
Use of Primary Prevention Implantable Cardioverter
... to determine whether management of patients with an acute coronary syndrome, congestive heart failure (CHF), or atrial fibrillation could be improved through a multilateral heathcare stakeholder effort using a disease management strategy. The study enrolled all patients admitted to any hospital thro ...
... to determine whether management of patients with an acute coronary syndrome, congestive heart failure (CHF), or atrial fibrillation could be improved through a multilateral heathcare stakeholder effort using a disease management strategy. The study enrolled all patients admitted to any hospital thro ...
Doping and effects of anabolic androgenic steroids on the heart: histological,
... Therefore, in the management of arrhythmic athletes, the cardiologist should always consider the possibility that the arrhythmias may be due to the consumption of illicit drugs (sometimes more than one type), especially if no signs of cardiac diseases are apparent. However, in the presence of latent ...
... Therefore, in the management of arrhythmic athletes, the cardiologist should always consider the possibility that the arrhythmias may be due to the consumption of illicit drugs (sometimes more than one type), especially if no signs of cardiac diseases are apparent. However, in the presence of latent ...
Preoperative hospital length of stay as a modifiable risk factor for
... This study demonstrates that extended preoperative hospital stay is a significant risk factor for mediastinitis by both univariate and adjusted models. Each week of hospital stay preoperatively was associated with a 15% increased risk of mediastinitis. This is a novel and also potentially modifiable ...
... This study demonstrates that extended preoperative hospital stay is a significant risk factor for mediastinitis by both univariate and adjusted models. Each week of hospital stay preoperatively was associated with a 15% increased risk of mediastinitis. This is a novel and also potentially modifiable ...
Induction and Patterning of the Cardiac Conduction System
... At present, there are two models for the heterogeneity of the SA node; one, the «gradient model», is one in which there is a gradual change in the properties of node cells from the periphery to the center; secondly, the «mosaic model», is where there is a variable mix of atrial and SA node cells fro ...
... At present, there are two models for the heterogeneity of the SA node; one, the «gradient model», is one in which there is a gradual change in the properties of node cells from the periphery to the center; secondly, the «mosaic model», is where there is a variable mix of atrial and SA node cells fro ...
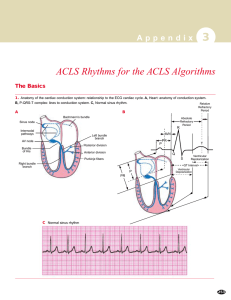
ACLS Rhythms for the ACLS Algorithms
... ■ Palpitations felt by patient at the paroxysmal onset; becomes anxious, uncomfortable ■ Exercise tolerance low with very high rates ■ Symptoms of unstable tachycardia may occur ...
... ■ Palpitations felt by patient at the paroxysmal onset; becomes anxious, uncomfortable ■ Exercise tolerance low with very high rates ■ Symptoms of unstable tachycardia may occur ...
Atrial Fibrillation, Atrioventricular Nodal Ablation and Biventricular
... heart rhythm and/or heart rate 3. In recent years, the “ablate and pace” approach –radiofrequency ablation of the atrioventricular node (AV), followed by implantation of a permanent pacemaker– has proved to be a useful practice for either avoiding or treating the “tachycardiomyopathy” caused by the ...
... heart rhythm and/or heart rate 3. In recent years, the “ablate and pace” approach –radiofrequency ablation of the atrioventricular node (AV), followed by implantation of a permanent pacemaker– has proved to be a useful practice for either avoiding or treating the “tachycardiomyopathy” caused by the ...
Continuous Flow Left ventricular Assist Device
... saline bubbles in the left heart chambers within three beats or less of their appearance in the right side of the heart is typically felt to represent the presence of an intracardiac shunt, most commonly a PFO. It is, however, important to remember that in patients with advanced heart failure and si ...
... saline bubbles in the left heart chambers within three beats or less of their appearance in the right side of the heart is typically felt to represent the presence of an intracardiac shunt, most commonly a PFO. It is, however, important to remember that in patients with advanced heart failure and si ...
130 Right heart physiology n
... ventricle has a smaller muscle mass and is therefore ‘weaker’ than the left ventricle. Due to this relative ‘weakness’ the right ventricle cannot adapt acutely to large changes in pulmonary vascular resistance (afterload) and this is the main cause of right heart failure. Conversely, the right ventr ...
... ventricle has a smaller muscle mass and is therefore ‘weaker’ than the left ventricle. Due to this relative ‘weakness’ the right ventricle cannot adapt acutely to large changes in pulmonary vascular resistance (afterload) and this is the main cause of right heart failure. Conversely, the right ventr ...
[PDF]
... rule-based expert system that emulates the ECG interpretation skills of an expert cardiologist. The knowledge of an expert is confined to him and is not freely available for decision-making. An expert system is developed to overcome this problem. In this rule-based expert system, patient’s heart rat ...
... rule-based expert system that emulates the ECG interpretation skills of an expert cardiologist. The knowledge of an expert is confined to him and is not freely available for decision-making. An expert system is developed to overcome this problem. In this rule-based expert system, patient’s heart rat ...
Public Summary Document - Word 261 KB
... Issues with the descriptor were identified that require clarification: whether to describe the device more precisely as a pulmonary artery pressure sensor rather than a haemodynamic sensor; possible separation of MBS items to insert, remove and replace the device (noting that the last of these i ...
