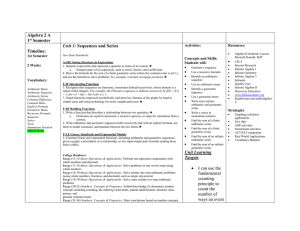
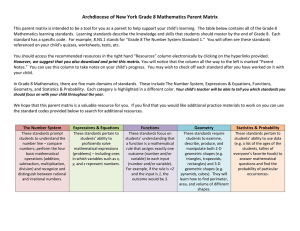
Guidelines for Equations, Units, and Mathematical Notation 1
... a) The physical state of the reactants and products (solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution) are often indicated by italic letters in parentheses, as shown in Examples A and B. b) The “Math is prose” rule can be adapted for the case of chemical equations also but, very often, chemical equations are st ...
... a) The physical state of the reactants and products (solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution) are often indicated by italic letters in parentheses, as shown in Examples A and B. b) The “Math is prose” rule can be adapted for the case of chemical equations also but, very often, chemical equations are st ...
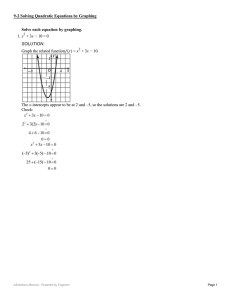
Section 9.5 and 9.6
... 2. Raise each side of the equation to a power equal to the index. 3. Solve the resulting equation: a. If linear, isolate the variable b. If quadratic, solve by factoring 4. If you have more than one solution, sometimes one of them won’t work. You might want to check them. ...
... 2. Raise each side of the equation to a power equal to the index. 3. Solve the resulting equation: a. If linear, isolate the variable b. If quadratic, solve by factoring 4. If you have more than one solution, sometimes one of them won’t work. You might want to check them. ...