here
... is the vaccine • Therefore OPV use will cease in posteradication period • The plan to stop vaccination is based on the assumption that there are no nonhuman reservoirs of poliovirus, and circulation of attenuated strains and their derivatives (VDPV) is limited ...
... is the vaccine • Therefore OPV use will cease in posteradication period • The plan to stop vaccination is based on the assumption that there are no nonhuman reservoirs of poliovirus, and circulation of attenuated strains and their derivatives (VDPV) is limited ...
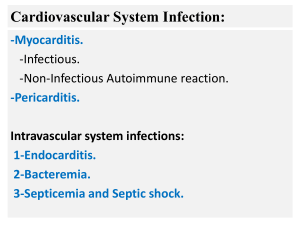
Cardiovascular System Infection
... -Erythroviruses belong to the Parvoviridae family. -Small DNA viruses. -It is a non-enveloped, icosahedral virus that contains a single-stranded linear DNA genome. -It is classified as Erythrovirus because of its capability to invade Red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow. Transmission: -The v ...
... -Erythroviruses belong to the Parvoviridae family. -Small DNA viruses. -It is a non-enveloped, icosahedral virus that contains a single-stranded linear DNA genome. -It is classified as Erythrovirus because of its capability to invade Red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow. Transmission: -The v ...
cellbacteria_virus_s..
... Bacteria are vital to the living world. Some are producers that carry out photosynthesis. Others are decomposers that break down dead matter. Some soil bacteria convert nitrogen gas into a form that plants can use through a process called nitrogen fixation. Humans use bacteria in industry, food prod ...
... Bacteria are vital to the living world. Some are producers that carry out photosynthesis. Others are decomposers that break down dead matter. Some soil bacteria convert nitrogen gas into a form that plants can use through a process called nitrogen fixation. Humans use bacteria in industry, food prod ...
Interaction between hepatitis delta virus
... proteins to HBV envelope proteins may occur in domains other than the 19 carboxy-terminal residues of p27. Whether these interactions have a function in morphogenesis or infectivity of HDV particles remains to be elucidated. Early studies suggested a possible function of the Pro}Gly-rich region (res ...
... proteins to HBV envelope proteins may occur in domains other than the 19 carboxy-terminal residues of p27. Whether these interactions have a function in morphogenesis or infectivity of HDV particles remains to be elucidated. Early studies suggested a possible function of the Pro}Gly-rich region (res ...
Types of Pathogens
... Give examples of diseases caused by living organisms. Why do people in developing countries suffer more than in developed countries? List the four major groups of pathogens. Describe how bacteria play a beneficial role. Describe environmental factors influencing how bacteria grow. Explain how viruse ...
... Give examples of diseases caused by living organisms. Why do people in developing countries suffer more than in developed countries? List the four major groups of pathogens. Describe how bacteria play a beneficial role. Describe environmental factors influencing how bacteria grow. Explain how viruse ...
Hepatitis A - National Health Care for the Homeless Council
... Hepatitis A is a viral infection of the liver that may cause a short-term sickness but generally does not cause prolonged liver disease. Both children and adults are affected. Adults tend to have a more severe course of illness. In fact, many children are infected but never show signs of hepatitis. ...
... Hepatitis A is a viral infection of the liver that may cause a short-term sickness but generally does not cause prolonged liver disease. Both children and adults are affected. Adults tend to have a more severe course of illness. In fact, many children are infected but never show signs of hepatitis. ...
VIRAL INFECTIONS OF REPTILES: A REAL THREATFOR HEALTH
... years, 11 of them died [2]. In 2001 first cases of alligator disease were reported from the state of Florida alligator farms; next year such reports were from farms of Georgia as well as from a Nile crocodile farm in Israel and from Mexico where the disease had been detected among wild crocodiles [2 ...
... years, 11 of them died [2]. In 2001 first cases of alligator disease were reported from the state of Florida alligator farms; next year such reports were from farms of Georgia as well as from a Nile crocodile farm in Israel and from Mexico where the disease had been detected among wild crocodiles [2 ...
Ebola-Virus-Advice - Hardwick Primary School
... Any person arriving in the UK having travelled from any Ebola affected countries will be screened. If they are free of symptoms they are not infectious so there should be no restrictions on their school attendance or normal activities. ...
... Any person arriving in the UK having travelled from any Ebola affected countries will be screened. If they are free of symptoms they are not infectious so there should be no restrictions on their school attendance or normal activities. ...
Media Release
... the bacteria Wolbachia, and found that a section of the genome is made up of eukaryotic-like genes. The genes are closely related to insect and spider genes for toxins, mediating host–microbe interactions, host cell suicide, and transport across cell membranes. Since Wolbachia itself infects insect ...
... the bacteria Wolbachia, and found that a section of the genome is made up of eukaryotic-like genes. The genes are closely related to insect and spider genes for toxins, mediating host–microbe interactions, host cell suicide, and transport across cell membranes. Since Wolbachia itself infects insect ...
fifth disease - District 196
... redness and swelling of the joints. Joint pain and swelling may last 1-3 months. Most people who get fifth disease do not become very ill. However, children with sickle cell anemia, chronic anemia, or a weakened immune system may become seriously ill and require medical care when infected with parvo ...
... redness and swelling of the joints. Joint pain and swelling may last 1-3 months. Most people who get fifth disease do not become very ill. However, children with sickle cell anemia, chronic anemia, or a weakened immune system may become seriously ill and require medical care when infected with parvo ...
