steady state solution
... Free body diagram Kinematics F=ma for each particle. M c 0 (for rigid bodies or frames only) Solve for unknown forces or accelerations ...
... Free body diagram Kinematics F=ma for each particle. M c 0 (for rigid bodies or frames only) Solve for unknown forces or accelerations ...
QUANTUM PARTICLES PASSING THROUGH A MATTER
... The wave property of a massive particle proposed by Louis de Broglie is an essential ingredient in the development of quantum mechanics. Besides the classical experiments of the diffraction of electrons and neutrons,1 numerous experiments have been performed recently to demonstrate the property with ...
... The wave property of a massive particle proposed by Louis de Broglie is an essential ingredient in the development of quantum mechanics. Besides the classical experiments of the diffraction of electrons and neutrons,1 numerous experiments have been performed recently to demonstrate the property with ...
v` mf - EngineeringDuniya.com
... from other particles, so that its fall is not affected by them, the process is called free settling. • If the motion of the particle is impeded by other particles, which will happen when the particles are near each other even though they may not actually be colliding, the process is called hindered ...
... from other particles, so that its fall is not affected by them, the process is called free settling. • If the motion of the particle is impeded by other particles, which will happen when the particles are near each other even though they may not actually be colliding, the process is called hindered ...
Particle-based Collision Detection
... (a) The model of Rocker Arm with randomly distributed particles (b) Final distribution of particles on the model of Rocker Arm (c) The Dragon model with randomly distributed particles (d) Final distribution of particles on the Dragon model ...
... (a) The model of Rocker Arm with randomly distributed particles (b) Final distribution of particles on the model of Rocker Arm (c) The Dragon model with randomly distributed particles (d) Final distribution of particles on the Dragon model ...
Peridynamics simulation of the comminution of particles containing
... the upper plate moves downward. The contacts between the particle and the plates are modeled by adding a normal repulsive force to the particle’s nodes touching the plates. A regularized Coulomb friction law with a friction coefficient of 0.5 and a viscosity of 0.8 was used. The compression continues ...
... the upper plate moves downward. The contacts between the particle and the plates are modeled by adding a normal repulsive force to the particle’s nodes touching the plates. A regularized Coulomb friction law with a friction coefficient of 0.5 and a viscosity of 0.8 was used. The compression continues ...
Lecture 2 Quantum mechanics in one dimension
... The scattering properties are characterised by eigenvalues of the S-matrix, e 2iδi . For potentials in which E < Vmax , particle transfer across the barrier is mediated by tunneling. For an extended periodic potential (e.g. Kronig-Penney model), the spectrum of allow energies show “band gaps” where ...
... The scattering properties are characterised by eigenvalues of the S-matrix, e 2iδi . For potentials in which E < Vmax , particle transfer across the barrier is mediated by tunneling. For an extended periodic potential (e.g. Kronig-Penney model), the spectrum of allow energies show “band gaps” where ...
MATH10232: EXAMPLE SHEET X
... (a) Find and sketch potential V (x) for the three cases i. a = 1, b = 5, n = 1. ii. a = −1, b = 5, n = −1. iii. a = 1, b = −5, n = −1. Henceforth, consider only the case a = 1, b = −5, n = −1. (b) Show that the energy of the particle E ≥ E0 , where E0 is a constant to be determined. (c) A particle i ...
... (a) Find and sketch potential V (x) for the three cases i. a = 1, b = 5, n = 1. ii. a = −1, b = 5, n = −1. iii. a = 1, b = −5, n = −1. Henceforth, consider only the case a = 1, b = −5, n = −1. (b) Show that the energy of the particle E ≥ E0 , where E0 is a constant to be determined. (c) A particle i ...
Question 1 Consider the mechanical system with three degrees of
... your answer to 3 decimal places. Take the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity to be 9.81 ms-2.Hint : Apply Newton’s 2nd Law to each of the two particles A and B. ...
... your answer to 3 decimal places. Take the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity to be 9.81 ms-2.Hint : Apply Newton’s 2nd Law to each of the two particles A and B. ...
Course Syllabus
... (k) An ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice ...
... (k) An ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice ...
Chapter 9
... • During a collision, the total linear momentum is always conserved if the system is isolated (no external force) • It may not necessarily apply to the total kinetic energy • If the total kinetic energy is conserved during the collision, then such a collision is called elastic • If the total kinetic ...
... • During a collision, the total linear momentum is always conserved if the system is isolated (no external force) • It may not necessarily apply to the total kinetic energy • If the total kinetic energy is conserved during the collision, then such a collision is called elastic • If the total kinetic ...
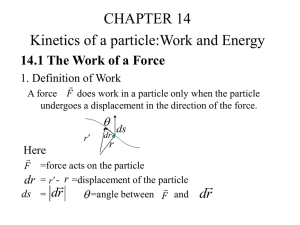
14.1 The Work of a Force
... The particle’s initial kinetic energy plus the work done by all the forces acting on the particle as it moves from its initial to its final position is equal to the particle’s final kinetic energy. T1 U12 T2 or 12 mv12 U12 12 mv2 2 ...
