Particle properties of radiation
... For the case of a particle we can locate its location and momentum precisely But how do we ‘locate’ a wave? Wave spreads out in a region of space and is not located in any specific point in space like the case of a particle To be more precise we says that a plain wave exists within some region in sp ...
... For the case of a particle we can locate its location and momentum precisely But how do we ‘locate’ a wave? Wave spreads out in a region of space and is not located in any specific point in space like the case of a particle To be more precise we says that a plain wave exists within some region in sp ...
Welcome to PHYS 406!
... Overview • What we have already learn? – Mechanics: statics and dynamics of single-/few-body problems – E&M: interactions between charged objects – Quantum Mechanics: single-particle wave-functions in fields ...
... Overview • What we have already learn? – Mechanics: statics and dynamics of single-/few-body problems – E&M: interactions between charged objects – Quantum Mechanics: single-particle wave-functions in fields ...
Quantization of Mechanical Motion
... Wave Function Since a measurement on a given quantum object has no deterministic result, the only way to describe it is to introduce the probability to find a specific value of a physical variable in a large set of results of identical measurements. This information is addressed by the introduction ...
... Wave Function Since a measurement on a given quantum object has no deterministic result, the only way to describe it is to introduce the probability to find a specific value of a physical variable in a large set of results of identical measurements. This information is addressed by the introduction ...
Presentation #3
... In classical mechanics we define a STATE as “The specification of the position and velocity of all the particles present, at some time, and the specification of all the forces acting on the particles.” Then Newton’s (or any other) classical equations of motion allow us to determine the state of the ...
... In classical mechanics we define a STATE as “The specification of the position and velocity of all the particles present, at some time, and the specification of all the forces acting on the particles.” Then Newton’s (or any other) classical equations of motion allow us to determine the state of the ...
The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle In all previous attempts to describe the electron’s behavior inside an atom, including in the Bohr model, scientists tried to describe the path the electron would follow around the nucleus. The theorists wanted to describe where the electron was located and how i ...
... The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle In all previous attempts to describe the electron’s behavior inside an atom, including in the Bohr model, scientists tried to describe the path the electron would follow around the nucleus. The theorists wanted to describe where the electron was located and how i ...
end of section a
... Answers to Section A should be marked on the Multiple-choice Answer Sheet while answers to Section B should be written in the spaces provided on Question-Answer Book B. The Answer Sheet for Section A and the Question-Answer Book for Section B must be handed in separately at the end of the examinatio ...
... Answers to Section A should be marked on the Multiple-choice Answer Sheet while answers to Section B should be written in the spaces provided on Question-Answer Book B. The Answer Sheet for Section A and the Question-Answer Book for Section B must be handed in separately at the end of the examinatio ...
Quantum Field Theory I
... many purposes and is widely used in condensed matter physics, elementary particle physics, quantum optics, and in some cases also in atomic/molecular physics and nuclear physics. It is particularly suited to multi-body problems. In systems where the number of particles changes, or where one needs su ...
... many purposes and is widely used in condensed matter physics, elementary particle physics, quantum optics, and in some cases also in atomic/molecular physics and nuclear physics. It is particularly suited to multi-body problems. In systems where the number of particles changes, or where one needs su ...
What is light
... • Electromagnetic waves can be generated with a vast range of frequencies • The complete range is called the electromagnetic spectrum • We give different names to different frequencies of electromagnetic waves ...
... • Electromagnetic waves can be generated with a vast range of frequencies • The complete range is called the electromagnetic spectrum • We give different names to different frequencies of electromagnetic waves ...
the squared modulus of the wave function is the probability density
... has an EXACT ANALYTICAL solution! (this is one of the few problems in Quantum Mechanics that does have such a solution – most problems in QM cannot be solved exactly). The bad news, however, is that the procedure of solving the equation is extremely complicated. In a standard QM textbook it usually ...
... has an EXACT ANALYTICAL solution! (this is one of the few problems in Quantum Mechanics that does have such a solution – most problems in QM cannot be solved exactly). The bad news, however, is that the procedure of solving the equation is extremely complicated. In a standard QM textbook it usually ...
Quantum Mathematics
... • Nothing in our large scale classical world, nothing in our evolutionary experience, prepares our mind for superposition of amplitudes within a Hilbert space. • Superposition was born amid mystery and paradox in the period 1900-1927. ...
