Alterations in Cardiovascular Function
... • due to abnormally small pulmonary vessels • which restrict flow of blood, so the heart hypertrophies to work harder to provide the blood flow to organs. • however, CO increases initially but eventually hypertrophied muscle becomes ineffective. • initially R sided failure, progressing to L sided an ...
... • due to abnormally small pulmonary vessels • which restrict flow of blood, so the heart hypertrophies to work harder to provide the blood flow to organs. • however, CO increases initially but eventually hypertrophied muscle becomes ineffective. • initially R sided failure, progressing to L sided an ...
Atrial Fibrillation - Anticoagulation Europe
... If you are healthy and your heart is working normally you are likely to have a regular resting heart rate of around 60 to 90 beats per minute. If you are experiencing atrial fibrillation (AF), however, you may notice your heartbeat becoming irregular and speeding up for no apparent reason. These fee ...
... If you are healthy and your heart is working normally you are likely to have a regular resting heart rate of around 60 to 90 beats per minute. If you are experiencing atrial fibrillation (AF), however, you may notice your heartbeat becoming irregular and speeding up for no apparent reason. These fee ...
the heart <3
... ♦ The blood makes up about onethirteenth of the body’s weight. ♦ The adult heart weighs about 280 grams (10 oz.) ♦ At rest, the heart pumps out about 80 millimeters (2.6 oz) of blood with each beat. ♦ The heart beats, on average, 70 times each minute at rest. ♦ This means all the blood is circulated ...
... ♦ The blood makes up about onethirteenth of the body’s weight. ♦ The adult heart weighs about 280 grams (10 oz.) ♦ At rest, the heart pumps out about 80 millimeters (2.6 oz) of blood with each beat. ♦ The heart beats, on average, 70 times each minute at rest. ♦ This means all the blood is circulated ...
159º - Santeon
... correlated with a position of the LV electrode to the right in the frontal plane; a more septal heart axis correlated with a lateral position in the transversal plane (see figure 1); a more cranial orientated heart axis correlated with a caudal position in the sagittal plane (see figure 2). ...
... correlated with a position of the LV electrode to the right in the frontal plane; a more septal heart axis correlated with a lateral position in the transversal plane (see figure 1); a more cranial orientated heart axis correlated with a caudal position in the sagittal plane (see figure 2). ...
The Circulatory System The circulatory system consists of the heart
... A narrowing or obstruction in the coronary arteries reduces the blood supply to the myocardium. This results in a deficiency in oxygen and nutrients to the muscle. Acute myocardial infarction is the most serious and acute form of ischaemic heart disease. A coronary artery becomes blocked and the myo ...
... A narrowing or obstruction in the coronary arteries reduces the blood supply to the myocardium. This results in a deficiency in oxygen and nutrients to the muscle. Acute myocardial infarction is the most serious and acute form of ischaemic heart disease. A coronary artery becomes blocked and the myo ...
Warfarin Use in Thrombocytopenic Young Adult Male with Atrial
... Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in adult less than 40 years is about 0.1% per year. Fever and thrombocytopenia in rheumatic heart disease are frequently misdiagnosed with viral illness, restraining patient from vitamin K antagonist use which might be life saving, particularly in atrial fibrillatio ...
... Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in adult less than 40 years is about 0.1% per year. Fever and thrombocytopenia in rheumatic heart disease are frequently misdiagnosed with viral illness, restraining patient from vitamin K antagonist use which might be life saving, particularly in atrial fibrillatio ...
File
... … This is the sound of blood entering the previously closed artery. At this point, the sphygmomanometer measures the pressure exerted by the blood during ventricular contraction. This is caused systolic blood pressure. ...
... … This is the sound of blood entering the previously closed artery. At this point, the sphygmomanometer measures the pressure exerted by the blood during ventricular contraction. This is caused systolic blood pressure. ...
AHS CVS Lecture 1
... of contraction through cardiac muscle Atria contract as a unit Ventricles contract as a unit Atrial contraction precedes ventricle contraction AHS Physiology - Cardiovascular System 11-12 ...
... of contraction through cardiac muscle Atria contract as a unit Ventricles contract as a unit Atrial contraction precedes ventricle contraction AHS Physiology - Cardiovascular System 11-12 ...
The Intracellular pH and Potassium Content of
... A radiofibrinogen catabolism study has been performed in forty patients with glomerulonephritis. Increased catabolism has been shown to correspond with disease activity of immune complex disorders. Illustrations will be made by reference to a patient with post-streptococcal acute nephritis, a patien ...
... A radiofibrinogen catabolism study has been performed in forty patients with glomerulonephritis. Increased catabolism has been shown to correspond with disease activity of immune complex disorders. Illustrations will be made by reference to a patient with post-streptococcal acute nephritis, a patien ...
