commercial / industrial customer information sheet
... kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW ...
... kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW kW ...
PEQWS_Mod08_Prob09_v06
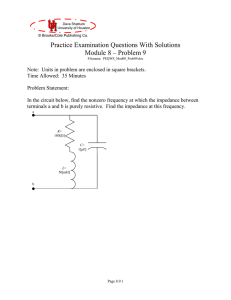
... Notice that we have isolated the real and imaginary parts of the numerator and denominator in parentheses in this last expression. If this expression for Zab is going to be real, that means that the imaginary part must be zero. However, getting an expression for the Im{Zab} is not easy; we would nee ...
... Notice that we have isolated the real and imaginary parts of the numerator and denominator in parentheses in this last expression. If this expression for Zab is going to be real, that means that the imaginary part must be zero. However, getting an expression for the Im{Zab} is not easy; we would nee ...
7154 VFD
... Every mechanical system has a resonant frequency(s). Drive operation at that resonant frequency can cause problems and potentially damage the system VFDs can be programmed to skip over these frequencies (i.e. not dwell on them) ...
... Every mechanical system has a resonant frequency(s). Drive operation at that resonant frequency can cause problems and potentially damage the system VFDs can be programmed to skip over these frequencies (i.e. not dwell on them) ...
AB66 Wien Bridge Oscillator Operating Manual Ver.1.1 An ISO 9001
... Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic waveforms without input other than perhaps a trigger. They generally use some form of active device, lamp, or crystal, surrounded by passive devices such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, to generate the output. There are two main classes of osci ...
... Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic waveforms without input other than perhaps a trigger. They generally use some form of active device, lamp, or crystal, surrounded by passive devices such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, to generate the output. There are two main classes of osci ...
MAX477 300MHz High-Speed Op Amp
... unity-gain-stable op amp featuring low noise, low differential gain and phase errors, high slew rate, high precision, and high output current. The MAX477’s architecture uses a standard voltage-feedback topology that can be configured into any desired gain setting, as with ...
... unity-gain-stable op amp featuring low noise, low differential gain and phase errors, high slew rate, high precision, and high output current. The MAX477’s architecture uses a standard voltage-feedback topology that can be configured into any desired gain setting, as with ...
FREQUENCY RESPONSE ANALYZERS
... Both AC and DC on, both AC and DC off, only AC off, SLOW control that gradually changes AC and DC Withstand voltage: 42 Vpk or 30 Vrms Electrostatic capacitance against casing: 250 pF or less ...
... Both AC and DC on, both AC and DC off, only AC off, SLOW control that gradually changes AC and DC Withstand voltage: 42 Vpk or 30 Vrms Electrostatic capacitance against casing: 250 pF or less ...
Output voltage for Step 4 (volts)
... filter. A low-pass filter was used first to keep frequency response down at high frequencies, and a high-pass filter was then used to keep the response down at low frequencies. To test the response of the amplifiers with each of the filters, measurements were made at various frequencies. The results ...
... filter. A low-pass filter was used first to keep frequency response down at high frequencies, and a high-pass filter was then used to keep the response down at low frequencies. To test the response of the amplifiers with each of the filters, measurements were made at various frequencies. The results ...
Circuit Note CN-0114
... Rev. A “Circuits from the Lab” from Analog Devices have been designed and built by Analog Devices engineers. Standard engineering practices have been employed in the design and construction of each circuit, and their function and performance have been tested and verified in a lab environment at room ...
... Rev. A “Circuits from the Lab” from Analog Devices have been designed and built by Analog Devices engineers. Standard engineering practices have been employed in the design and construction of each circuit, and their function and performance have been tested and verified in a lab environment at room ...
SNA-286 DC-6.0 GHz, Cascadable GaAs MMIC Amplifier Product Description
... Sirenza Microdevices SNA-286 is a GaAs monolithic broadband amplifier (MMIC) housed in a low-cost surface-mountable plastic package. At 1950 MHz, this amplifier provides 15.5dB of gain and +14dBm of P1dB power when biased at 50mA. The use of an external resistor allows for bias flexibility and stabi ...
... Sirenza Microdevices SNA-286 is a GaAs monolithic broadband amplifier (MMIC) housed in a low-cost surface-mountable plastic package. At 1950 MHz, this amplifier provides 15.5dB of gain and +14dBm of P1dB power when biased at 50mA. The use of an external resistor allows for bias flexibility and stabi ...
RF1238 - Wireless | Murata Manufacturing
... Unless noted otherwise, all measurements are made with the filter installed in the specified test fixture which is connected to a 50 Ω test system with VSWR ≤ 1.2:1. The test fixture L and C are adjusted for minimum insertion loss at the filter center frequency, fc. Note that insertion loss, bandwid ...
... Unless noted otherwise, all measurements are made with the filter installed in the specified test fixture which is connected to a 50 Ω test system with VSWR ≤ 1.2:1. The test fixture L and C are adjusted for minimum insertion loss at the filter center frequency, fc. Note that insertion loss, bandwid ...
Exam with Model Answer
... • The isolation barrier is the region where the input and output are totally isolated. • The isolation and coupling may be optically, thermally or magnetically. ...
... • The isolation barrier is the region where the input and output are totally isolated. • The isolation and coupling may be optically, thermally or magnetically. ...
Bode plot
In electrical engineering and control theory, a Bode plot /ˈboʊdi/ is a graph of the frequency response of a system. It is usually a combination of a Bode magnitude plot, expressing the magnitude of the frequency response, and a Bode phase plot, expressing the phase shift. Both quantities are plotted against a horizontal axis proportional to the logarithm of frequency.