Lost legacy: How 1989 marked the rise of environmental politics
... A more overlooked impulse closely linked to 1989 was environmentalism – or, less anachronistically – concern with the sustainability of the modernist project of continual physical expansion and top-down command and control national government. Early European dissidents on the 1960s and 1970s, many o ...
... A more overlooked impulse closely linked to 1989 was environmentalism – or, less anachronistically – concern with the sustainability of the modernist project of continual physical expansion and top-down command and control national government. Early European dissidents on the 1960s and 1970s, many o ...
Sustainable Development
... A country’s environment is a valuable natural resource. These resources can be critical inputs to economic activity, job creation, and growth. Prudent management of fisheries can help provide sustainable source of food for fisheries and their families or support large scale commercial fishing ...
... A country’s environment is a valuable natural resource. These resources can be critical inputs to economic activity, job creation, and growth. Prudent management of fisheries can help provide sustainable source of food for fisheries and their families or support large scale commercial fishing ...
Environmental Economics and Pollution
... • I am! “Will society be better or worse off with 4 this regulation or a different one?” ...
... • I am! “Will society be better or worse off with 4 this regulation or a different one?” ...
AP Environmental Science Chapter 1 Objectives
... size or economic output, increases at a constant rate per unit of time Free access resources—resources people are normally free to use Frontier environmental worldview—view by European colonists settling North America in the 1600s that the continent had vast resources and was a wilderness to be conq ...
... size or economic output, increases at a constant rate per unit of time Free access resources—resources people are normally free to use Frontier environmental worldview—view by European colonists settling North America in the 1600s that the continent had vast resources and was a wilderness to be conq ...
Chapter 1
... supply - does not apply to nonrenewable energy sources- use less or try to find a substitute or do without. ...
... supply - does not apply to nonrenewable energy sources- use less or try to find a substitute or do without. ...
Intro-Environmental Science
... when deciding whether to proceed with a project – if it can affect the environment should they carry on with it or should they put the precautionary principle into affect? Different answer for different views… ...
... when deciding whether to proceed with a project – if it can affect the environment should they carry on with it or should they put the precautionary principle into affect? Different answer for different views… ...
Environmental Science
... their ennvrironment is called the agricultural revolution C. Effect: exponential human population growth, populations concentrated in smaller areas. ...
... their ennvrironment is called the agricultural revolution C. Effect: exponential human population growth, populations concentrated in smaller areas. ...
View Webinar - Greening Forward
... Environmental Leadership Hierarchy Inspiring others to become active stakeholders in the environmental movement is powerful. This can be done through advocacy, service, activism, and philanthropy. ...
... Environmental Leadership Hierarchy Inspiring others to become active stakeholders in the environmental movement is powerful. This can be done through advocacy, service, activism, and philanthropy. ...
September 10, 2012 Notes Session B
... actions that promote sustainable development in order to achieve or maintain a healthy environmental and a healthy economy . . . ” ...
... actions that promote sustainable development in order to achieve or maintain a healthy environmental and a healthy economy . . . ” ...
[Chapter 1] Environmental Problems, Their Causes, and
... of, and not apart from, the rest of the nature. - environmental science: an interdisciplinary study of how humans interact with the environment of living and non-living things. integrates info and ideas from the natural sciences (biology, chemistry, geology), social sciences (geography, economics, p ...
... of, and not apart from, the rest of the nature. - environmental science: an interdisciplinary study of how humans interact with the environment of living and non-living things. integrates info and ideas from the natural sciences (biology, chemistry, geology), social sciences (geography, economics, p ...
Chapter 1 * Science and the Environment
... Zoology is the study of animals Botany is the study of plants Microbiology is the study of microorganisms Ecology is the study how organisms interact with their environment and each other. Geology is the study of Earth’s surface, interior processes, and history. Paleontology is the study of fossils ...
... Zoology is the study of animals Botany is the study of plants Microbiology is the study of microorganisms Ecology is the study how organisms interact with their environment and each other. Geology is the study of Earth’s surface, interior processes, and history. Paleontology is the study of fossils ...
theme environment3
... tree covers has occurred due to the need of more agricultural and residual lands to meet the challenges due to over-population. Industrial effluents, forest fire and unplanned growth have led to severe water and air pollution. Major current environmental issues include climate change, species extinc ...
... tree covers has occurred due to the need of more agricultural and residual lands to meet the challenges due to over-population. Industrial effluents, forest fire and unplanned growth have led to severe water and air pollution. Major current environmental issues include climate change, species extinc ...
Old gas tanks leak mercury and cancer causing chemicals into
... beneath them was contaminated. More than 20 houses were built adjacent to the site of an old gasworks in 1991. Homeowners have been advised not to eat home-grown fruit or vegetables or let their children play in the garden as the soil contains dangerous levels of mercury and other cancer causing che ...