... • Nothing in our large scale classical world, nothing in our evolutionary experience, prepares our mind for superposition of amplitudes within a Hilbert space. • Superposition was born amid mystery and paradox in the period 1900-1927. ...
Small Amplitude Short Period Crystal Undulators
... Ulrik I. Uggerhøj Department of Physics and Astronomy Aarhus University, Denmark On behalf of the collaborations CERN NA63 and SLAC E-212 ...
... Ulrik I. Uggerhøj Department of Physics and Astronomy Aarhus University, Denmark On behalf of the collaborations CERN NA63 and SLAC E-212 ...
What is light
... • Electromagnetic waves can be generated with a vast range of frequencies • The complete range is called the electromagnetic spectrum • We give different names to different frequencies of electromagnetic waves ...
... • Electromagnetic waves can be generated with a vast range of frequencies • The complete range is called the electromagnetic spectrum • We give different names to different frequencies of electromagnetic waves ...
Atomic Spectra
... one-electron situation such as He+, Li+2, Be+3) can be found from the equation: ...
... one-electron situation such as He+, Li+2, Be+3) can be found from the equation: ...
Ch 24: Quantum Mechanics
... 21. The momentum of an electron is measured to an accuracy of ± 5.1 × 10-24 kg·m/s. What is the corresponding uncertainty in the position of the same electron at the same moment? Express your answer in Angstroms (1 Å = 10-10 m, about the size of a typical atom). 22. Thor, a baseball player, passes o ...
... 21. The momentum of an electron is measured to an accuracy of ± 5.1 × 10-24 kg·m/s. What is the corresponding uncertainty in the position of the same electron at the same moment? Express your answer in Angstroms (1 Å = 10-10 m, about the size of a typical atom). 22. Thor, a baseball player, passes o ...
Sem 2 Course Review
... A small handheld flashlight has 2 – 1.5 V (AA size) batteries. This gives a potential difference of 3 V across it. The bulb has a resistance of 5.0Ω. How much current is in the bulb filament? ...
... A small handheld flashlight has 2 – 1.5 V (AA size) batteries. This gives a potential difference of 3 V across it. The bulb has a resistance of 5.0Ω. How much current is in the bulb filament? ...
Solutions - Stanford University
... Note that P is a strictly decreasing function of b at any E. Thus the impurities always reduce the probability to transmit through the junction. This makes sense intuitively since even if µ1 = µ2 impurities lead to a finite chance to reflect. Problem 2 (Particle Mixing): In quantum field theory, it ...
... Note that P is a strictly decreasing function of b at any E. Thus the impurities always reduce the probability to transmit through the junction. This makes sense intuitively since even if µ1 = µ2 impurities lead to a finite chance to reflect. Problem 2 (Particle Mixing): In quantum field theory, it ...
Discussion of Experimental Proof for the Paradox of Einstein, Rosen
... First of all, Bohr' has proposed that the observing apparatus plus what is observed form a single indivisible combined system not capable at the quantummechanical level of being analyzed correctly into separate and distinct parts. Each particular kind of apparatus then forms with an electron for exa ...
... First of all, Bohr' has proposed that the observing apparatus plus what is observed form a single indivisible combined system not capable at the quantummechanical level of being analyzed correctly into separate and distinct parts. Each particular kind of apparatus then forms with an electron for exa ...
Chapter 2: Atoms and Electrons
... The main effort of science is to describe what happens in nature, in as complete and concise a form as possible. In physics this effort involves observing natural phenomena, relating these observations to previously established theory, and finally establishing a physical model for the observations. ...
... The main effort of science is to describe what happens in nature, in as complete and concise a form as possible. In physics this effort involves observing natural phenomena, relating these observations to previously established theory, and finally establishing a physical model for the observations. ...
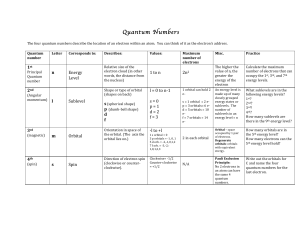
Quantum Numbers Handout File
... The!higher!the! value!of!n,!the! greater!the! energy!of!the! electron! ...
... The!higher!the! value!of!n,!the! greater!the! energy!of!the! electron! ...