12866_2017_1009_MOESM5_ESM
... Species and strain names in Taxonomy [OC] “ribosomal protein” in Protein name [DE] “mitochondrial protein” in Protein name [DE] with NOT (to exclude mitochondrial ribosomal proteins) Conduct BLAST homology search and compare with the amino acid sequence of A. fumigatus A1163, which have already veri ...
... Species and strain names in Taxonomy [OC] “ribosomal protein” in Protein name [DE] “mitochondrial protein” in Protein name [DE] with NOT (to exclude mitochondrial ribosomal proteins) Conduct BLAST homology search and compare with the amino acid sequence of A. fumigatus A1163, which have already veri ...
PowerPoint bemutató
... - An uncleaved internal signal membrane-anchor sequence - A stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequence - An uncleaved internal signal membrane-anchor sequence Etc. ...
... - An uncleaved internal signal membrane-anchor sequence - A stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequence - An uncleaved internal signal membrane-anchor sequence Etc. ...
PowerPoint bemutató
... - An uncleaved internal signal membrane-anchor sequence - A stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequence - An uncleaved internal signal membrane-anchor sequence Etc. ...
... - An uncleaved internal signal membrane-anchor sequence - A stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequence - An uncleaved internal signal membrane-anchor sequence Etc. ...
Enzymes: Principles of Catalysis
... 3. Protein Regulation by Degradation (Lifetime) The lifetime of a protein is a simple method of regulation ...
... 3. Protein Regulation by Degradation (Lifetime) The lifetime of a protein is a simple method of regulation ...
GPI Anchor
... 2.A small number of loci that exhibit covalent histone modifications by histone acetyltransferases (HAT), such as hyperacetylation. 3.The hyperacetylated domains occur exclusively at loci containing highly expressed, tissue-specific genes, and that they are involved in the activation of these genes. ...
... 2.A small number of loci that exhibit covalent histone modifications by histone acetyltransferases (HAT), such as hyperacetylation. 3.The hyperacetylated domains occur exclusively at loci containing highly expressed, tissue-specific genes, and that they are involved in the activation of these genes. ...
GPI Anchor
... Signals and Combinatorial Functions of Histone Modifications 1. Alterations of chromatin structure are crucial for response to cell signaling and for programmed gene expression in development. 2. Posttranslational histone modifications influence changes in chromatin structure both directly and by t ...
... Signals and Combinatorial Functions of Histone Modifications 1. Alterations of chromatin structure are crucial for response to cell signaling and for programmed gene expression in development. 2. Posttranslational histone modifications influence changes in chromatin structure both directly and by t ...
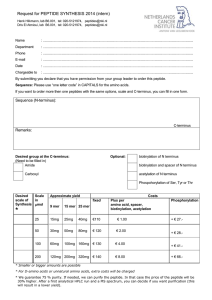
Scale - Netherlands Cancer Institute
... Henk Hilkmann, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] Dris El Atmioui, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] ...
... Henk Hilkmann, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] Dris El Atmioui, lab B6.001, tel: 020-5121974, [email protected] ...
The Cell Cycle
... S-Phase Controls • Replication must occur only 1 time / cell cycle • Origin “licensing” • ORC – origin recognition complex • SPF – S-phase promoting factor • Mcms – helicases that are only loaded once ...
... S-Phase Controls • Replication must occur only 1 time / cell cycle • Origin “licensing” • ORC – origin recognition complex • SPF – S-phase promoting factor • Mcms – helicases that are only loaded once ...
The structure and Function of Macromolecules
... • Polysaccharides – macromolecules, 100’s to 1,000’s, ex. = starch (energy storage in plants) and glycogen (energy storage in animals), cellulose (plant cell walls), chitin (arthropod exoskeletons) ...
... • Polysaccharides – macromolecules, 100’s to 1,000’s, ex. = starch (energy storage in plants) and glycogen (energy storage in animals), cellulose (plant cell walls), chitin (arthropod exoskeletons) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... • Promoted by histone acetyltransferase (HAT) • Acetylation causes opening of histone protein arms, making DNA in chromatin more accessible • Acetylated histones are a mark of gene activity ...
... • Promoted by histone acetyltransferase (HAT) • Acetylation causes opening of histone protein arms, making DNA in chromatin more accessible • Acetylated histones are a mark of gene activity ...
Normal Protein Trafficking and the Unfolded Protein Response
... MIS-FOLDED AND UNFOLDED PROTEINS AND STRESS If proteins do not fold properly in the RER they may cause a “traffic jam” - the proteins remain in the RER and are unable to be shipped to the Golgi. This leads to ER Stress. When ER stress occurs, the unfolded protein response is triggered. During the u ...
