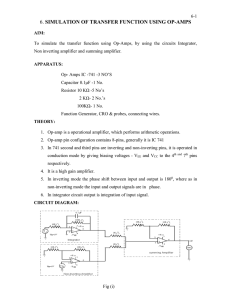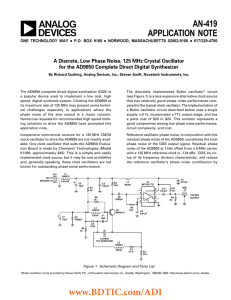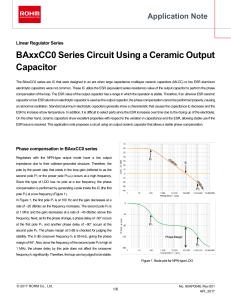
BAxxCC0 Series Circuit Using aCeramic Output Capacitor : Power
... 9) ROHM shall have no responsibility for any damages or injury arising from non-compliance with the recommended usage conditions and specifications contained herein. 10) ROHM has used reasonable care to ensure the accuracy of the information contained in this document. However, ROHM does not warrant ...
... 9) ROHM shall have no responsibility for any damages or injury arising from non-compliance with the recommended usage conditions and specifications contained herein. 10) ROHM has used reasonable care to ensure the accuracy of the information contained in this document. However, ROHM does not warrant ...
TB417: Designing Stable Compensation Networks for
... The guidelines given for designing a Type II network were followed in order to calculate the following component values: R1 = 4.12kΩ (chosen as the feedback component) R2 = 125.8kΩ C1 = 8.464pF C2 = 2.373nF These calculated values need to be replaced by standard resistor values before the gain and p ...
... The guidelines given for designing a Type II network were followed in order to calculate the following component values: R1 = 4.12kΩ (chosen as the feedback component) R2 = 125.8kΩ C1 = 8.464pF C2 = 2.373nF These calculated values need to be replaced by standard resistor values before the gain and p ...
Experiment 16: DC and AC Operating Point Analysis of an RF
... an RF Amplifier Purpose and Discussion The purpose of this simulation is to demonstrate the characteristics and operation of an RF amplifier using DC and AC analysis in the course of our study. Radio frequency amplifiers perform the function that their name implies. They select and amplify a narrow ...
... an RF Amplifier Purpose and Discussion The purpose of this simulation is to demonstrate the characteristics and operation of an RF amplifier using DC and AC analysis in the course of our study. Radio frequency amplifiers perform the function that their name implies. They select and amplify a narrow ...
Paper Title (use style: paper title)
... The Simulink model of the conventional sequential tri-states D flip-flop based PFD is shown in the Figure 1. A PFD with three states is widely used because of its wide linear range and ability to capture phase and frequency [1]. The reference signal and the feedback signal are given to the two input ...
... The Simulink model of the conventional sequential tri-states D flip-flop based PFD is shown in the Figure 1. A PFD with three states is widely used because of its wide linear range and ability to capture phase and frequency [1]. The reference signal and the feedback signal are given to the two input ...
How to Measure the Loop Transfer Function of Power Supplies (Rev
... feedback path. A good value is a 20Ω resistor. With such a resistor the adjusted output voltage will be negligibly influenced but the nodes to inject a small signal and measure the system are established. Any RC phase lead network which might exist in parallel with the R1 feedback resistor should st ...
... feedback path. A good value is a 20Ω resistor. With such a resistor the adjusted output voltage will be negligibly influenced but the nodes to inject a small signal and measure the system are established. Any RC phase lead network which might exist in parallel with the R1 feedback resistor should st ...
module – 4
... The order in which the voltages in the voltages in the phases reach their maximum positive values is called the phase sequence. For example, in Fig. 3.80(a), the three coils ...
... The order in which the voltages in the voltages in the phases reach their maximum positive values is called the phase sequence. For example, in Fig. 3.80(a), the three coils ...
display
... Summary: The analog board gain must be 4500V/V (±400V/V). Two analog boards will be made with identical components and verified to operate similarly. ...