... beneath them was contaminated. More than 20 houses were built adjacent to the site of an old gasworks in 1991. Homeowners have been advised not to eat home-grown fruit or vegetables or let their children play in the garden as the soil contains dangerous levels of mercury and other cancer causing che ...
Document
... • Upstream policy/budget issues and not only projects • Thus donors focus on SEA, ‘country systems’ and climate ...
... • Upstream policy/budget issues and not only projects • Thus donors focus on SEA, ‘country systems’ and climate ...
ch-1-ppt - WordPress.com
... science is to understand and solve environmental problems. To accomplish this goal, environmental scientists study two main types of interactions between humans and their environment: 1) How our actions alter our environment. 2) The use of natural resources like water, coal, and oil. ...
... science is to understand and solve environmental problems. To accomplish this goal, environmental scientists study two main types of interactions between humans and their environment: 1) How our actions alter our environment. 2) The use of natural resources like water, coal, and oil. ...
AP Environmental Science 2014-2015 Syllabus Course Overview
... Course Overview: The Advanced Placement Environmental Science (APES) course is designed to be the equivalent of an introductory college course in environmental science. The goal is to provide you with the scientific principles, concepts, and methodologies necessary to understand the interrelationshi ...
... Course Overview: The Advanced Placement Environmental Science (APES) course is designed to be the equivalent of an introductory college course in environmental science. The goal is to provide you with the scientific principles, concepts, and methodologies necessary to understand the interrelationshi ...
The Agricultural Revolution
... In North America, a combination of rapid climate changes and overhunting by hunter-gatherers may have led to the disappearance of some large mammal species, including: 1) giant sloths 2) giant bison 3) mastodons 4) cave bears ...
... In North America, a combination of rapid climate changes and overhunting by hunter-gatherers may have led to the disappearance of some large mammal species, including: 1) giant sloths 2) giant bison 3) mastodons 4) cave bears ...
LG/13/21
... Cross-cutting accounts are assumed to provide crosscutting applications, even if some specific elements are included in Section 1 Where specific natural resource accounts deal with a particular environmental issue, then keep it as an application of the integrated account (e.g. wastewater, water qual ...
... Cross-cutting accounts are assumed to provide crosscutting applications, even if some specific elements are included in Section 1 Where specific natural resource accounts deal with a particular environmental issue, then keep it as an application of the integrated account (e.g. wastewater, water qual ...
Ch. 2 Environmental Laws, Economics and
... Industry with air pollutants causing acid rain Children with chronic asthma, bronchitis, and heart problems ...
... Industry with air pollutants causing acid rain Children with chronic asthma, bronchitis, and heart problems ...
The emergence and current challenges of ecological
... – Willingness to cooperate with natural scientists – Cooperate with the influential to get political influence and academic recognition – The publish or perish pressure – Policing the boundaries: power of definition ...
... – Willingness to cooperate with natural scientists – Cooperate with the influential to get political influence and academic recognition – The publish or perish pressure – Policing the boundaries: power of definition ...
Environmental Science
... Environmental Degradation: process that occurs when a resource is used at a rate greater than its natural replacement rate. ...
... Environmental Degradation: process that occurs when a resource is used at a rate greater than its natural replacement rate. ...
Document
... services needed to improve life for everyone without overtaxing the environmental systems and natural resources on which we all depend? To be truly enduring, the benefits of sustainable development must be available to all humans, not just to the members of a privileged group. ...
... services needed to improve life for everyone without overtaxing the environmental systems and natural resources on which we all depend? To be truly enduring, the benefits of sustainable development must be available to all humans, not just to the members of a privileged group. ...
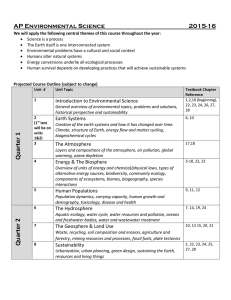
Quarter 1 Quarter 2
... We will apply the following central themes of this course throughout the year: Science is a process The Earth itself is one interconnected system Environmental problems have a cultural and social context Humans alter natural systems Energy conversions underlie all ecological processes Hu ...
... We will apply the following central themes of this course throughout the year: Science is a process The Earth itself is one interconnected system Environmental problems have a cultural and social context Humans alter natural systems Energy conversions underlie all ecological processes Hu ...
ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
... can be replaced relatively quickly by natural processes Nonrenewable resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals are used up at a much faster rate than they are consumed ...
... can be replaced relatively quickly by natural processes Nonrenewable resources, such as fossil fuels and minerals are used up at a much faster rate than they are consumed ...









![[Chapter 1] Environmental Problems, Their Causes, and](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001566031_1-d8d520048ec83a59f37af3d97992e068-300x300.png)