Unified Field Theory
... combines the treatment of two or more types of fields in order to deduce previously unrecognized interrelationships, especially such a theory unifying the theories of nuclear, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces. In physics, a field refers to an area under the influence of some force, such as ...
... combines the treatment of two or more types of fields in order to deduce previously unrecognized interrelationships, especially such a theory unifying the theories of nuclear, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces. In physics, a field refers to an area under the influence of some force, such as ...
The Hydrogen Atom
... The Bohr Model In 1913 Niels Bohr proposed a theory of the hydrogen atom that could account for its stability and for the frequencies of its spectral lines. • An electron can circle the nucleus without losing energy only in certain specific orbits. • The energy of the electron depends on which orbi ...
... The Bohr Model In 1913 Niels Bohr proposed a theory of the hydrogen atom that could account for its stability and for the frequencies of its spectral lines. • An electron can circle the nucleus without losing energy only in certain specific orbits. • The energy of the electron depends on which orbi ...
Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the
... which the classical Newtonian mechanical theory is unsuccessful at explaining. The microscopic world is the realm of atoms, photons, nuclei, electrons, neutrons, and a whole host of other subatomic particles. These particles are the “building blocks” of our universe, in the sense that everything tha ...
... which the classical Newtonian mechanical theory is unsuccessful at explaining. The microscopic world is the realm of atoms, photons, nuclei, electrons, neutrons, and a whole host of other subatomic particles. These particles are the “building blocks” of our universe, in the sense that everything tha ...
Introduction Vacuum effects due to Dirac Sea When do the
... • Dispersion relations used in QFT first by Gell- Mann, Thirring and Goldberger , Phys. Rev. 95, 1612 (1954). • Is there a minimum length scale involved which the wavelength of light is not allowed to fall below? How many atoms constitutes the minimum number before you can apply the idea of a refrac ...
... • Dispersion relations used in QFT first by Gell- Mann, Thirring and Goldberger , Phys. Rev. 95, 1612 (1954). • Is there a minimum length scale involved which the wavelength of light is not allowed to fall below? How many atoms constitutes the minimum number before you can apply the idea of a refrac ...
vuletic
... Cooling and trapping techniques Stabilizing Ions with Light Ions are a promising qubit for quantum computation. Ions are standardly trapped with time varying (RF) electric fields. These traps are limited in size and by micromotion, residual motion inherent in these RF traps. We are developing a new ...
... Cooling and trapping techniques Stabilizing Ions with Light Ions are a promising qubit for quantum computation. Ions are standardly trapped with time varying (RF) electric fields. These traps are limited in size and by micromotion, residual motion inherent in these RF traps. We are developing a new ...
Adventures with Superstrings
... all particle types are the same kind of string vibrating or rotating in different ways the spectrum and size of the string states is ...
... all particle types are the same kind of string vibrating or rotating in different ways the spectrum and size of the string states is ...
slides
... themselves serve as the ``local beables of the theory. These are the mathematical counterparts in the theory to real events at definite places and times in the real world (as distinct from the many purely mathematical constructions that occur in the working out of physical theories, as distinct from ...
... themselves serve as the ``local beables of the theory. These are the mathematical counterparts in the theory to real events at definite places and times in the real world (as distinct from the many purely mathematical constructions that occur in the working out of physical theories, as distinct from ...
Chapter 7 -- Radiative Corrections: some formal developments Chapter 7:
... For example, consider the radiative corrections for Compton scattering. ...
... For example, consider the radiative corrections for Compton scattering. ...
Non perturbative QCD
... of the standard model 1965 -1975 Quark model Unified Electroweak Theory Strong interaction theory (Quantum Chromodynamics -QCD) Both are quantum field theories, with a gauge invariance. Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa CP violation mechanism. Successful prediction of a third generation of quarks. ...
... of the standard model 1965 -1975 Quark model Unified Electroweak Theory Strong interaction theory (Quantum Chromodynamics -QCD) Both are quantum field theories, with a gauge invariance. Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa CP violation mechanism. Successful prediction of a third generation of quarks. ...
Quantum Algorithms
... By exploiting the quantum mechanical behaviour of the communication medium, we can detect eavesdroppers (leading to quantum cryptography, section 12.6) and solve distributed computation tasks more efficiently. Unfortunately, we won’t be covering this in this course, but we will lay the foundation fo ...
... By exploiting the quantum mechanical behaviour of the communication medium, we can detect eavesdroppers (leading to quantum cryptography, section 12.6) and solve distributed computation tasks more efficiently. Unfortunately, we won’t be covering this in this course, but we will lay the foundation fo ...
course materials
... Ria Broer and Remco Havenith, Theoretical Chemistry, University of Groningen This course considers the theoretical treatment of the geometrical and electronic structure of solids and surfaces and of molecule-surface interactions. For molecules a much-used approximation is molecular orbital (MO) theo ...
... Ria Broer and Remco Havenith, Theoretical Chemistry, University of Groningen This course considers the theoretical treatment of the geometrical and electronic structure of solids and surfaces and of molecule-surface interactions. For molecules a much-used approximation is molecular orbital (MO) theo ...
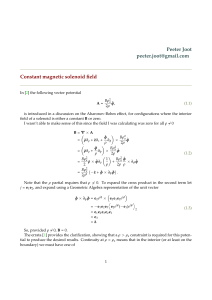
Constant magnetic solenoid field
... j = e1 e2 , and expand using a Geometric Algebra representation of the unit vector ...
... j = e1 e2 , and expand using a Geometric Algebra representation of the unit vector ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI M.Sc. THIRD
... Plot the eigenfunctions and probability density distribution as a function of ‘x’ for the lowest two energy ...
... Plot the eigenfunctions and probability density distribution as a function of ‘x’ for the lowest two energy ...
Course Syllabus
... Feynman Lectures represents a famous experiment at teaching Quantum Mechanics “correctly” at the sophomore level. In addition, the old Berkeley Physics Course, Vol. 4, Quantum Physics, is a must-read piece for those who have not been trained to think about basic things such as orders of magnitude, q ...
... Feynman Lectures represents a famous experiment at teaching Quantum Mechanics “correctly” at the sophomore level. In addition, the old Berkeley Physics Course, Vol. 4, Quantum Physics, is a must-read piece for those who have not been trained to think about basic things such as orders of magnitude, q ...
2.1.7 particle movement in magnetic fields
... can be to change speed or direction. The effect of a magnetic field on a charged particle can only be to change its direction. This is because the force applied is always perpendicular to its motion. ...
... can be to change speed or direction. The effect of a magnetic field on a charged particle can only be to change its direction. This is because the force applied is always perpendicular to its motion. ...