, several images of the He post-flare loop prominence during the process of its development. It ...
... to be connected with the flare-like bright patches. The brightest part of the post-flare loop is on the top, which is in agreement with the work of Nolte et al. (1979). In Figure 1 are shown, schematically, several images of the He post-flare loop prominence during the process of its development. It ...
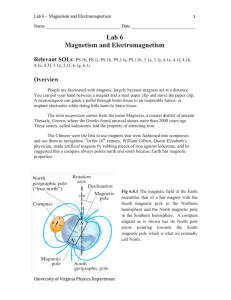
Lab 6 Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Galileo
... being made into magnets; they are normally iron, nickel, cobalt, or alloys that are made of rare-earth metals. A magnet is created when certain conditions cause separate domains in a ferromagnetic item to be all aligned in the same direction. However the method used in most cases can make only weak ...
... being made into magnets; they are normally iron, nickel, cobalt, or alloys that are made of rare-earth metals. A magnet is created when certain conditions cause separate domains in a ferromagnetic item to be all aligned in the same direction. However the method used in most cases can make only weak ...
Section 24.5 Magnetic Fields Exert Forces on Moving Charges
... • Using the right-hand rule for forces, we can see that when I2 is in the same direction as I1, the second wire is attracted to the first wire. • If they were in opposite directions, the second wire would be repelled. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Using the right-hand rule for forces, we can see that when I2 is in the same direction as I1, the second wire is attracted to the first wire. • If they were in opposite directions, the second wire would be repelled. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.