A.C. Chow and D.J. Perreault, “Active EMI Filters for Automotive Motor Drives,” 2002 IEEE Workshop on Power Electronics in Transportation , Auburn Hills, MI, October 2002, pp. 127-134.
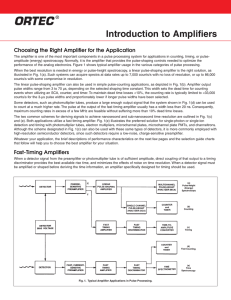
... drive a brushless motor for the EHPS system. The electrical motor replaces the belt-drive for a hydraulic fluid pump, and allows for more efficient operation of the power steering system. The inverter has a fundamental switching frequency of 10 KHz and a peak input current of 70 amps. The structure ...
... drive a brushless motor for the EHPS system. The electrical motor replaces the belt-drive for a hydraulic fluid pump, and allows for more efficient operation of the power steering system. The inverter has a fundamental switching frequency of 10 KHz and a peak input current of 70 amps. The structure ...
Very Low Power, Negative Rail Input, Rail-to
... This fully differential op amp features accurate output common-mode control that allows for dc-coupling when driving analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). This control, coupled with an input common-mode range below the negative rail as well as rail-to-rail output, allows for easy interfacing between ...
... This fully differential op amp features accurate output common-mode control that allows for dc-coupling when driving analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). This control, coupled with an input common-mode range below the negative rail as well as rail-to-rail output, allows for easy interfacing between ...
Design of a proper set-up for low current
... Arduino UNO is the device that will be used to read the values and send them to the computer to be logged. It will take some time and processes to adjust and program the device so the results are the expected ones. Arduino is a prototype board, easy to use and without the need to add significant har ...
... Arduino UNO is the device that will be used to read the values and send them to the computer to be logged. It will take some time and processes to adjust and program the device so the results are the expected ones. Arduino is a prototype board, easy to use and without the need to add significant har ...
Quad Low Noise, Low Cost Variable Gain Amplifier AD8335
... Assuming a 20 MHz noise bandwidth (NBW), the Nyquist frequency for a 40 MHz ADC, the input SNR is 92 dB. The HLxx pin optimizes the output SNR for 10-bit and 12-bit ADCs with 1 V p-p or 2 V p-p full-scale (FS) inputs. Channel 1 and Channel 2 are enabled through the EN12 pin and Channel 3 and Channel ...
... Assuming a 20 MHz noise bandwidth (NBW), the Nyquist frequency for a 40 MHz ADC, the input SNR is 92 dB. The HLxx pin optimizes the output SNR for 10-bit and 12-bit ADCs with 1 V p-p or 2 V p-p full-scale (FS) inputs. Channel 1 and Channel 2 are enabled through the EN12 pin and Channel 3 and Channel ...
MAX4400–MAX4403 Single/Dual/Quad, Low-Cost, Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail Op Amps with Shutdown General Description
... amps offer rail-to-rail outputs, draw only 320µA of quiescent current, and operate from a single +2.5V to +5.5V supply. For additional power conservation, the MAX4401 offers a low-power shutdown mode that reduces supply current to 1µA (max) and puts the amplifier’s output in a high-impedance state. ...
... amps offer rail-to-rail outputs, draw only 320µA of quiescent current, and operate from a single +2.5V to +5.5V supply. For additional power conservation, the MAX4401 offers a low-power shutdown mode that reduces supply current to 1µA (max) and puts the amplifier’s output in a high-impedance state. ...
UCC28250 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... soft-start, used in conjunction with an internal pre-biased startup circuit, allows the controller to gradually reach a steady-state operating point under all output conditions. The UCC28250 can be configured for primary or secondary-side control and either voltage or current mode control can be imp ...
... soft-start, used in conjunction with an internal pre-biased startup circuit, allows the controller to gradually reach a steady-state operating point under all output conditions. The UCC28250 can be configured for primary or secondary-side control and either voltage or current mode control can be imp ...
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances.Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive.Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, but it also occurs naturally within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback systems are studied in control systems engineering.