... MIS-FOLDED AND UNFOLDED PROTEINS AND STRESS If proteins do not fold properly in the RER they may cause a “traffic jam” - the proteins remain in the RER and are unable to be shipped to the Golgi. This leads to ER Stress. When ER stress occurs, the unfolded protein response is triggered. During the u ...
Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Human E. coli
... Members of the Hedgehog (Hh) family are highly conserved proteins that are widely represented throughout the animal kingdom. The three known mammalian Hh proteins, Sonic (Shh), Desert (Dhh) and Indian (Ihh), are structurally related, and share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh ...
... Members of the Hedgehog (Hh) family are highly conserved proteins that are widely represented throughout the animal kingdom. The three known mammalian Hh proteins, Sonic (Shh), Desert (Dhh) and Indian (Ihh), are structurally related, and share a high degree of amino acid sequence identity (e.g. Shh ...
Document
... 2. Any organic molecule can be thought of as having a carbon-based core with specific groups of atoms with definite chemical properties attached. These groups of atoms are known as _____________. 3. Complete this table summarizing the characteristics of the most biologically significant functional g ...
... 2. Any organic molecule can be thought of as having a carbon-based core with specific groups of atoms with definite chemical properties attached. These groups of atoms are known as _____________. 3. Complete this table summarizing the characteristics of the most biologically significant functional g ...
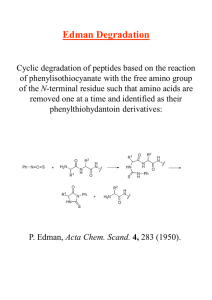
Edman Degradation
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
... Edman Degradation Cyclic degradation of peptides based on the reaction of phenylisothiocyanate with the free amino group of the N-terminal residue such that amino acids are removed one at a time and identified as their phenylthiohydantoin derivatives: ...
Bio200 Au13 Lec19 10-29 Slides
... • A 5’ protein cap and a 3’ poly-A tail are added to give stability • Non-coding introns are spliced out of the mRNA by the spliceosome ...
... • A 5’ protein cap and a 3’ poly-A tail are added to give stability • Non-coding introns are spliced out of the mRNA by the spliceosome ...
Histone Methylation
... Transcriptional - These mechanisms prevent transcription. Posttranscriptional - These mechanisms control or regulate mRNA after it has been produced. Translational - These mechanisms prevent translation. They often involve protein factors needed for translation. Posttranslational - These mechanism ...
... Transcriptional - These mechanisms prevent transcription. Posttranscriptional - These mechanisms control or regulate mRNA after it has been produced. Translational - These mechanisms prevent translation. They often involve protein factors needed for translation. Posttranslational - These mechanism ...
The P53-Mdm2 Network: From Oscillations To Apoptosis
... Abstract. The p53 tumour suppressor gene, often characterized as the “guardian of the genome” plays a central role in protecting cells from malignant transformation. It is the most frequently mutated of genes in human cancer. The gene constitutes a highly connected node in a network of signaling pat ...
... Abstract. The p53 tumour suppressor gene, often characterized as the “guardian of the genome” plays a central role in protecting cells from malignant transformation. It is the most frequently mutated of genes in human cancer. The gene constitutes a highly connected node in a network of signaling pat ...
Structures define the functions of proteins
... In the acetylated form, the positve charge of the lysine e-amino group is neuralized. This eliminate its interaction with a DNA phosphate group. So the greater the acetylation of histone N-terminus, the less likely chromatin is to form condensed 30-nm fibers and possibly higher-order folded ...
... In the acetylated form, the positve charge of the lysine e-amino group is neuralized. This eliminate its interaction with a DNA phosphate group. So the greater the acetylation of histone N-terminus, the less likely chromatin is to form condensed 30-nm fibers and possibly higher-order folded ...
PTM
... 1. Dealing with the N-terminal residue In bacteria, the N-terminal residue of the newlysynthesized protein is modified to remove the formyl group. The N-terminal methionine may also be removed. In some cases the carboxy terminal residues are removed enzymatically 2. Loss of signal sequences • 15-30 ...
... 1. Dealing with the N-terminal residue In bacteria, the N-terminal residue of the newlysynthesized protein is modified to remove the formyl group. The N-terminal methionine may also be removed. In some cases the carboxy terminal residues are removed enzymatically 2. Loss of signal sequences • 15-30 ...
Acetylation

Acetylation (or in IUPAC nomenclature ethanoylation) describes a reaction that introduces an acetyl functional group into a chemical compound. (Deacetylation is the removal of the acetyl group.)Acetylation refers to the process of introducing an acetyl group (resulting in an acetoxy group) into a compound, namely the substitution of an acetyl group for an active hydrogen atom. A reaction involving the replacement of the hydrogen atom of a hydroxyl group with an acetyl group (CH3 CO) yields a specific ester, the acetate. Acetic anhydride is commonly used as an acetylating agent reacting with free hydroxyl groups. For example, it is used in the synthesis of aspirin and heroin.