GEOL 109 - Continuing Education
... Chapter 6: Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal? Evolution is the cornerstone for the interpretation of the fossil record and is accepted by virtually all scientists as a fact. Charles Darwin and Alfred R. Wallace recognised the importance of variability in offspring as an important component in th ...
... Chapter 6: Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal? Evolution is the cornerstone for the interpretation of the fossil record and is accepted by virtually all scientists as a fact. Charles Darwin and Alfred R. Wallace recognised the importance of variability in offspring as an important component in th ...
ch15 - earthjay science
... The era we call Cenozoic is divided into three periods: Paleogene; Neogene; and Quaternary. The Cenozoic, although covering only the last 65 million years of Earth’s history, encompasses major worldwide changes. One such change occurred when the North Atlantic rift extended to the north, separating ...
... The era we call Cenozoic is divided into three periods: Paleogene; Neogene; and Quaternary. The Cenozoic, although covering only the last 65 million years of Earth’s history, encompasses major worldwide changes. One such change occurred when the North Atlantic rift extended to the north, separating ...
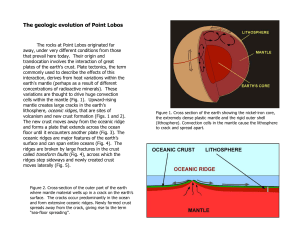
The geologic evolution of Point Lobos
... Where the plates collide head-on a different process occurs. If the other plate consists of continental crust, the thinner, more dense oceanic plate tends to slide beneath the continental plate in a process called subduction. The force of the collision generates heat and pressure; water carried into ...
... Where the plates collide head-on a different process occurs. If the other plate consists of continental crust, the thinner, more dense oceanic plate tends to slide beneath the continental plate in a process called subduction. The force of the collision generates heat and pressure; water carried into ...
alberta dinosaur fact sheet
... casts and real fossils. A rough ballpark would be over 150 major or scientifically significant original specimens from Alberta are on display worldwide, most in Canada and the USA, with some in Argentina, China, and England. Q: How many dinosaur fossils were taken out of Alberta before laws came int ...
... casts and real fossils. A rough ballpark would be over 150 major or scientifically significant original specimens from Alberta are on display worldwide, most in Canada and the USA, with some in Argentina, China, and England. Q: How many dinosaur fossils were taken out of Alberta before laws came int ...
Geology of Hungary :: 6. The Tisia
... Rocks: Middle Triassic dolomites are covered by Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous deep-marine marls. No younger deposits up to the Middle Miocene can be found. Structure: Based on few borehole data from the SE Great Plain and surface data from the Apuseni Mts. foldedimbricated and nappe structures ...
... Rocks: Middle Triassic dolomites are covered by Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous deep-marine marls. No younger deposits up to the Middle Miocene can be found. Structure: Based on few borehole data from the SE Great Plain and surface data from the Apuseni Mts. foldedimbricated and nappe structures ...
Title
... average seafloor level will be elevated, and the sea surface will rise accordingly. In the mid-Cretaceous, rising sea levels drowned much of what is dry land today; for example, my birthplace in Iowa was then at the bottom of the ocean. When the water receded, it left deposits of limestone and chalk ...
... average seafloor level will be elevated, and the sea surface will rise accordingly. In the mid-Cretaceous, rising sea levels drowned much of what is dry land today; for example, my birthplace in Iowa was then at the bottom of the ocean. When the water receded, it left deposits of limestone and chalk ...
Geology Field Notes: Big Bend National Park, Texas Big Bend is a
... overlying sandstones and clays to the onslaught of erosion. Limestone cliffs throughout the region continue to be eroded today; most of the more easily removed sandstone and clay is gone from the mountains. For almost 10 million years after uplift ended, non-marine sediments of the Tertiary period c ...
... overlying sandstones and clays to the onslaught of erosion. Limestone cliffs throughout the region continue to be eroded today; most of the more easily removed sandstone and clay is gone from the mountains. For almost 10 million years after uplift ended, non-marine sediments of the Tertiary period c ...
Stratigraphy & geochemistry of the Nipigon basin
... Geochemical evidence for Archean plate tectonics in the 2.7 to 3.0 Ga Uchi Subprovince, northern Ontario Pete Hollings Lakehead University ...
... Geochemical evidence for Archean plate tectonics in the 2.7 to 3.0 Ga Uchi Subprovince, northern Ontario Pete Hollings Lakehead University ...
