L1.1.MysteryDisease
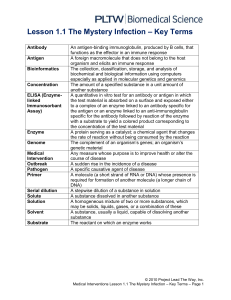
... An antigen-binding immunoglobulin, produced by B cells, that functions as the effector in an immune response A foreign macromolecule that does not belong to the host organism and elicits an immune response The collection, classification, storage, and analysis of biochemical and biological informatio ...
... An antigen-binding immunoglobulin, produced by B cells, that functions as the effector in an immune response A foreign macromolecule that does not belong to the host organism and elicits an immune response The collection, classification, storage, and analysis of biochemical and biological informatio ...
Low Risk - LSU Health New Orleans
... HIV virus. Though infected individuals may not initially have symptoms of HIV infection, it may still be possible for them to spread disease. • Hepatitis B is an infectious illness caused by HBV which causes inflammation of the liver, liver infection, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Hepatitis B is far ...
... HIV virus. Though infected individuals may not initially have symptoms of HIV infection, it may still be possible for them to spread disease. • Hepatitis B is an infectious illness caused by HBV which causes inflammation of the liver, liver infection, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Hepatitis B is far ...
Characterization of opsonizing antibodies against FMD virus, A. Summerfield
... virus infection of macrophages and dendritic cells resulting in virus destruction and IFNa responses. 2. Often mAbs which efficiently neutralize are also efficient at opsonization. Non-neutralizing mAbs (against homologous virus) can probably not opsonize FMDV. However, opsonization of non-neutraliz ...
... virus infection of macrophages and dendritic cells resulting in virus destruction and IFNa responses. 2. Often mAbs which efficiently neutralize are also efficient at opsonization. Non-neutralizing mAbs (against homologous virus) can probably not opsonize FMDV. However, opsonization of non-neutraliz ...
Ch. 14 Notes - 7th - Lee County Schools
... Students are legally required to get vaccines before they are allowed to go to school ...
... Students are legally required to get vaccines before they are allowed to go to school ...
Ch31-Asepsis_notes
... Passive Immunity – is where the host receives natural or artificial antibodies produced from another source. - Antibodies transferred naturally from an immune mother to baby through the placenta or in colostrums; may lasts 6 months to 1 year - Occurs when immune serum (antibody) from an animal or an ...
... Passive Immunity – is where the host receives natural or artificial antibodies produced from another source. - Antibodies transferred naturally from an immune mother to baby through the placenta or in colostrums; may lasts 6 months to 1 year - Occurs when immune serum (antibody) from an animal or an ...
infection control and tb
... Practice good infection control • When you are sick keep your germs to yourself and stay home from work or school. Notify supervisor for medical help, report infection exposure. • When you are well stay a safe distance (2-3 feet) from those who are sick. • If you are given medication to treat an inf ...
... Practice good infection control • When you are sick keep your germs to yourself and stay home from work or school. Notify supervisor for medical help, report infection exposure. • When you are well stay a safe distance (2-3 feet) from those who are sick. • If you are given medication to treat an inf ...
- U
... • Control and Prevention of spread. – Vaccination & Antiviral drugs • Ex.) chickenpox vaccine, AZT, Acyclovir, protease inhibitors. ...
... • Control and Prevention of spread. – Vaccination & Antiviral drugs • Ex.) chickenpox vaccine, AZT, Acyclovir, protease inhibitors. ...
传染病学总论
... • Caused by pathogens: virus、chlamydia、richettsia、 prion、bacteria、spirochete、fungus and parasite( helminth、protozoa)or medical insect • Infectious disease: involve any organ or system of the body and thus embraces all medical disciplines. • Communicability is another factor which differentiates infe ...
... • Caused by pathogens: virus、chlamydia、richettsia、 prion、bacteria、spirochete、fungus and parasite( helminth、protozoa)or medical insect • Infectious disease: involve any organ or system of the body and thus embraces all medical disciplines. • Communicability is another factor which differentiates infe ...
ear infection?
... are viral and resolve without treatment. Acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used for pain and fever control. For infections that turn into bacterial infections, antibiotics may be prescribed. ...
... are viral and resolve without treatment. Acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used for pain and fever control. For infections that turn into bacterial infections, antibiotics may be prescribed. ...
