nphys\nphys231
... often arising from mechanisms that nature uses again and again. Physics and mathematics can help to explain these patterns — and themselves benefit from a range of new and important challenges1. Life is ultimately shaped by evolution and natural selection. The revolution in molecular biology sparked ...
... often arising from mechanisms that nature uses again and again. Physics and mathematics can help to explain these patterns — and themselves benefit from a range of new and important challenges1. Life is ultimately shaped by evolution and natural selection. The revolution in molecular biology sparked ...
Dealing with infectious diseases
... All illnesses/ diseases will be checked on Schedule 3 of the Health (Infectious Diseases) Regulations 2001 ( see attached Appendix B) and if required we will contact DET or the Health Department. The telephone number for the Department of Education and Early Childhood Development Communicable Diseas ...
... All illnesses/ diseases will be checked on Schedule 3 of the Health (Infectious Diseases) Regulations 2001 ( see attached Appendix B) and if required we will contact DET or the Health Department. The telephone number for the Department of Education and Early Childhood Development Communicable Diseas ...
VIRUS TAKS QUESTIONS Spring 2003 – 11 (6) Most viruses infect
... J* must be reproduced in living cells July 2004 – 11 42 One characteristic shared by a virus and a living cell is that both — F* store genetic information in nucleic acids G have a crystalline structure H gain energy directly from the sun J use glucose for respiration October 2005 – 11 9 Which of th ...
... J* must be reproduced in living cells July 2004 – 11 42 One characteristic shared by a virus and a living cell is that both — F* store genetic information in nucleic acids G have a crystalline structure H gain energy directly from the sun J use glucose for respiration October 2005 – 11 9 Which of th ...
Infectious disseases in hospitals
... variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (nvCJD) (thought to be the human equivalent) - Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease – kuru and fatal insomnia. -Prions are mutated proteins -majority of prion related diseases involve neurological damage. -not all scientists accept they are the cause of disease. ...
... variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (nvCJD) (thought to be the human equivalent) - Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease – kuru and fatal insomnia. -Prions are mutated proteins -majority of prion related diseases involve neurological damage. -not all scientists accept they are the cause of disease. ...
Microbiology Babylon university 2nd stage pharmacy collage Viral
... cord is possible. There tends to be a correlation between the level of viremia achieved by a blood-borne neurotropic virus and its neuroinvasiveness. The other pathway to the central nervous system is via peripheral nerves. Virions can be taken up at sensory nerve or motor endings and be moved withi ...
... cord is possible. There tends to be a correlation between the level of viremia achieved by a blood-borne neurotropic virus and its neuroinvasiveness. The other pathway to the central nervous system is via peripheral nerves. Virions can be taken up at sensory nerve or motor endings and be moved withi ...
Bloodborne Pathogens - Stuart T. Wilson, CPA PC
... MRSA is a type of staph bacteria that does not react to certain antibiotics. It typically causes skin infections, but can also cause other infection, including pneumonia. MRSA does not usually, but can lead to death. It is spread by skin-to-skin contact, touching a personal item that touched the inf ...
... MRSA is a type of staph bacteria that does not react to certain antibiotics. It typically causes skin infections, but can also cause other infection, including pneumonia. MRSA does not usually, but can lead to death. It is spread by skin-to-skin contact, touching a personal item that touched the inf ...
2-Infectious diseases
... Infectious diseases are particularly important causes of death among: 1- the elderly people. 2-patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). 3- patients with chronic diseases. 4-patients who receive immunosuppressive drugs. ...
... Infectious diseases are particularly important causes of death among: 1- the elderly people. 2-patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). 3- patients with chronic diseases. 4-patients who receive immunosuppressive drugs. ...
bloodborne pathogens 2016-2017 - Western Dubuque Community
... • Many people do not know they are infected or do not have symptoms, but can still transmit disease • Rates of HBV in the US have declined 82% since 1990 with routine vaccination of all children (CDC, 2009) • Hepatitis B virus can survive outside the body at least 7 days. During that time, the virus ...
... • Many people do not know they are infected or do not have symptoms, but can still transmit disease • Rates of HBV in the US have declined 82% since 1990 with routine vaccination of all children (CDC, 2009) • Hepatitis B virus can survive outside the body at least 7 days. During that time, the virus ...
ILC 2017: European countries restrict access to life
... HCV is a leading cause of chronic liver disease, end-stage cirrhosis and liver cancer.4 It is estimated to infect over 71 million people worldwide, of whom 784,000 die each year.5,6 Until the approval of the DAAs, HCV was treated with pegylated interferon and ribavirin, which caused serious adverse ...
... HCV is a leading cause of chronic liver disease, end-stage cirrhosis and liver cancer.4 It is estimated to infect over 71 million people worldwide, of whom 784,000 die each year.5,6 Until the approval of the DAAs, HCV was treated with pegylated interferon and ribavirin, which caused serious adverse ...
Document
... • May be considered when vaccinating adolescents in groups with high rates of HBV infection – Alaskan Natives – Pacific Islanders – Children of immigrants from endemic countries – Family members of HBV carriers ...
