
Chapter 1: A Brief Summary of the Atmosphere (pdf format)
... Variability in vertical is much larger than the horizontal and temporal variability. In the lowest 100km, the logarithm of pressure drops off nearly linearly with height. Derivation Meteorology 301 ...
... Variability in vertical is much larger than the horizontal and temporal variability. In the lowest 100km, the logarithm of pressure drops off nearly linearly with height. Derivation Meteorology 301 ...
Biosynthesis - Planetary Biology
... looking, it is based upon some very basic principles that Here it is. Living things do not inhabit the Earth as should make understandable. totally independent entities, free from Earthly needs. The Earth is made up of many materials, some of which Instead, they exist in a state of constant need for ...
... looking, it is based upon some very basic principles that Here it is. Living things do not inhabit the Earth as should make understandable. totally independent entities, free from Earthly needs. The Earth is made up of many materials, some of which Instead, they exist in a state of constant need for ...
Standard B-6
... ○ Once there is enough soil and nutrients, small plants, such as small flowers, ferns, and shrubs, grow. These plants break down the rock further, and provide more soil. ○ Then seeds of other plants and small trees are able to germinate and grow. ○ Over time more species grow and die. Their decompos ...
... ○ Once there is enough soil and nutrients, small plants, such as small flowers, ferns, and shrubs, grow. These plants break down the rock further, and provide more soil. ○ Then seeds of other plants and small trees are able to germinate and grow. ○ Over time more species grow and die. Their decompos ...
SC Biology Standards (LBee)
... ○ Once there is enough soil and nutrients, small plants, such as small flowers, ferns, and shrubs, grow. These plants break down the rock further, and provide more soil. ○ Then seeds of other plants and small trees are able to germinate and grow. ○ Over time more species grow and die. Their decompos ...
... ○ Once there is enough soil and nutrients, small plants, such as small flowers, ferns, and shrubs, grow. These plants break down the rock further, and provide more soil. ○ Then seeds of other plants and small trees are able to germinate and grow. ○ Over time more species grow and die. Their decompos ...
140818 PPR Redef of Anthroposphere R7.1
... the soil, to the great variety of plants and animals that we use for food, clothes and housing, all the way back down to those organisms that consume our wastes. But the biosphere of the Earth can be said to be more than the sum of its parts. The biosphere in which our species evolved and of which o ...
... the soil, to the great variety of plants and animals that we use for food, clothes and housing, all the way back down to those organisms that consume our wastes. But the biosphere of the Earth can be said to be more than the sum of its parts. The biosphere in which our species evolved and of which o ...
Life in extreme arid environments and implications for astrobiology
... The occurrence of water is the basic requirement for life. Despite that, extremely arid environments (Fig. 1) harbour communities of microorganisms that find in the interior of the rocks sufficient water to live and reproduce. These communities are called endoliths and their mode of life includes se ...
... The occurrence of water is the basic requirement for life. Despite that, extremely arid environments (Fig. 1) harbour communities of microorganisms that find in the interior of the rocks sufficient water to live and reproduce. These communities are called endoliths and their mode of life includes se ...
1.4.1 - 1.4.4 Ecology, Ecosystem, Biosphere, Habitat
... Can you name some more? Ecosystems can be very large ...
... Can you name some more? Ecosystems can be very large ...
Unit Three - Montana State University Extended University
... archaea and bacteria, such as those living around deep-sea thermal vents, instead harvest energy from sulfur and iron compounds in a process called chemosynthesis. Regardless of the source, any organism that can harvest energy directly from the non-living environment is called an autotroph, a word t ...
... archaea and bacteria, such as those living around deep-sea thermal vents, instead harvest energy from sulfur and iron compounds in a process called chemosynthesis. Regardless of the source, any organism that can harvest energy directly from the non-living environment is called an autotroph, a word t ...
Standard B-6:
... ○ Once there is enough soil and nutrients, small plants, such as small flowers, ferns, and shrubs, grow. These plants break down the rock further, and provide more soil. ○ Then seeds of other plants and small trees are able to germinate and grow. ○ Over time more species grow and die. Their decompos ...
... ○ Once there is enough soil and nutrients, small plants, such as small flowers, ferns, and shrubs, grow. These plants break down the rock further, and provide more soil. ○ Then seeds of other plants and small trees are able to germinate and grow. ○ Over time more species grow and die. Their decompos ...
Mission 1
... layer on our planet’s surface that contains life • The biosphere exists over the whole planet, both on land and in the sea • The biosphere is divided into smaller units called ecosystems. ...
... layer on our planet’s surface that contains life • The biosphere exists over the whole planet, both on land and in the sea • The biosphere is divided into smaller units called ecosystems. ...
Resilient Planet
... layer on our planet’s surface that contains life • The biosphere exists over the whole planet, both on land and in the sea • The biosphere is divided into smaller units called ecosystems. ...
... layer on our planet’s surface that contains life • The biosphere exists over the whole planet, both on land and in the sea • The biosphere is divided into smaller units called ecosystems. ...
Ecology - science
... shelter, the temperature, and the amount of moisture the organism needs to survive ...
... shelter, the temperature, and the amount of moisture the organism needs to survive ...
Relationships Nature`s Way of Recycling Ecology Trophic Levels
... An ecological unit that includes all the interacting parts of an environment in an area. Ex. a cave, a pond ...
