Monday, Sept. 23, 2013
... Planck assumed that the radiation in the cavity was emitted (and absorbed) by some sort of “oscillators” that were contained in the walls. He used Boltzman’s statistical methods to arrive at the following formula that fit the blackbody radiation data. ...
... Planck assumed that the radiation in the cavity was emitted (and absorbed) by some sort of “oscillators” that were contained in the walls. He used Boltzman’s statistical methods to arrive at the following formula that fit the blackbody radiation data. ...
4 4.1. Particle motion in the presence of a potential barrier
... can lift single atoms out of the metallic surface, one at a time and form a new structure at the nano-scale. It is of great value in construction of ultrasmall circuits and the creation of new, artificial molecules. Lectures in Physics, summer 2008/09 ...
... can lift single atoms out of the metallic surface, one at a time and form a new structure at the nano-scale. It is of great value in construction of ultrasmall circuits and the creation of new, artificial molecules. Lectures in Physics, summer 2008/09 ...
Preface and Table of Contents
... we are comparing a particular model of Nature with experiments; however, the standard model of fundamental interactions—quantum chromodynamics for strong interactions and the Glashow–Weinberg–Salam theory of electroweak interactions—are all based on relativistic quantum mechanics. In atomic physics, ...
... we are comparing a particular model of Nature with experiments; however, the standard model of fundamental interactions—quantum chromodynamics for strong interactions and the Glashow–Weinberg–Salam theory of electroweak interactions—are all based on relativistic quantum mechanics. In atomic physics, ...
Slide 1 - Southwest High School
... This is still the mental picture many people have of the atom; what is wrong with it? • Orbiting electrons are accelerating and should radiate. • The frequency of radiation emitted by a continuously radiating electron would have a continuous spectrum, rather than the individual frequencies that are ...
... This is still the mental picture many people have of the atom; what is wrong with it? • Orbiting electrons are accelerating and should radiate. • The frequency of radiation emitted by a continuously radiating electron would have a continuous spectrum, rather than the individual frequencies that are ...
GENERAL CHEMISTRY SECTION I: ATOMIC THEORY
... (“phi”), that get us around the sphere in a manner similar to knowing the latitude and longitude on the earth. These two angles yield Y(θ, Φ), which is the angular wave function. ...
... (“phi”), that get us around the sphere in a manner similar to knowing the latitude and longitude on the earth. These two angles yield Y(θ, Φ), which is the angular wave function. ...
LESSON No. 2 – Structure of atom
... (10)Write short note on Dalton atomic theory. (11)Define Avogadro number and mole. What is their importance? (12)Explain empirical and molecules formula& relationship. (13)Explain hilarity, molarity. (14)Calculate the amounts in grams of :- (a)2.5gm atoms of nitrogen (b)3.6gm mole of Co2. (15)How ma ...
... (10)Write short note on Dalton atomic theory. (11)Define Avogadro number and mole. What is their importance? (12)Explain empirical and molecules formula& relationship. (13)Explain hilarity, molarity. (14)Calculate the amounts in grams of :- (a)2.5gm atoms of nitrogen (b)3.6gm mole of Co2. (15)How ma ...
Wave Nature of Light
... • That is, while a beam of light has many wavelike characteristics, it also can be thought of as a stream of tiny particles, or bundles of energy, called photons • Thus, a photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy. ...
... • That is, while a beam of light has many wavelike characteristics, it also can be thought of as a stream of tiny particles, or bundles of energy, called photons • Thus, a photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy. ...
Quantization of Charge, Light, and Energy
... unusual assumptions derived a function u(λ) that agreed with experimental data. Planck assumed that the radiation in the cavity was emitted (and absorbed) by some sort of “oscillators.” Classically, the electromagnetic waves in the cavity are produced by accelerated electric charges in the walls vib ...
... unusual assumptions derived a function u(λ) that agreed with experimental data. Planck assumed that the radiation in the cavity was emitted (and absorbed) by some sort of “oscillators.” Classically, the electromagnetic waves in the cavity are produced by accelerated electric charges in the walls vib ...
Wednesday, Mar. 26, 2014
... event is impossible (what principle is this?) • The expectation value is the expected result of the average of many measurements of a given quantity. The expectation value of x is denoted by.
• Any measurable quantity for which we can calculate the expectation
value is called a physical observab ...
... event is impossible (what principle is this?) • The expectation value is the expected result of the average of many measurements of a given quantity. The expectation value of x is denoted by
Harmonic Oscillator Physics
... For the classical variance, we had σx2 = 12 x20 , but this is related to the classical energy. Remember we start from rest at x0 , so the total energy (which is conserved) is just E = 21 m ω 2 x20 , indicating that we can write the variance as E σx2 = ...
... For the classical variance, we had σx2 = 12 x20 , but this is related to the classical energy. Remember we start from rest at x0 , so the total energy (which is conserved) is just E = 21 m ω 2 x20 , indicating that we can write the variance as E σx2 = ...
The Quantum Hall Effects: Discovery, basic theory and open problems
... Pfieffer & West, Physica E, 20, p57-64 (2003) ...
... Pfieffer & West, Physica E, 20, p57-64 (2003) ...
Physics 200 Class #1 Outline
... observed for hydrogen and other atoms. Planetary Model: Initially, the nuclear model was also unpromising. In the first place, classical physics showed that electrons bound to a positively charged nucleus must revolve in orbits. But why would they have only those particular orbits that represented t ...
... observed for hydrogen and other atoms. Planetary Model: Initially, the nuclear model was also unpromising. In the first place, classical physics showed that electrons bound to a positively charged nucleus must revolve in orbits. But why would they have only those particular orbits that represented t ...
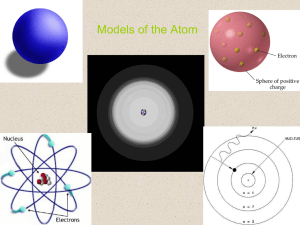
Models of the Atom
... The Bohr Model • Niels Bohr (1885 – 1962) – Danish Physicist/ Student of Rutherford – An electron is found only in specific circular paths, or orbits, around the nucleus. – The energy of an atom changes when it absorbs or emits light. – Each orbit has a fixed energy (each orbital is a different ene ...
... The Bohr Model • Niels Bohr (1885 – 1962) – Danish Physicist/ Student of Rutherford – An electron is found only in specific circular paths, or orbits, around the nucleus. – The energy of an atom changes when it absorbs or emits light. – Each orbit has a fixed energy (each orbital is a different ene ...
Electron Configuration Notes File
... Impossible to know both the velocity and position of an electron at the same time ...
... Impossible to know both the velocity and position of an electron at the same time ...
Quantum Numbers, Orbitals, Electron Configurations, Periodic Trends
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...
... Convert the numbers is questions 1a – 1d into scientific notation. a) c) b) d) Convert the following numbers that are in scientific notation into decimal form. a) 1.2340 × 107 d) 7.0 × 104 b) 3.980 × 102 e) 5.00134 × 10-4 c) 9.23 × 10-5 f) 6.626 × 10-34 A box measures 2.56 in × 4.21 in × 12.00 in. W ...