... • May be considered when vaccinating adolescents in groups with high rates of HBV infection – Alaskan Natives – Pacific Islanders – Children of immigrants from endemic countries – Family members of HBV carriers ...
Breakout 3 - Nikos Vasilakis
... Only brain was positive by RT-PCR (tested placenta, heart, lung, liver, spleen, kidney, thymus and skin) ...
... Only brain was positive by RT-PCR (tested placenta, heart, lung, liver, spleen, kidney, thymus and skin) ...
New insights into hepatitis B and C virus co-infection
... virus (HCV). Infections with these viruses are the leading cause of chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As a consequence, major research efforts have been devoted to HBV and HCV. However, relatively little is known about interactions between HBV and HCV in patients ...
... virus (HCV). Infections with these viruses are the leading cause of chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As a consequence, major research efforts have been devoted to HBV and HCV. However, relatively little is known about interactions between HBV and HCV in patients ...
Document
... Pathogen – Any living organism or particle that can cause an infectious disease. • Infectious – capable of causing an infection • Disease damaging change in structure or function of cells, tissues, etc… • Communicable – able to be passed from host to host • “Contagious” • Host cell – cell infected b ...
... Pathogen – Any living organism or particle that can cause an infectious disease. • Infectious – capable of causing an infection • Disease damaging change in structure or function of cells, tissues, etc… • Communicable – able to be passed from host to host • “Contagious” • Host cell – cell infected b ...
Bloodborne Pathogens (Powerpoint Presentation)
... is a virus that infection and inflammation of the liver is transmitted primarily through "blood to blood" contact can lead to serious conditions such as cirrhosis & liver cancer can survive in dried blood for up to seven days ...
... is a virus that infection and inflammation of the liver is transmitted primarily through "blood to blood" contact can lead to serious conditions such as cirrhosis & liver cancer can survive in dried blood for up to seven days ...
Parasitism and Disease - Powerpoint for Oct. 26.
... 1) increase with increasing density of susceptible hosts - N 2) increase with increasing transmission rate beta β 3) increase with increasing fraction of infected hosts that survive long enough to be infectious to other hosts symbolized by f 4) increase with increasing average time that host remains ...
... 1) increase with increasing density of susceptible hosts - N 2) increase with increasing transmission rate beta β 3) increase with increasing fraction of infected hosts that survive long enough to be infectious to other hosts symbolized by f 4) increase with increasing average time that host remains ...
Review of AASLD Abstracts, October 2004
... continues to be a major public health challenge. Worldwide, more than 400 million people have chronic hepatitis B (CHB), with a major concentration of those infected living in or coming from the AsiaPacific region. The overall prevalence of the virus in the United States is around 5% but the prevale ...
... continues to be a major public health challenge. Worldwide, more than 400 million people have chronic hepatitis B (CHB), with a major concentration of those infected living in or coming from the AsiaPacific region. The overall prevalence of the virus in the United States is around 5% but the prevale ...
Primary liver cancer and chronic hepatitis B
... screening and treatment Preventing HCC is contingent on educating and engaging the affected population to become active participants in their care. South-West Sydney has the highest burden of both chronic hepatitis B16 and HCC17 in Australia. B Positive is a local program based in South-West Sydney ...
... screening and treatment Preventing HCC is contingent on educating and engaging the affected population to become active participants in their care. South-West Sydney has the highest burden of both chronic hepatitis B16 and HCC17 in Australia. B Positive is a local program based in South-West Sydney ...
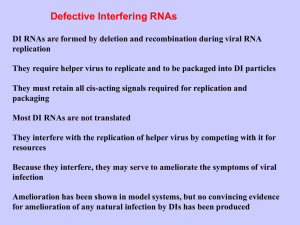
Viroids are small (~300 nt) circular RNA molecules that are
... the agent in lymph nodes followed by invasion of peripheral nerves. ...
... the agent in lymph nodes followed by invasion of peripheral nerves. ...
IMMUNE RESPONSE TO INFECTIOUS DISEASE
... during acute infection and in protecting against reinfection? ANTIBODIES If antibody is produced to the viral receptor, it can block infection altogether by preventing viral binding to the host cells i.e. Secretory IgA in mucous secretions ...
... during acute infection and in protecting against reinfection? ANTIBODIES If antibody is produced to the viral receptor, it can block infection altogether by preventing viral binding to the host cells i.e. Secretory IgA in mucous secretions ...
PDF - Microbiology Society
... are trying to develop a vaccine, but it is not possible to grow norovirus in the laboratory and there are so many strains that no one vaccine could protect against them all. ...
... are trying to develop a vaccine, but it is not possible to grow norovirus in the laboratory and there are so many strains that no one vaccine could protect against them all. ...
Serology Review
... clearing. A false-positive is another possibility (HIV-positive people with this particular test result should have their HBV viral load checked). ...
... clearing. A false-positive is another possibility (HIV-positive people with this particular test result should have their HBV viral load checked). ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.