... An ecological unit that includes all the interacting parts of an environment in an area. Ex. a cave, a pond ...
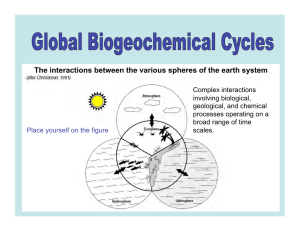
The interactions between the various spheres of the earth system
... responsible for 70–90% of anthropogenic CO2 emissions to the atmosphere. CO2 in the atmosphere increased by 30% since the industrial revolution. ...
... responsible for 70–90% of anthropogenic CO2 emissions to the atmosphere. CO2 in the atmosphere increased by 30% since the industrial revolution. ...
ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
... Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered questions or statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best answers each questions or best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, ...
... Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered questions or statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best answers each questions or best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, ...
4.LECTURE-Systems of the Earth [Compatibility Mode]
... species make a population, while the species that are interrelated or have similar demands from the environment constitute communities of species. A species community and its non-living environment inhabited, make a system of a higher category – an ecosystem. Each species is unique, and it has speci ...
... species make a population, while the species that are interrelated or have similar demands from the environment constitute communities of species. A species community and its non-living environment inhabited, make a system of a higher category – an ecosystem. Each species is unique, and it has speci ...
Ecosystems
... Niche – role of an organism in an ecosystem (physical, chemical, and biological conditions that a species needs to live and reproduce) • Organisms occupation ...
... Niche – role of an organism in an ecosystem (physical, chemical, and biological conditions that a species needs to live and reproduce) • Organisms occupation ...
Fall Ecology Unit 1
... 2. How have major catastrophic events shaped Earth’s history over time? 3. Briefly, and very generally, describe how Earth (including the atmosphere, land masses, and species) has changed over time. 4. What is ecological succession? 5. What is primary succession? Causes? 6. What are pioneer species? ...
... 2. How have major catastrophic events shaped Earth’s history over time? 3. Briefly, and very generally, describe how Earth (including the atmosphere, land masses, and species) has changed over time. 4. What is ecological succession? 5. What is primary succession? Causes? 6. What are pioneer species? ...
unit 9 review sheet
... There are naturally occurring Earth processes that help ecosystems maintain a balance. The portion of Earth that is inhabited by life (the biosphere) is connected with other Earth systems: the atmosphere (air), the hydrosphere (water), and the geosphere (soil). All of these systems must interact eff ...
... There are naturally occurring Earth processes that help ecosystems maintain a balance. The portion of Earth that is inhabited by life (the biosphere) is connected with other Earth systems: the atmosphere (air), the hydrosphere (water), and the geosphere (soil). All of these systems must interact eff ...
ecosystem - Wando High School
... leaves. Some crops and other plants may grow more vigorously and use water more efficiently in response to increased atmospheric CO2. ...
... leaves. Some crops and other plants may grow more vigorously and use water more efficiently in response to increased atmospheric CO2. ...
Chapter 19 – Introduction to Ecology
... Ex: Reptiles and amphibians “hide” underground and become dormant during the winter to survive the cold temperatures ...
... Ex: Reptiles and amphibians “hide” underground and become dormant during the winter to survive the cold temperatures ...
the earth and the natural places
... consists of all organisms living in a particular area, as well as the physical elements such as air, soil, water, and sunlight with which those organisms interact. ...
... consists of all organisms living in a particular area, as well as the physical elements such as air, soil, water, and sunlight with which those organisms interact. ...
Components of the Earth
... • All organisms are intrinsically linked to their physical environment and the relationship between an organism and its environment is the study of ecology. • The biosphere can be divided into distinct ecosystems that represent the interactions between a group of organisms forming a trophic pyramid ...
... • All organisms are intrinsically linked to their physical environment and the relationship between an organism and its environment is the study of ecology. • The biosphere can be divided into distinct ecosystems that represent the interactions between a group of organisms forming a trophic pyramid ...
Terraforming

Terraforming (literally, ""Earth-shaping"") of a planet, moon, or other body is the hypothetical process of deliberately modifying its atmosphere, temperature, surface topography or ecology to be similar to the environment of Earth to make it habitable by Earth-like life.The term ""terraforming"" is sometimes used more generally as a synonym for planetary engineering, although some consider this more general usage an error. The concept of terraforming developed from both science fiction and actual science. The term was coined by Jack Williamson in a science-fiction story (Collision Orbit) published during 1942 in Astounding Science Fiction, but the concept may pre-date this work.Based on experiences with Earth, the environment of a planet can be altered deliberately; however, the feasibility of creating an unconstrained planetary environment that mimics Earth on another planet has yet to be verified. Mars is usually considered to be the most likely candidate for terraforming. Much study has been done concerning the possibility of heating the planet and altering its atmosphere, and NASA has even hosted debates on the subject. Several potential methods of altering the climate of Mars may fall within humanity's technological capabilities, but at present the economic resources required to do so are far beyond that which any government or society is willing to allocate to it. The long timescales and practicality of terraforming are the subject of debate. Other unanswered questions relate to the ethics, logistics, economics, politics, and methodology of altering the environment of an extraterrestrial world.















![4.LECTURE-Systems of the Earth [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014265275_1-c3f0353eb192762d4742baddbdbd9cf1-300x300.png)






