Quantum Proofs for Classical Theorems
... is to go to complex numbers: using the identity eix = cos x + i sin x we have ei(x+y) = eix eiy = (cos x + i sin x)(cos y + i sin y) = cos x cos y − sin x sin y + i(cos x sin y + sin x cos y) . Taking the real parts of the two sides gives our identity. Another example is the probabilistic method, as ...
... is to go to complex numbers: using the identity eix = cos x + i sin x we have ei(x+y) = eix eiy = (cos x + i sin x)(cos y + i sin y) = cos x cos y − sin x sin y + i(cos x sin y + sin x cos y) . Taking the real parts of the two sides gives our identity. Another example is the probabilistic method, as ...
Observations on Hyperplane: II. Dynamical Variables and
... To firm up the definition, let’s reserve ‘quanton’ for any particle-like quanta of a quantized field or any bound state of such quanta due to interactions which have, themselves, no macroscopic classical field manifestation, i.e., so far as we know, interactions other than electromagnetism or gravit ...
... To firm up the definition, let’s reserve ‘quanton’ for any particle-like quanta of a quantized field or any bound state of such quanta due to interactions which have, themselves, no macroscopic classical field manifestation, i.e., so far as we know, interactions other than electromagnetism or gravit ...
Experimental one-way quantum computing
... Standard quantum computation is based on sequences of unitary quantum logic gates that process qubits. The one-way quantum computer proposed by Raussendorf and Briegel is entirely different. It has changed our understanding of the requirements for quantum computation and more generally how we think ...
... Standard quantum computation is based on sequences of unitary quantum logic gates that process qubits. The one-way quantum computer proposed by Raussendorf and Briegel is entirely different. It has changed our understanding of the requirements for quantum computation and more generally how we think ...
Photoionization microscopy in terms of local-frame-transformation theory eas, Robicheaux, reene
... a variational R-matrix method. This allows us to disentangle errors associated with the WKB approximation from those deriving from the LFT approximation itself, as was shown in Ref. [15]. For the most part this causes only small differences from the original WKB treatment consistent with Ref. [15], ...
... a variational R-matrix method. This allows us to disentangle errors associated with the WKB approximation from those deriving from the LFT approximation itself, as was shown in Ref. [15]. For the most part this causes only small differences from the original WKB treatment consistent with Ref. [15], ...
Finite Element Approach of Electronic Structures THÈSE
... a structural beam or as a plate from an engineering point of view. At that macroscopic scale, i.e. the length scale on which objects are of a size that is observable by the naked eye, the mechanical behavior of concrete is generally modeled as isotropic, continuous, and homogeneous. Under the elasti ...
... a structural beam or as a plate from an engineering point of view. At that macroscopic scale, i.e. the length scale on which objects are of a size that is observable by the naked eye, the mechanical behavior of concrete is generally modeled as isotropic, continuous, and homogeneous. Under the elasti ...
Self-assembled quantum dots
... For a purely hydrostatic strain (εxx=εyy=εzz) we have thus B(ε)=0, as all linear dimensions are deformed in the same way. On the other hand pure axial deformation results in Tr(ε)=0, while B(ε)≠0, which corresponds to volume conserving strain. Let us reiterate that general deformations can be compl ...
... For a purely hydrostatic strain (εxx=εyy=εzz) we have thus B(ε)=0, as all linear dimensions are deformed in the same way. On the other hand pure axial deformation results in Tr(ε)=0, while B(ε)≠0, which corresponds to volume conserving strain. Let us reiterate that general deformations can be compl ...
pdf
... expectations and Wigner functions play a central role in the analysis of quantum systems, in particular in the semiclassical regime; see [?, §IV] or [?, §7.1]. The idea of combining different spectrograms can also be found in the time-frequency literature; see e.g. [17] and the references given there ...
... expectations and Wigner functions play a central role in the analysis of quantum systems, in particular in the semiclassical regime; see [?, §IV] or [?, §7.1]. The idea of combining different spectrograms can also be found in the time-frequency literature; see e.g. [17] and the references given there ...
Seeing a single photon without destroying it
... Light detection is usually a destructive process, in that detectors annihilate photons and convert them into electrical signals, making it impossible to see a single photon twice. But this limitation is not fundamentalÐquantum non-demolition strategies1±3 permit repeated measurements of physically o ...
... Light detection is usually a destructive process, in that detectors annihilate photons and convert them into electrical signals, making it impossible to see a single photon twice. But this limitation is not fundamentalÐquantum non-demolition strategies1±3 permit repeated measurements of physically o ...
entanglement properties of quantum many
... point in parameter space where the transition takes place, long-range correlations develop in the ground state. Osterloh et al. and ON proposed that there must exist an intimate relation between quantum phase transitions and entanglement, and that the behavior of a suitable entanglement measure shou ...
... point in parameter space where the transition takes place, long-range correlations develop in the ground state. Osterloh et al. and ON proposed that there must exist an intimate relation between quantum phase transitions and entanglement, and that the behavior of a suitable entanglement measure shou ...
Quantum technology: the second quantum revolution
... (v) Entanglement: the superposition principle applied to certain non-local correlations. If a correlation can be realized in two or more indistinguishable ways, the state of the system is a superposition of all such correlations simultaneously. (vi) Decoherence: what happens to quantum superposition ...
... (v) Entanglement: the superposition principle applied to certain non-local correlations. If a correlation can be realized in two or more indistinguishable ways, the state of the system is a superposition of all such correlations simultaneously. (vi) Decoherence: what happens to quantum superposition ...
Section 11.3 Atomic Orbitals
... • Pauli Exclusion Principle - No 2electrons in the same atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers. An atomic orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons and those 2 electrons must have opposite spins • Hund’s Rule – every orbital in a subshell is singly occupied with one electron before any one ...
... • Pauli Exclusion Principle - No 2electrons in the same atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers. An atomic orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons and those 2 electrons must have opposite spins • Hund’s Rule – every orbital in a subshell is singly occupied with one electron before any one ...
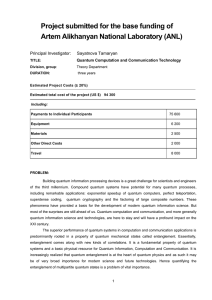
Microsoft Word - ANL_form6
... On the basis of the multipartite teleportation we will elaborate a quantum communication technology capable to transmit an unlimited amount of information through noisy channels. Note, that a long-distance quantum communication channel of high capacity enables us to solve several problems of practic ...
... On the basis of the multipartite teleportation we will elaborate a quantum communication technology capable to transmit an unlimited amount of information through noisy channels. Note, that a long-distance quantum communication channel of high capacity enables us to solve several problems of practic ...