Hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (HEV) infection in piglets
... outbreak in this herd. HEV infection in mixed-parity sow herds is usually self-limiting, with a 2-3 week clinical course, and infection wanes with stimulation of maternal immunity. In this P1 herd, the clinical problem lingered for 12-14 weeks but was eventually controlled using strict feedback prot ...
... outbreak in this herd. HEV infection in mixed-parity sow herds is usually self-limiting, with a 2-3 week clinical course, and infection wanes with stimulation of maternal immunity. In this P1 herd, the clinical problem lingered for 12-14 weeks but was eventually controlled using strict feedback prot ...
Maria De Shazer Pre-optometry Class of 2013 Conjunctivitis
... conjunctivitis is caused by irritants like air pollution, chlorine in swimming pools, and exposure to other harmful chemicals. Pink eye is highly contagious and should be treated early. While considered a minor eye infection, it may develop into a more serious problem. Conjunctivitis can be diagnose ...
... conjunctivitis is caused by irritants like air pollution, chlorine in swimming pools, and exposure to other harmful chemicals. Pink eye is highly contagious and should be treated early. While considered a minor eye infection, it may develop into a more serious problem. Conjunctivitis can be diagnose ...
Ebola Virus Information
... Fahrenheit and additional symptoms such as severe headache, muscle pain, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, or unexplained hemorrhage; and 2) risk factors within the past 3 weeks before the onset of symptoms, such as contact with blood or other body fluids of a patient known to have or suspected to ...
... Fahrenheit and additional symptoms such as severe headache, muscle pain, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, or unexplained hemorrhage; and 2) risk factors within the past 3 weeks before the onset of symptoms, such as contact with blood or other body fluids of a patient known to have or suspected to ...
Management of Patients with HIV & AIDS
... HIV – GP 120 protein – attaches to CD4+ receptors on surface of host T-cell ...
... HIV – GP 120 protein – attaches to CD4+ receptors on surface of host T-cell ...
Slide 1 - UAB School of Optometry
... Slide 14: The virus attaches to the target cell by the interaction of a number of glycoproteins. It interacts with the cell surface proteoglycans and some specific receptors that are members of the nectin family. A lot of the tropism for all the human herpes viruses is mediated by these different re ...
... Slide 14: The virus attaches to the target cell by the interaction of a number of glycoproteins. It interacts with the cell surface proteoglycans and some specific receptors that are members of the nectin family. A lot of the tropism for all the human herpes viruses is mediated by these different re ...
MORBIDITY and MORTALITY CONFERENCE
... Fluconazole (800-mg [12-mg/kg] loading dose, then 400 mg [6 mg/kg] daily), caspofungin (70-mg loading dose, then 50mg daily), anidulafungin (200-mg loading dose, then 100 mg daily), or micafungin (100 mg daily) is recommended as initial therapy (B-III) ...
... Fluconazole (800-mg [12-mg/kg] loading dose, then 400 mg [6 mg/kg] daily), caspofungin (70-mg loading dose, then 50mg daily), anidulafungin (200-mg loading dose, then 100 mg daily), or micafungin (100 mg daily) is recommended as initial therapy (B-III) ...
urinary tract infection - University of Virginia
... PAIN RELIEVERS such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help bladder discomfort. Your physician or nurse practitioner may recommend a urinary pain reliever if you have a lot of pain when you urinate. In addition, urinary analgesics that contain phenazopyridine (brands A20-Gesic, A20-standard, others) ...
... PAIN RELIEVERS such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help bladder discomfort. Your physician or nurse practitioner may recommend a urinary pain reliever if you have a lot of pain when you urinate. In addition, urinary analgesics that contain phenazopyridine (brands A20-Gesic, A20-standard, others) ...
Happy Valley Union ESD Administrative Regulation
... symptoms and are not aware they are infected. No age group, socio‐ economic class, state or city is exempt. Treat all human blood and body fluids as if they were known to be infected with HIV, HBV or other bloodborne pathogens. It takes just one exposure to become infe ...
... symptoms and are not aware they are infected. No age group, socio‐ economic class, state or city is exempt. Treat all human blood and body fluids as if they were known to be infected with HIV, HBV or other bloodborne pathogens. It takes just one exposure to become infe ...
Types of Blood Borne Pathogens
... -Any liquid or semi-liquid blood or other potentially infectious materials. -Contaminated items that would release blood or other potentially infectious materials in a liquid or semi-liquid state if compressed-Items that are caked with dried blood or other potentially infectious materials ...
... -Any liquid or semi-liquid blood or other potentially infectious materials. -Contaminated items that would release blood or other potentially infectious materials in a liquid or semi-liquid state if compressed-Items that are caked with dried blood or other potentially infectious materials ...
Standard Precautions
... Gloves: For touching blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions, contaminated items; for touching mucus membranes and non-intact skin; Gown: During procedures and patient-care activities when contact of clothing/exposed skin with blood/body fluids, secretions, and excretions is anticipated; Mask, Ey ...
... Gloves: For touching blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions, contaminated items; for touching mucus membranes and non-intact skin; Gown: During procedures and patient-care activities when contact of clothing/exposed skin with blood/body fluids, secretions, and excretions is anticipated; Mask, Ey ...
Guidance on management of proven or suspected Staphylococcus
... •Discuss the need for a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) with a cardiologist for all patients with SAB while the patient is receiving IV anti-staphylococcal therapy. •Consider transoesophageal echocardiogram (TOE) in patients at high risk of endocarditis ; persistent bacteraemia > 4 days, permanen ...
... •Discuss the need for a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) with a cardiologist for all patients with SAB while the patient is receiving IV anti-staphylococcal therapy. •Consider transoesophageal echocardiogram (TOE) in patients at high risk of endocarditis ; persistent bacteraemia > 4 days, permanen ...
