Hypertension Presentation
... • If the second measurement is substantially different from the first, take a third measurement. • Record the lower of the last two measurements as the clinic blood pressure. ...
... • If the second measurement is substantially different from the first, take a third measurement. • Record the lower of the last two measurements as the clinic blood pressure. ...
PERI – ARREST ARRHYTHMIAS
... diagnosis. A 12 - lead ECG is essential for the management of tachycardias associated with a broad QRS complex. When the mechanism of a Broad Complex Tachycardia cannot be determined regard it as VT (ventricular tachycardia ), especially in the clinical context of ischaemic heart disease. PRINCIPLES ...
... diagnosis. A 12 - lead ECG is essential for the management of tachycardias associated with a broad QRS complex. When the mechanism of a Broad Complex Tachycardia cannot be determined regard it as VT (ventricular tachycardia ), especially in the clinical context of ischaemic heart disease. PRINCIPLES ...
a printable chart for recording your
... in the limbs that reduces circulation and can up amputation risk ...
... in the limbs that reduces circulation and can up amputation risk ...
Fetal circulation
... i.e.: when umbilical venous return is progressively reduced the percentage of umbilical venous blood passing through the ductus venosus increases progressively ...
... i.e.: when umbilical venous return is progressively reduced the percentage of umbilical venous blood passing through the ductus venosus increases progressively ...
CVS Pathology Lecture Notes (L3)
... Clinical : previous rheumatic fever or rheumatic heart disease, arthralgia, fever Laboratory :acute phase reactions – ESR, c-reactive protein, leukocytosis, prolonged P-R ...
... Clinical : previous rheumatic fever or rheumatic heart disease, arthralgia, fever Laboratory :acute phase reactions – ESR, c-reactive protein, leukocytosis, prolonged P-R ...
AED Study Guide
... An AED will only work for patients with certain heart rhythms, namely ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia. An AED will not work for the 'flat line' asystolic patient, although CPR can help induce a shockable rhythm in an asystolic patient. ...
... An AED will only work for patients with certain heart rhythms, namely ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia. An AED will not work for the 'flat line' asystolic patient, although CPR can help induce a shockable rhythm in an asystolic patient. ...
Aborted Sudden Cardiac Death Associated with Short QT Syndrome
... KCNH2,2,3) KCNQ1,4) KCNJ2,5) as well as KCNE1 and KCNE2. However, as a result no mutations of those genes were found. Twelve-lead ECG tracings from his parents and children were examined, and no abnormal findings were recognized. Discussion Unlike QT prolongation, an abbreviation of the QT interval h ...
... KCNH2,2,3) KCNQ1,4) KCNJ2,5) as well as KCNE1 and KCNE2. However, as a result no mutations of those genes were found. Twelve-lead ECG tracings from his parents and children were examined, and no abnormal findings were recognized. Discussion Unlike QT prolongation, an abbreviation of the QT interval h ...
Drug Information Sheet("Kusuri-no-Shiori") Internal Published: 12
... Dosing schedule (How to take this medicine) ・Your dosing schedule prescribed by your doctor is<< to be written by a healthcare professional>> ・For hypertension: In general, for adults, take 5 to 10 mg of the active ingredient at a time, once a day. The dosage may be adjusted according to the disease ...
... Dosing schedule (How to take this medicine) ・Your dosing schedule prescribed by your doctor is<< to be written by a healthcare professional>> ・For hypertension: In general, for adults, take 5 to 10 mg of the active ingredient at a time, once a day. The dosage may be adjusted according to the disease ...
Heart Failure Related Deaths - 5
... Heart Failure: More than Just the Left ventricle or Low Ejection Fraction - 7 Left Ventricle HF • HF with reduced EF (usually EF ≤ 45%) – This is the type mostly associated with heart failure • Heart failure is subclassed as Asymptomatic (ALVD) OR Symptomatic, and treatment is based upon whether a p ...
... Heart Failure: More than Just the Left ventricle or Low Ejection Fraction - 7 Left Ventricle HF • HF with reduced EF (usually EF ≤ 45%) – This is the type mostly associated with heart failure • Heart failure is subclassed as Asymptomatic (ALVD) OR Symptomatic, and treatment is based upon whether a p ...
Circulatory Systems III
... Left ventricle contracts much more forcefully than the right ventricle and develops a much higher pressure: ◦ Left Ventricle to body high resistance ◦ Right ventricle to lungs low resistance ...
... Left ventricle contracts much more forcefully than the right ventricle and develops a much higher pressure: ◦ Left Ventricle to body high resistance ◦ Right ventricle to lungs low resistance ...
Cardiac Defects: Tricuspid Atresia
... Tricuspid atresia is usually diagnosed a few hours or days after birth. Pediatricians refer newborns to pediatric cardiologists when they notice symptoms and signs such as a “blue baby with a heart murmur.” Pulse oximetry is a painless way to monitor the oxygen level of the blood. Some or all of the ...