... Summary: The analog board gain must be 4500V/V (±400V/V). Two analog boards will be made with identical components and verified to operate similarly. ...
Voltage-controlled Oscillators (VCO), Phase Locked Loop, and
... control voltage. VCOs are used in many communication applications such as frequency modulation, in the phase locked loop (PLL) for signal tracking and FM demodulation. There are many ways to design an electronic circuit for a VCO. One method uses a special diode called Varactor. This diode has capac ...
... control voltage. VCOs are used in many communication applications such as frequency modulation, in the phase locked loop (PLL) for signal tracking and FM demodulation. There are many ways to design an electronic circuit for a VCO. One method uses a special diode called Varactor. This diode has capac ...
Lab #9 AC Circuits - Northern Arizona University
... 4. Current through a capacitor leads the voltage across it by Δt of T/4, meaning that the current peak occurs before the voltage peak by 1/4th of a period. Remember ELI the ICE man from lab 7? 5. For sinusoidal voltage and current, the current through a capacitor leads the voltage across it by a pha ...
... 4. Current through a capacitor leads the voltage across it by Δt of T/4, meaning that the current peak occurs before the voltage peak by 1/4th of a period. Remember ELI the ICE man from lab 7? 5. For sinusoidal voltage and current, the current through a capacitor leads the voltage across it by a pha ...
Homework Ch 4 - ECM
... 9. A change is frequency from 100 radians per second (rps) to 1000 rps causes a minus 10 db change in gain. a. True b. False ...
... 9. A change is frequency from 100 radians per second (rps) to 1000 rps causes a minus 10 db change in gain. a. True b. False ...
Chapter 11 Homework - Digilent Learn site
... 11.1 For the circuit below, the input voltage Vin(t) = 3cos(2t-20) – 2cos(3t+30) + cos(4t). Determine: a. The steady-state response of the voltage v(t). b. The steady-state response of the current iR(t). (Hint: take advantage of your results from part a) 1Ω ...
... 11.1 For the circuit below, the input voltage Vin(t) = 3cos(2t-20) – 2cos(3t+30) + cos(4t). Determine: a. The steady-state response of the voltage v(t). b. The steady-state response of the current iR(t). (Hint: take advantage of your results from part a) 1Ω ...
The Differential Mode Op-Amp
... What is the Differential Mode ? • The op-amp can be connected up in various ways or modes. • What it does depends on how it is connected up. • When connected up in the differential mode, it finds the difference between the two input voltages and multiplies it by the gain. ...
... What is the Differential Mode ? • The op-amp can be connected up in various ways or modes. • What it does depends on how it is connected up. • When connected up in the differential mode, it finds the difference between the two input voltages and multiplies it by the gain. ...
Assign. 3 File
... and a 5 mVp sinusoid with frequency of 1 KHz but out of phase with each other. In other words, vi6 – vi7 is a 1 kHz 10 mVp (20 mVp-p) sinusoid. The statement .tran 3u 3m instructs LTSpice to do calculations from 0 – 3 ms (3 periods of the input sinusoid) with time step of 3 µs. Simulate the circuit. ...
... and a 5 mVp sinusoid with frequency of 1 KHz but out of phase with each other. In other words, vi6 – vi7 is a 1 kHz 10 mVp (20 mVp-p) sinusoid. The statement .tran 3u 3m instructs LTSpice to do calculations from 0 – 3 ms (3 periods of the input sinusoid) with time step of 3 µs. Simulate the circuit. ...
Bode plot
In electrical engineering and control theory, a Bode plot /ˈboʊdi/ is a graph of the frequency response of a system. It is usually a combination of a Bode magnitude plot, expressing the magnitude of the frequency response, and a Bode phase plot, expressing the phase shift. Both quantities are plotted against a horizontal axis proportional to the logarithm of frequency.