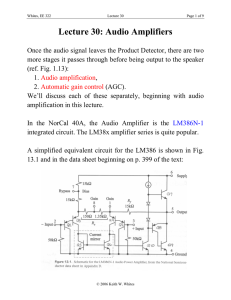
Phys204(Electronics). - University of Belize
... 4.2. use truth tables to represent the function of logic gates with no more than two inputs; 4.3. analyze circuits using combinations of logic gates to perform control functions; 4.4. construct and interpret truth tables for a combination of logic gates; 4.5. use V-t diagrams to represent the respon ...
... 4.2. use truth tables to represent the function of logic gates with no more than two inputs; 4.3. analyze circuits using combinations of logic gates to perform control functions; 4.4. construct and interpret truth tables for a combination of logic gates; 4.5. use V-t diagrams to represent the respon ...
review for elec 105 midterm exam #1 (fall 2001)
... resistance o test-source method for finding Thévenin (Norton) resistance o treatment of dependent vs. independent sources - concept of a signal; voltage and current signals - concept of a circuit “port” (pair of terminals) - input and output resistances of amplifiers, sources, and loads - distinguis ...
... resistance o test-source method for finding Thévenin (Norton) resistance o treatment of dependent vs. independent sources - concept of a signal; voltage and current signals - concept of a circuit “port” (pair of terminals) - input and output resistances of amplifiers, sources, and loads - distinguis ...
hw3
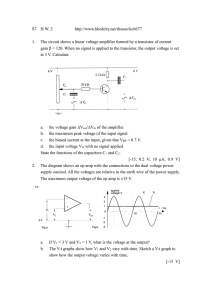
... b. What is the change in the input and overdrive voltage as the output varies from 9V to 1V? c. Write an expression for gm and ro as a function of output bias point. d. Write an expression for Av0 as a function of output bias point. e. For each of the output bias points {9V, 6V, 1V}, calculate the c ...
... b. What is the change in the input and overdrive voltage as the output varies from 9V to 1V? c. Write an expression for gm and ro as a function of output bias point. d. Write an expression for Av0 as a function of output bias point. e. For each of the output bias points {9V, 6V, 1V}, calculate the c ...
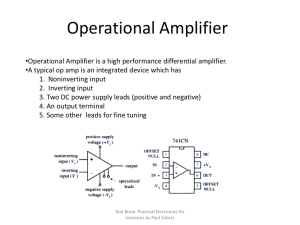
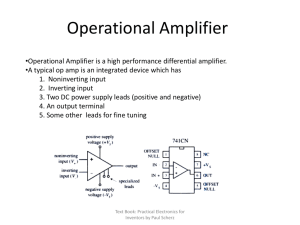
A v
... • Saturates at very low input voltages (Max vout=power supply voltage) • To operate as an amp, v+-v-
... • Saturates at very low input voltages (Max vout=power supply voltage) • To operate as an amp, v+-v-
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances.Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive.Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, but it also occurs naturally within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback systems are studied in control systems engineering.