MPM2D Big Ideas
... Determine the basic properties of quadratic relations o Collect data (investigation or secondary sources) that can be represented as a quadratic relation, graph it and draw a curve of best fit o Recognize y = ax2 + bx + c is a parabola and table of values yields a constant second difference o Key fe ...
... Determine the basic properties of quadratic relations o Collect data (investigation or secondary sources) that can be represented as a quadratic relation, graph it and draw a curve of best fit o Recognize y = ax2 + bx + c is a parabola and table of values yields a constant second difference o Key fe ...
solutions
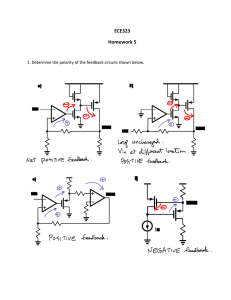
... 3. In problem 2, assume opamp A1 has a transfer function H OL ( s ) 1 s / , determine the closed p ...
... 3. In problem 2, assume opamp A1 has a transfer function H OL ( s ) 1 s / , determine the closed p ...
Lecture Notes Chapter 3
... Comparison between Elevation and Voltage Branch Voltages Vs. Node Voltages Nodes and Extraordinary (Critical) Nodes Node Analysis Process Node Analysis with Dependent Sources Supernodes ...
... Comparison between Elevation and Voltage Branch Voltages Vs. Node Voltages Nodes and Extraordinary (Critical) Nodes Node Analysis Process Node Analysis with Dependent Sources Supernodes ...
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW QUESTIONS:
... 9. Which best describes the transformation from the graph of f (x ) = -x + 5 to the graph of f (x ) = x + 6? A. shifted 1 unit up and reflected over the x-axis B. shifted 1 unit up and reflected over the y-axis C. shifted 6 units up and reflected over the y-axis D. shifted 6 units up and reflected ...
... 9. Which best describes the transformation from the graph of f (x ) = -x + 5 to the graph of f (x ) = x + 6? A. shifted 1 unit up and reflected over the x-axis B. shifted 1 unit up and reflected over the y-axis C. shifted 6 units up and reflected over the y-axis D. shifted 6 units up and reflected ...
Document
... Amplitude is the height of the wave. The amplitude works in both directions. Every wave has a positive amplitude, meaning you take the absolute value of the amplitude of the wave. The amplitude works in both directions. The amplitude is usually written as a numerical value in front of the function. ...
... Amplitude is the height of the wave. The amplitude works in both directions. Every wave has a positive amplitude, meaning you take the absolute value of the amplitude of the wave. The amplitude works in both directions. The amplitude is usually written as a numerical value in front of the function. ...
Section 6.6, First-Order Linear Differential Equations
... dx x This equation is not separable, since we cannot separate the variables to have dy multiplying all the terms with y on one side, and dx multiplying all the terms with x on the other. This kind of equation is called a first-order linear differential equation. Our goal for this section will be to ...
... dx x This equation is not separable, since we cannot separate the variables to have dy multiplying all the terms with y on one side, and dx multiplying all the terms with x on the other. This kind of equation is called a first-order linear differential equation. Our goal for this section will be to ...