... Tricuspid atresia is usually diagnosed a few hours or days after birth. Pediatricians refer newborns to pediatric cardiologists when they notice symptoms and signs such as a “blue baby with a heart murmur.” Pulse oximetry is a painless way to monitor the oxygen level of the blood. Some or all of the ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... Hypoplastic left heart syndrome with an intact atrial septum is a rare finding, reported in only 1% of pathologic specimens with hypoplasia of the aortic tract complex 4.With prenatal restriction, or complete premature closure of the foramen ovale (i.e., intact atrial septum), flow is diverted away ...
... Hypoplastic left heart syndrome with an intact atrial septum is a rare finding, reported in only 1% of pathologic specimens with hypoplasia of the aortic tract complex 4.With prenatal restriction, or complete premature closure of the foramen ovale (i.e., intact atrial septum), flow is diverted away ...
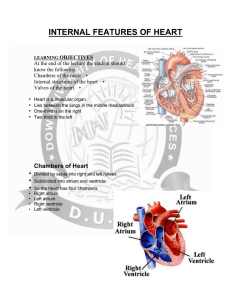
THE HUMAN HEART
... prevent blood from flowing back into the heart chambers after it has contracted atrioventricular valves are found between the atrium and ventricle of each side of the heart semilunar valves are found in the arteries leaving the heart to prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles ...
... prevent blood from flowing back into the heart chambers after it has contracted atrioventricular valves are found between the atrium and ventricle of each side of the heart semilunar valves are found in the arteries leaving the heart to prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles ...
Topic 9 revision notes - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... Thus the blood flowing to the lungs in the pulmonary artery has a much lower pressure than the blood in the aorta. State that blood is pumped away from the heart into arteries and returns to the heart in veins Explain the relative thickness: – of the muscle wall of the left and right ventricles – ...
... Thus the blood flowing to the lungs in the pulmonary artery has a much lower pressure than the blood in the aorta. State that blood is pumped away from the heart into arteries and returns to the heart in veins Explain the relative thickness: – of the muscle wall of the left and right ventricles – ...
CPR Anytime
... due to sudden cardiac arrest, suffered outside the hospital setting and in hospital emergency departments. About 900 Americans die every day due to sudden cardiac arrest. ...
... due to sudden cardiac arrest, suffered outside the hospital setting and in hospital emergency departments. About 900 Americans die every day due to sudden cardiac arrest. ...
Cardiovascular system
... The S-T segment represents ventricular systole, increased pressure opens the pulmonary and aortic valves, rushing blood out the arteries. The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, or when the ventricles relax, this action causes the pulmonary and aortic valves to shut creating the “dub” ...
... The S-T segment represents ventricular systole, increased pressure opens the pulmonary and aortic valves, rushing blood out the arteries. The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, or when the ventricles relax, this action causes the pulmonary and aortic valves to shut creating the “dub” ...
End-systolic pressure-volume relation and ventricular
... identifies a low risk subset for coronary events • However, the potentially prognostically relevant information on cardiovascular hemodynamics for heart failure-related events is unsettled ...
... identifies a low risk subset for coronary events • However, the potentially prognostically relevant information on cardiovascular hemodynamics for heart failure-related events is unsettled ...
Circulatory System - Fall River Public Schools
... • Heartbeat has two phases: – Systole – occurs when ventricles contract • Pumps blood out of the heart ...
... • Heartbeat has two phases: – Systole – occurs when ventricles contract • Pumps blood out of the heart ...
Congenital Heart Defects
... • Large defect R V pressures • May do well for several weeks due PVR (compensated heart failure) • As PVR , LR shunt (uncompensated heart failure) • Fail to gain weight thin, large stomachs • Develop pulm edema & die ...
... • Large defect R V pressures • May do well for several weeks due PVR (compensated heart failure) • As PVR , LR shunt (uncompensated heart failure) • Fail to gain weight thin, large stomachs • Develop pulm edema & die ...
Pharmacotherapy in the Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction
... surgery, uncontrolled hypertension, trauma or active bleeding etc. The incidence of stroke in elderly patients receiving thrombolytic therapy is also high. Primary PTCA offers an attractive alternative in view of life threatening complication rates of 1-3 % with a artery patency rate of only 50-80% ...
... surgery, uncontrolled hypertension, trauma or active bleeding etc. The incidence of stroke in elderly patients receiving thrombolytic therapy is also high. Primary PTCA offers an attractive alternative in view of life threatening complication rates of 1-3 % with a artery patency rate of only 50-80% ...
Tetralogy of Fallot - American Heart Association
... and, if needed, enlarging the branch pulmonary arteries that go to each lung. Sometimes a tube is placed between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. This is sometimes called a Rastelli repair. It’s similar to the type of repair used for some other heart defects. Will my child’s activities ...
... and, if needed, enlarging the branch pulmonary arteries that go to each lung. Sometimes a tube is placed between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. This is sometimes called a Rastelli repair. It’s similar to the type of repair used for some other heart defects. Will my child’s activities ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.