This study was carried out to assess the prevalence of HBsAg
... civilian communities throughout the world.2 Initially transmission of disease was attributed to nonparenteral routes, such as person to person contact or exposure to contaminated food or water. This was known as epidemic (infectious) hepatitis.3 However in 1885, in Bremen, Germany significant event ...
... civilian communities throughout the world.2 Initially transmission of disease was attributed to nonparenteral routes, such as person to person contact or exposure to contaminated food or water. This was known as epidemic (infectious) hepatitis.3 However in 1885, in Bremen, Germany significant event ...
bacillary_hb_urea
... either isolating the bacteria from the liver (by culture, fluorescent antibody, or immunohistochemistry), or the toxin from in the liver or abdominal cavity fluid. Proper diagnosis is important as there are other diseases that may present similarly including; anaplasmosis, anthrax, bracken fern pois ...
... either isolating the bacteria from the liver (by culture, fluorescent antibody, or immunohistochemistry), or the toxin from in the liver or abdominal cavity fluid. Proper diagnosis is important as there are other diseases that may present similarly including; anaplasmosis, anthrax, bracken fern pois ...
Introduction and research objectives
... and prevent severe infections. The Fc portion of the IgG molecule contains sites that are recognized by a class of cellular receptors called Fcγ R responsible for cell-mediated recognition of antibody-antigen complexes. These receptors are found primarily on polymorphonuclear cells (PMN’s), monocyte ...
... and prevent severe infections. The Fc portion of the IgG molecule contains sites that are recognized by a class of cellular receptors called Fcγ R responsible for cell-mediated recognition of antibody-antigen complexes. These receptors are found primarily on polymorphonuclear cells (PMN’s), monocyte ...
What is a virus - Virology World
... Viruses and bacteria are completely different in their structure and the way they reproduce and it is actually very important to clearly distinguish between them, not just for scientists studying them, but more importantly because treatments for bacterial and viral infections are quite different. An ...
... Viruses and bacteria are completely different in their structure and the way they reproduce and it is actually very important to clearly distinguish between them, not just for scientists studying them, but more importantly because treatments for bacterial and viral infections are quite different. An ...
Lecture 20
... material (a vaccine) to stimulate the immune system of an individual to develop adaptive immunity to a disease. – artificial induction of immunity, • 'priming' the immune system with an 'immunogen'. • Antibodies and long term memory cells are formed ...
... material (a vaccine) to stimulate the immune system of an individual to develop adaptive immunity to a disease. – artificial induction of immunity, • 'priming' the immune system with an 'immunogen'. • Antibodies and long term memory cells are formed ...
Hepatitis B
... Hepatitis B Diagnosis • Hepatitis B is detected by looking for a number of different antigens and antibodies: – Hepatitis B e antibody (HBeAb or anti-HBe): • Produced by the immune system temporarily during acute HBV infection or consistently during or after a burst in viral replication. • Spontane ...
... Hepatitis B Diagnosis • Hepatitis B is detected by looking for a number of different antigens and antibodies: – Hepatitis B e antibody (HBeAb or anti-HBe): • Produced by the immune system temporarily during acute HBV infection or consistently during or after a burst in viral replication. • Spontane ...
Bloodborne Pathogens - California State University, Long Beach
... – Hepatitis C – a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus. It is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States. • Symptoms are similar to hepatitis B infection, including fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and jaundice. • There is no vaccine for hep ...
... – Hepatitis C – a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus. It is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States. • Symptoms are similar to hepatitis B infection, including fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and jaundice. • There is no vaccine for hep ...
In`s and Out`s of Neutropenia Inpatient and Ambulatory Care
... 13 then have one dose of Pneumovax 23 ...
... 13 then have one dose of Pneumovax 23 ...
Transmission of Little cherry virus
... (Rott and Jelkmann 2005;Jelkmann, Fechtner et al. 1997). The viruses can be found individually and in mixed infections. The disease is distributed worldwide in ornamental and sweet cherry and has a great impact on fruit quality of infected trees. Symptoms of infection consist of small angular and po ...
... (Rott and Jelkmann 2005;Jelkmann, Fechtner et al. 1997). The viruses can be found individually and in mixed infections. The disease is distributed worldwide in ornamental and sweet cherry and has a great impact on fruit quality of infected trees. Symptoms of infection consist of small angular and po ...
Are Viruses Alive?
... Viruses all are infectious particles that consist of a DNA or an RNA molecule packaged in a protein capsid, a protective coat that allows their transfer from one cell to another. Viruses infect host cells and use the host for their reproduction and metabolism. Viruses exist in two distinct states. W ...
... Viruses all are infectious particles that consist of a DNA or an RNA molecule packaged in a protein capsid, a protective coat that allows their transfer from one cell to another. Viruses infect host cells and use the host for their reproduction and metabolism. Viruses exist in two distinct states. W ...
Biological Weapons
... vomiting. Inhalation of the organism may produce a fever alone or combined with a pneumonia like illness. The victims can take antibiotics to cure the disease, and one will develop a degree of immunity against the disease. ...
... vomiting. Inhalation of the organism may produce a fever alone or combined with a pneumonia like illness. The victims can take antibiotics to cure the disease, and one will develop a degree of immunity against the disease. ...
Sexually Transmitted Infections
... Females aged between 20-24 are 3 times more at risk than males. 5 diagnosis were made in MSM. ...
... Females aged between 20-24 are 3 times more at risk than males. 5 diagnosis were made in MSM. ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.