Geology of Dubbo - Dubbo Field Nats Home
... the Binnaway, Ballimore, Dapper, Wongarbon, Mugga Hill and Minore areas, the maximum thickness is probably about 100m but to the north-west the thickness increases greatly to form the main water-bearing horizon in the eastern part of the Great Artesian Basin. In its area of outcrop the Pilliga Sands ...
... the Binnaway, Ballimore, Dapper, Wongarbon, Mugga Hill and Minore areas, the maximum thickness is probably about 100m but to the north-west the thickness increases greatly to form the main water-bearing horizon in the eastern part of the Great Artesian Basin. In its area of outcrop the Pilliga Sands ...
chapter 11—the mesozoic era
... albedo (482): The fraction of solar energy reflected back into space is termed the Earth’s albedo. channeled scablands (480): With the recession of the glacier, the ice dam broke, and tremendous floods of water rushed out catastrophically across eastern Washington, causing severe erosion and deposit ...
... albedo (482): The fraction of solar energy reflected back into space is termed the Earth’s albedo. channeled scablands (480): With the recession of the glacier, the ice dam broke, and tremendous floods of water rushed out catastrophically across eastern Washington, causing severe erosion and deposit ...
No Slide Title
... Six Major Paleozoic Continents – Kazakhstan - a triangular continent centered on Kazakhstan, but considered by some to be an extension of the Paleozoic Siberian continent – Laurentia - most of present North America, Greenland, northwestern Ireland, and Scotland – and Siberia - Russia east of the Ur ...
... Six Major Paleozoic Continents – Kazakhstan - a triangular continent centered on Kazakhstan, but considered by some to be an extension of the Paleozoic Siberian continent – Laurentia - most of present North America, Greenland, northwestern Ireland, and Scotland – and Siberia - Russia east of the Ur ...
Geology of Paraná - Mineropar
... west of where it is now. Paranaguá and Guaratuba bays were much larger then, and the number and conformation of islands was quite different from today's. After 5,600 years, the sea level dropped to its current position, which led the younger parts of the coastal plains of Paraná to take shape.. ...
... west of where it is now. Paranaguá and Guaratuba bays were much larger then, and the number and conformation of islands was quite different from today's. After 5,600 years, the sea level dropped to its current position, which led the younger parts of the coastal plains of Paraná to take shape.. ...
Continental Drift Theory of Alfred Wegener
... Continental Drift Theory of Alfred Wegener Continental drift is the movement of the Earth's continents relative to each other by appearing to drift across the ocean bed. The speculation that continents might have 'drifted' was first put forward by Abraham Ortelius in 1596. The concept was independen ...
... Continental Drift Theory of Alfred Wegener Continental drift is the movement of the Earth's continents relative to each other by appearing to drift across the ocean bed. The speculation that continents might have 'drifted' was first put forward by Abraham Ortelius in 1596. The concept was independen ...
Sedimentary rocks - s3.amazonaws.com
... • There are a few theories about dino extinction, but scientists may never know for certain. • Theories include: asteroid impact, climate change, volcanic eruptions, & disease carrying insects ...
... • There are a few theories about dino extinction, but scientists may never know for certain. • Theories include: asteroid impact, climate change, volcanic eruptions, & disease carrying insects ...
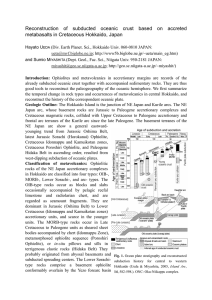
Reconstruction of subducted oceanic crust based on accreted
... deposits. They resemble MORB with slightly poorer in incompatible elements, and are regarded as accreted oceanic plateau. The arc-type metavolcanics, together with gabbro-tonalite and serpentinite, are contained in the mid-Cretaceous part (Oku-Niikappu complex) of the Idonnappu Zone as a dismembere ...
... deposits. They resemble MORB with slightly poorer in incompatible elements, and are regarded as accreted oceanic plateau. The arc-type metavolcanics, together with gabbro-tonalite and serpentinite, are contained in the mid-Cretaceous part (Oku-Niikappu complex) of the Idonnappu Zone as a dismembere ...
Computer exercises in tectonics
... that the North American continent has grown with time. Episodes of mountain building (tectonism or orogeny) and volcanism are often related to the collision or break-up of continents. One part of this process is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2A shows a cross-section of a passive continental margin, simi ...
... that the North American continent has grown with time. Episodes of mountain building (tectonism or orogeny) and volcanism are often related to the collision or break-up of continents. One part of this process is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2A shows a cross-section of a passive continental margin, simi ...