... The particle’s initial kinetic energy plus the work done by all the forces acting on the particle as it moves from its initial to its final position is equal to the particle’s final kinetic energy. T1 U12 T2 or 12 mv12 U12 12 mv2 2 ...
Chapter 4 Molecular Dynamics and Other Dynamics
... Note that the coordinates q have to be evaluated first since the new values at time t + h are used to evaluate the forces. The algorithm C is also second-order in step size h. From the derivation it is not obvious that it is necessarily superior than Verlet algorithm. However, the symplectic algori ...
... Note that the coordinates q have to be evaluated first since the new values at time t + h are used to evaluate the forces. The algorithm C is also second-order in step size h. From the derivation it is not obvious that it is necessarily superior than Verlet algorithm. However, the symplectic algori ...
Document
... external forces acting on a system of particles is equipollent with the system of effective forces of the system. • The mass center of a system of particles will be defined and its motion described. • Application of the work-energy principle and the impulse-momentum principle to a system of particle ...
... external forces acting on a system of particles is equipollent with the system of effective forces of the system. • The mass center of a system of particles will be defined and its motion described. • Application of the work-energy principle and the impulse-momentum principle to a system of particle ...
Lecture11(CavitiesI) 2015 - Indico
... in resonant cavity and particles enter and leave by holes in end walls. Energy is continuously exchanged between electric and magnetic fields within cavity volume. The time-varying fields ensure finite energy increment at each passage through one or a chain of cavities. There is no build-up of volta ...
... in resonant cavity and particles enter and leave by holes in end walls. Energy is continuously exchanged between electric and magnetic fields within cavity volume. The time-varying fields ensure finite energy increment at each passage through one or a chain of cavities. There is no build-up of volta ...
Systems of Particles
... • Since the internal forces occur in equal and opposite collinear pairs, the resultant force and couple due to the internal forces are zero, ...
... • Since the internal forces occur in equal and opposite collinear pairs, the resultant force and couple due to the internal forces are zero, ...
IPhO 2016 - Theory - Large Hadron Collider
... In the following, the particles produced in a collision in a typical LHC detector are identified in a two stage detector, consisting of a tracking detector and a ToF detector. Figure 3 shows the setup of the two stage detector in the plane transverse and longitudinal to the proton beams. Both detecto ...
... In the following, the particles produced in a collision in a typical LHC detector are identified in a two stage detector, consisting of a tracking detector and a ToF detector. Figure 3 shows the setup of the two stage detector in the plane transverse and longitudinal to the proton beams. Both detecto ...
The Stillinger-Weber Potential
... Classical Molecular Dynamics Simulations consists in solving the Newton’s equations for an assembly of particles interacting through an empirical potentiaL; ...
... Classical Molecular Dynamics Simulations consists in solving the Newton’s equations for an assembly of particles interacting through an empirical potentiaL; ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter J2
... tube to change sign is constant. Hence the particle spends the same time travelling in any one tube. However, as the particle moves down the line it is moving faster because it is being accelerated and so the length of the tubes must be increasing. Eventually the particles are moving close to the sp ...
... tube to change sign is constant. Hence the particle spends the same time travelling in any one tube. However, as the particle moves down the line it is moving faster because it is being accelerated and so the length of the tubes must be increasing. Eventually the particles are moving close to the sp ...
5th Homework Due: 7 November 2008 1. In spherical
... For a general motion of the particle, all of r, θ and φ change with time. For such a general motion, calculate ~v and ~a. If one defines, ~v = vr r̂ + vθ θ̂ + vφ φ̂ and ~a = ar r̂ + aθ θ̂ + aφ φ̂, (a) Express vr,θ,φ and ar,θ,φ in terms of r, θ, φ and their derivatives. (b) Express the kinetic energy ...
... For a general motion of the particle, all of r, θ and φ change with time. For such a general motion, calculate ~v and ~a. If one defines, ~v = vr r̂ + vθ θ̂ + vφ φ̂ and ~a = ar r̂ + aθ θ̂ + aφ φ̂, (a) Express vr,θ,φ and ar,θ,φ in terms of r, θ, φ and their derivatives. (b) Express the kinetic energy ...
Solution 1: mg=GMm/r2, so GM=gR2. At the equator, mV2/R=GMm
... Since the heavy particles move much more slowly than the light particles, we may approximately solve the problem by calculating the average force between the heavy particles at a fixed position, and use that to determine the motion of the heavy particles. This average force has a repulsive component ...
... Since the heavy particles move much more slowly than the light particles, we may approximately solve the problem by calculating the average force between the heavy particles at a fixed position, and use that to determine the motion of the heavy particles. This average force has a repulsive component ...