... Issues with the descriptor were identified that require clarification: whether to describe the device more precisely as a pulmonary artery pressure sensor rather than a haemodynamic sensor; possible separation of MBS items to insert, remove and replace the device (noting that the last of these i ...
6.2.1 review related to post operative management of heart valve
... characterized by diastolic reflux of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle (LV). Acute AR typically causes severe pulmonary edema and hypotension and is a surgical emergency. Chronic severe AR causes combined LV volume and pressure overload. It is accompanied by systolic hypertension and wide ...
... characterized by diastolic reflux of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle (LV). Acute AR typically causes severe pulmonary edema and hypotension and is a surgical emergency. Chronic severe AR causes combined LV volume and pressure overload. It is accompanied by systolic hypertension and wide ...
Is Heart Rate Important for Patients With Heart Failure in Atrial
... preferred in patients with AF (7). Neither strategy was associated with any significant difference in mortality, hospitalizations, or symptoms during 3-year follow-up. Only 10% of the patients enrolled had a history of heart failure, and the mean LVEF was 51%, thus, extrapolation of the data to steer ...
... preferred in patients with AF (7). Neither strategy was associated with any significant difference in mortality, hospitalizations, or symptoms during 3-year follow-up. Only 10% of the patients enrolled had a history of heart failure, and the mean LVEF was 51%, thus, extrapolation of the data to steer ...
NSTEMI standing orders
... Recommendation who present with chest discomfort consistent with ACS. A cardiac-specific troponin is the preferred marker, and, if available, it should be measured in all patients who present with chest discomfort consistent with ACS. Patients with negative cardiac biomarkers within 6 h of the onset ...
... Recommendation who present with chest discomfort consistent with ACS. A cardiac-specific troponin is the preferred marker, and, if available, it should be measured in all patients who present with chest discomfort consistent with ACS. Patients with negative cardiac biomarkers within 6 h of the onset ...
The Cardiovascular System - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Weakening of the heart over time; heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet body’s needs ...
... Weakening of the heart over time; heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet body’s needs ...
Anatomy of the pig heart: comparisons with normal human cardiac
... Transgenic technology has potentially solved many of the immunological difficulties of using pig organs to support life in the human recipient. Nevertheless, other problems still remain. Knowledge of cardiac anatomy of the pig (Sus scrofa) is limited despite the general acceptance in the literature ...
... Transgenic technology has potentially solved many of the immunological difficulties of using pig organs to support life in the human recipient. Nevertheless, other problems still remain. Knowledge of cardiac anatomy of the pig (Sus scrofa) is limited despite the general acceptance in the literature ...
Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptors and Cardiac
... The present study may be important from a pharmacotherapeutic point of view. If AT1-R stimulation is indeed partly responsible for the increased LVM in subjects with HCM, the use of ACE inhibitors or AT1-R antagonists in this disease might be reconsidered. Both are currently not widely used in HCM, ...
... The present study may be important from a pharmacotherapeutic point of view. If AT1-R stimulation is indeed partly responsible for the increased LVM in subjects with HCM, the use of ACE inhibitors or AT1-R antagonists in this disease might be reconsidered. Both are currently not widely used in HCM, ...
Search for HRV‐parameters that detect a sympathetic - UvA-DARE
... attention in biomedical literature. It has been fairly well established that chronic heart failure patients (CHF) have different heart rate variability patterns compared to matched healthy controls (10, 35). However, many of those patients will be on ß‐blocker therapy, which has a strong influenc ...
... attention in biomedical literature. It has been fairly well established that chronic heart failure patients (CHF) have different heart rate variability patterns compared to matched healthy controls (10, 35). However, many of those patients will be on ß‐blocker therapy, which has a strong influenc ...
THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM, PRINCIPLES AND RECORDING
... The electrocardiograph is used to record the ECG. The main components of the electrocardiograph are: ► the signal acquisition system, which includes the electrodes and cables. The electrodes are electrical conductors used to make contact with a non-metallic part of an electrical circuit. To record t ...
... The electrocardiograph is used to record the ECG. The main components of the electrocardiograph are: ► the signal acquisition system, which includes the electrodes and cables. The electrodes are electrical conductors used to make contact with a non-metallic part of an electrical circuit. To record t ...
Effects of exercise training on left ventricular volumes
... pulsed Doppler, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the left ventricle in humans before and after training.1,3,7-10 In contrast to some early reports in humans and animals,5,6,11 these studies have shown that training does not lead to further ventricular dilatation, infarct expansion, or ventric ...
... pulsed Doppler, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the left ventricle in humans before and after training.1,3,7-10 In contrast to some early reports in humans and animals,5,6,11 these studies have shown that training does not lead to further ventricular dilatation, infarct expansion, or ventric ...
Under-utilization of evidence-based drug treatment in patients with
... reveals that the exclusion of patients with preserved left ventricular function (PLVF) and those with renal dysfunction is an important reason for the average of patients in trials being about a decade younger than the epidemiological population.21–23 Indeed, in CHARM preserved,29 which recruited on ...
... reveals that the exclusion of patients with preserved left ventricular function (PLVF) and those with renal dysfunction is an important reason for the average of patients in trials being about a decade younger than the epidemiological population.21–23 Indeed, in CHARM preserved,29 which recruited on ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.










![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008797539_1-0bf3f4445f12671fef8d4524d9ca3253-300x300.png)