Prepared by Erhan Turgut
... soft, fleshy parts. Many bones of vertebrates and many shells of mollusks, such as clams and oysters, can be found in the sedimentary rocks, whereas animals with only soft parts, such as jellyfish and worms, are rarely found in fossil form. The forms of life have been changing throughout geologic ti ...
... soft, fleshy parts. Many bones of vertebrates and many shells of mollusks, such as clams and oysters, can be found in the sedimentary rocks, whereas animals with only soft parts, such as jellyfish and worms, are rarely found in fossil form. The forms of life have been changing throughout geologic ti ...
Paleozoic large igneous provinces of Northern Eurasia: Correlation
... subduction zones — the African and Pacific low shear velocity provinces (Courtillot et al. (2003), Li and Zhong (2009), and references therein). Paleozoic and Precambrian LIPs are typically deeply eroded; they may occur in completely subducted oceans and therefore cannot be identified or well describe ...
... subduction zones — the African and Pacific low shear velocity provinces (Courtillot et al. (2003), Li and Zhong (2009), and references therein). Paleozoic and Precambrian LIPs are typically deeply eroded; they may occur in completely subducted oceans and therefore cannot be identified or well describe ...
Origins Of The Himalayan Treasure Chest
... Eurasia. There the Tethys oceanic crust partially melted. By about 60 million years ago, the oceanic crust of the Tethys had been pushed entirely beneath Eurasia. No longer separated by an ocean, India and Eurasia began to collide along what is known as the Indus-Tsangpo suture zone. This colliding ...
... Eurasia. There the Tethys oceanic crust partially melted. By about 60 million years ago, the oceanic crust of the Tethys had been pushed entirely beneath Eurasia. No longer separated by an ocean, India and Eurasia began to collide along what is known as the Indus-Tsangpo suture zone. This colliding ...
Argyll and the Islands - Scottish Natural Heritage
... are around 1,800 million years old, much older than the Dalradian rocks, but not as old as the oldest rocks on the British Isles, the Lewisian gneisses of the Outer Hebrides and North-west Highlands. The rocks of the Rhinns are also gneisses; they are coarsely crystalline and have a strongly banded ...
... are around 1,800 million years old, much older than the Dalradian rocks, but not as old as the oldest rocks on the British Isles, the Lewisian gneisses of the Outer Hebrides and North-west Highlands. The rocks of the Rhinns are also gneisses; they are coarsely crystalline and have a strongly banded ...
EarthComm_c2s6_185-197
... energy is released.) This provided further evidence against cooling. Heat from radioactive decay in Earth would work against the cooling and contraction process. According to Wegener, there was a huge supercontinent called Pangea. (Pangea is Greek for “all land.”) About 200 million years ago, it bro ...
... energy is released.) This provided further evidence against cooling. Heat from radioactive decay in Earth would work against the cooling and contraction process. According to Wegener, there was a huge supercontinent called Pangea. (Pangea is Greek for “all land.”) About 200 million years ago, it bro ...
Mr. Altorfer - Fair Lawn Public Schools
... Remains of the same plants and animals are present on different continents that are now separated by oceans. Fossils of plants and animals that lived in wet, warm climates are in areas that now have cold climates. Deposits of coal in Antarctica are evidence of continental drift. The fossilized ...
... Remains of the same plants and animals are present on different continents that are now separated by oceans. Fossils of plants and animals that lived in wet, warm climates are in areas that now have cold climates. Deposits of coal in Antarctica are evidence of continental drift. The fossilized ...
Chapter 14 - Mesozoic Geology
... • The general term Cordilleran orogeny – is applied to the mountain-building activity – that began during the Jurassic – and continued into the Cenozoic • The Cordilleran orogeny – consisted of a series – of individual mountain-building events – that occurred in different regions at different ...
... • The general term Cordilleran orogeny – is applied to the mountain-building activity – that began during the Jurassic – and continued into the Cenozoic • The Cordilleran orogeny – consisted of a series – of individual mountain-building events – that occurred in different regions at different ...
Geologic Time
... intervals known as eras and periods. We discuss how rocks can be matched between separate regions using their fossils in the section on Relative Time. The Geologic Time Scale section provides a review the history of Earth including the major changes in the biosphere over the last half-billion years. ...
... intervals known as eras and periods. We discuss how rocks can be matched between separate regions using their fossils in the section on Relative Time. The Geologic Time Scale section provides a review the history of Earth including the major changes in the biosphere over the last half-billion years. ...