Bloodborne Pathogens - Texas Gas Association
... HIV Symptoms Symptoms can vary, but often include: ...
... HIV Symptoms Symptoms can vary, but often include: ...
Surgical-Infections
... • Used Carbolic Acid (Phenol) to clean hands, instruments and wipe on surgical wounds drastically decreased infections. ...
... • Used Carbolic Acid (Phenol) to clean hands, instruments and wipe on surgical wounds drastically decreased infections. ...
Virus-Cell Interactions
... Subgroup A infected cells become resistant to superinfection by other subgroup A viruses due to saturation of subgroup A receptor, but are still sensitive to subgroup B viruses which use a different receptor (and vice versa) ...
... Subgroup A infected cells become resistant to superinfection by other subgroup A viruses due to saturation of subgroup A receptor, but are still sensitive to subgroup B viruses which use a different receptor (and vice versa) ...
Grandrounds Clinical Vignette
... – Denied any history of smoking, alcohol consumption or illicit drug ...
... – Denied any history of smoking, alcohol consumption or illicit drug ...
Swine flu update Last Updated September 4, 2009
... whether additional people have been infected with swine influenza viruses. The information below includes the interim guidance provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on infection control, antiviral treatment and chemoprophylaxis, and monitoring of close contacts of cases of ...
... whether additional people have been infected with swine influenza viruses. The information below includes the interim guidance provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on infection control, antiviral treatment and chemoprophylaxis, and monitoring of close contacts of cases of ...
ImmunIsatIon Is for lIfe
... people, especially small children, may not show any symptoms even though they may have the virus and can pass it onto others. yyWhile most people recover fully, it sometimes leads to death from overwhelming infection of the liver. ...
... people, especially small children, may not show any symptoms even though they may have the virus and can pass it onto others. yyWhile most people recover fully, it sometimes leads to death from overwhelming infection of the liver. ...
The Immune System
... Immune complexes , ie IgG or IgM with complement activated, cause damage to large area of host tissue Examples: Glomerulonephritis, Rheumatic Fever ...
... Immune complexes , ie IgG or IgM with complement activated, cause damage to large area of host tissue Examples: Glomerulonephritis, Rheumatic Fever ...
How does the body fight off a virus?
... genes and these accumulate as the virus passes from one person to another. During this process, the virus alters its appearance and our immune memory cells struggle to recognise it, leaving the virus free to infect us once more. This is why you can keep catching the flu - new mutated strains constan ...
... genes and these accumulate as the virus passes from one person to another. During this process, the virus alters its appearance and our immune memory cells struggle to recognise it, leaving the virus free to infect us once more. This is why you can keep catching the flu - new mutated strains constan ...
Antigens of Hepatitis B Virus: Failure to Detect HBeAg on the
... properties of an immunoglobulin and suggested it represents an idiotypic antibody; clearly a host response to HBV infection. The earlier results (Neurath et al. ~976) were explained by the possibility that a rheumatoid factor might have been present in their anti-HBe reagent. However, another report ...
... properties of an immunoglobulin and suggested it represents an idiotypic antibody; clearly a host response to HBV infection. The earlier results (Neurath et al. ~976) were explained by the possibility that a rheumatoid factor might have been present in their anti-HBe reagent. However, another report ...
Viruses - Mount Mansfield Union High School
... Swine Influenza (swine flu) is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses that causes regular outbreaks in pigs. People do not normally get swine flu, but human infections can and do happen. Swine flu viruses have been reported to spread from person-to-person, but in the ...
... Swine Influenza (swine flu) is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses that causes regular outbreaks in pigs. People do not normally get swine flu, but human infections can and do happen. Swine flu viruses have been reported to spread from person-to-person, but in the ...
Research Article - International Research Journal of Pharmacy
... Hepatitis-B is such a disease which is life threatening and contributing a large man power as well as economical loss worldwide. It is a serious and common infectious disease of the liver affecting millions of people worldwide. Hepatitis-B virus can cause the acute as well as chronic infection. The ...
... Hepatitis-B is such a disease which is life threatening and contributing a large man power as well as economical loss worldwide. It is a serious and common infectious disease of the liver affecting millions of people worldwide. Hepatitis-B virus can cause the acute as well as chronic infection. The ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.