Mt Kilimanjaro - Travel Doctor
... This material has been prepared for general information purposes only. It is not intended to be relied on as a substitute for professional medical advice. No person should act, fail to act, disregard professional medical advice, or delay in seeking professional medical advice on the basis of this ma ...
... This material has been prepared for general information purposes only. It is not intended to be relied on as a substitute for professional medical advice. No person should act, fail to act, disregard professional medical advice, or delay in seeking professional medical advice on the basis of this ma ...
capsid - Follett Science
... plants and gives their leaves a mosaic coloration In the late 1800s, researchers hypothesized that a particle smaller than bacteria caused the disease ...
... plants and gives their leaves a mosaic coloration In the late 1800s, researchers hypothesized that a particle smaller than bacteria caused the disease ...
elisa - immunology.unideb.hu
... and fully half the population was tuberculin-positive, it was well-known that an intercurrent measles infection would cause a well-contained tuberculosis infection to run rampant and result in death. The mechanism responsible is now known to be the supression of IL-2 synthesis after binding of measl ...
... and fully half the population was tuberculin-positive, it was well-known that an intercurrent measles infection would cause a well-contained tuberculosis infection to run rampant and result in death. The mechanism responsible is now known to be the supression of IL-2 synthesis after binding of measl ...
Quat-Stat - KellySolutions.com
... inactivates Canine Parvovirus (CPV) on hard, non-porous, environmental surfaces in the presence of 5% blood serum with a 10 minute contact time. KILLS HIV-1, HBV AND HCV ON PRE-CLEANED ENVIRONMENTAL SURFACES/OBJECTS PREVIOUSLY SOILED WITH BLOOD/BODY FLUIDS in health care settings (Hospitals, Nursing ...
... inactivates Canine Parvovirus (CPV) on hard, non-porous, environmental surfaces in the presence of 5% blood serum with a 10 minute contact time. KILLS HIV-1, HBV AND HCV ON PRE-CLEANED ENVIRONMENTAL SURFACES/OBJECTS PREVIOUSLY SOILED WITH BLOOD/BODY FLUIDS in health care settings (Hospitals, Nursing ...
Vaccines
... Clearly, here secreted antibodies are important. Although in the case of influenza serum antibodies may be important ...
... Clearly, here secreted antibodies are important. Although in the case of influenza serum antibodies may be important ...
HIV - human immunodeficiency virus
... Protease inhibitors (PIs): Protease inhibitors inhibit the activity of protease, an enzyme used by HIV to cleave nascent proteins for final assembly of new HIV virons, and so prevent viral replication. Fusion Inhibitors: Fusion inhibitors inhibit fusion (entry) of HIV with the cell membrane, prevent ...
... Protease inhibitors (PIs): Protease inhibitors inhibit the activity of protease, an enzyme used by HIV to cleave nascent proteins for final assembly of new HIV virons, and so prevent viral replication. Fusion Inhibitors: Fusion inhibitors inhibit fusion (entry) of HIV with the cell membrane, prevent ...
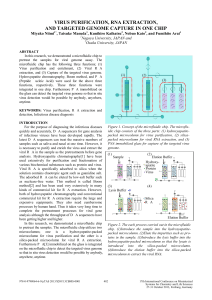
virus purification, rna extraction, and targeted genome capture in
... (Peptide Nucleic Acid) were used for the above three functions, respectively. These three functions were integrated in one chip. Furthermore PNA immobilized on the glass can detect the targeted virus genome so that in situ virus detection would be possible by anybody, anywhere, anytime. ...
... (Peptide Nucleic Acid) were used for the above three functions, respectively. These three functions were integrated in one chip. Furthermore PNA immobilized on the glass can detect the targeted virus genome so that in situ virus detection would be possible by anybody, anywhere, anytime. ...
bloodborne pathogens test
... d. All of the above 17. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is: a. a bacterial illness treated with antibiotics b. a virus which has no cure, but can be controlled with medicine c. the virus that causes AIDS. d. both b and c. 18. HIV is spread from person to person by a. shaking hands b. unprotected ...
... d. All of the above 17. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is: a. a bacterial illness treated with antibiotics b. a virus which has no cure, but can be controlled with medicine c. the virus that causes AIDS. d. both b and c. 18. HIV is spread from person to person by a. shaking hands b. unprotected ...
04.52 Infection Control Plan
... or destroy bloodborne, airborne, or foodborne on a surface or item to the point where they are no longer capable of transmitting infectious particles and the surface or item is rendered safe for handling, use, or disposal. Disinfection – The process used to inactivate virtually all recognized pathog ...
... or destroy bloodborne, airborne, or foodborne on a surface or item to the point where they are no longer capable of transmitting infectious particles and the surface or item is rendered safe for handling, use, or disposal. Disinfection – The process used to inactivate virtually all recognized pathog ...
Infection Control Techniques
... Soiled clothes with patient’s body fluids, secretions, or excretions Possible splashes/sprays of blood, body fluids, secretions, and excretions ...
... Soiled clothes with patient’s body fluids, secretions, or excretions Possible splashes/sprays of blood, body fluids, secretions, and excretions ...
Pathology of Infectious Diseases II
... many bacterial infections, you get antibodies formed naturally as a consequence of the infection. These antibodies help block attachment, penetration, and uncoating. Of course this is the basis for many viral vaccines that we have. The vaccines will block one or more of the steps of the viral replic ...
... many bacterial infections, you get antibodies formed naturally as a consequence of the infection. These antibodies help block attachment, penetration, and uncoating. Of course this is the basis for many viral vaccines that we have. The vaccines will block one or more of the steps of the viral replic ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.