Electrocardiography: Atrial Fibrillation - e
... guidelines, the prevalence of AF rises from an estimated 0.4% to 1% in the general population to 8% in persons older than 80 years.1 Symptoms In atrial fibrillation, symptoms depend on the rate at which the ventricles are beating. A mild increase in the ventricular rate, less than about 120 beats pe ...
... guidelines, the prevalence of AF rises from an estimated 0.4% to 1% in the general population to 8% in persons older than 80 years.1 Symptoms In atrial fibrillation, symptoms depend on the rate at which the ventricles are beating. A mild increase in the ventricular rate, less than about 120 beats pe ...
Normal Heart NOTES - Children`s Heart Clinic
... In the normal heart, blood returns to the right atrium from the body via the superior and inferior vena cavae. Blood then flows from the right atria to the right ventricle across the tricuspid valve. The tricuspid valve has three leaflets that allow the valve to open and bring blood into the right v ...
... In the normal heart, blood returns to the right atrium from the body via the superior and inferior vena cavae. Blood then flows from the right atria to the right ventricle across the tricuspid valve. The tricuspid valve has three leaflets that allow the valve to open and bring blood into the right v ...
Tricuspid Regurgitation (TR) - The Children`s Heart Clinic, PA
... In the normal heart, blood returns to the right atrium from the body via the superior and inferior vena cavae. Blood then flows from the right atria to the right ventricle across the tricuspid valve. The tricuspid valve has three leaflets that allow the valve to open and bring blood into the right v ...
... In the normal heart, blood returns to the right atrium from the body via the superior and inferior vena cavae. Blood then flows from the right atria to the right ventricle across the tricuspid valve. The tricuspid valve has three leaflets that allow the valve to open and bring blood into the right v ...
B1 Atrial Fibrillation
... - characterized by extremely rapid (300-600 bmp) and disorganized atrial activation. AV node filters this, resulting in a fast, irregular ventricular rate of 100-120 bpm - ventricular rate: atrial rate is 1:3; if know the ventricular rate (i.e. heart rate) then know the approximate atrial rate - may ...
... - characterized by extremely rapid (300-600 bmp) and disorganized atrial activation. AV node filters this, resulting in a fast, irregular ventricular rate of 100-120 bpm - ventricular rate: atrial rate is 1:3; if know the ventricular rate (i.e. heart rate) then know the approximate atrial rate - may ...
cardiac cycle - WordPress.com
... 2. Due to smaller openings, the velocity of blood ejection through the aortic and pulmonary valves is far greater than that through the much larger A-V valves. ...
... 2. Due to smaller openings, the velocity of blood ejection through the aortic and pulmonary valves is far greater than that through the much larger A-V valves. ...
template - Developing Anaesthesia
... The nomenclature is actually misleading, as the pathology is a delay in conduction rather than a total “block”. 1 The abnormality of itself is clinically benign. It may be a normal finding in some people such as athletes, however it may also indicate an underlying cardiac abnormality that may or may ...
... The nomenclature is actually misleading, as the pathology is a delay in conduction rather than a total “block”. 1 The abnormality of itself is clinically benign. It may be a normal finding in some people such as athletes, however it may also indicate an underlying cardiac abnormality that may or may ...
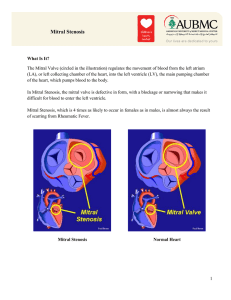
Mitral Stenosis
... The symptoms of Mitral Stenosis may be absent or very slight for long periods. However, they may gradually or suddenly worsen. If the blockage of the valve becomes severe, the left atrium will be unable to do its job adequately, blood will back up into the lungs and body tissues, and heart failure m ...
... The symptoms of Mitral Stenosis may be absent or very slight for long periods. However, they may gradually or suddenly worsen. If the blockage of the valve becomes severe, the left atrium will be unable to do its job adequately, blood will back up into the lungs and body tissues, and heart failure m ...
Pregnancy Management Guidelines in Women with Cardiac Diseases
... Optimum care of these potentially complicated pregnancies can only be achieved by a combined approach by cardiologists and obstetricians in specialist centres with an understanding of the obstetric and cardiac complications that can arise. ...
... Optimum care of these potentially complicated pregnancies can only be achieved by a combined approach by cardiologists and obstetricians in specialist centres with an understanding of the obstetric and cardiac complications that can arise. ...
File
... MVP Most common form of valvular heart disease, occurring in 2 – 6% of the population. Causes: Unknown Thought to be linked to heredity. May be due to: •ischemic damage (caused by decreased blood flow as a result of coronary artery disease) •damage to valvular structures during acute myocardial inf ...
... MVP Most common form of valvular heart disease, occurring in 2 – 6% of the population. Causes: Unknown Thought to be linked to heredity. May be due to: •ischemic damage (caused by decreased blood flow as a result of coronary artery disease) •damage to valvular structures during acute myocardial inf ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.