CHAPTER 15 Causes and spread of infection
... The difference between infectious and non-infectious disease is that infectious disease can be spread from person to person. Infection can pass from person to person by cross-contamination (cross-infection, indirect contamination) or by direct contact (direct contamination). Cross-contamination is w ...
... The difference between infectious and non-infectious disease is that infectious disease can be spread from person to person. Infection can pass from person to person by cross-contamination (cross-infection, indirect contamination) or by direct contact (direct contamination). Cross-contamination is w ...
Clinical features
... Porin channels (porA, porB) in the outer membrane play key roles in virulence and they act as invasin that mediates penetration of a host cell Gonococcal strains with porA may have inherent resistance to normal human serum and an increased ability to invade epithelial cells, explaining their associ ...
... Porin channels (porA, porB) in the outer membrane play key roles in virulence and they act as invasin that mediates penetration of a host cell Gonococcal strains with porA may have inherent resistance to normal human serum and an increased ability to invade epithelial cells, explaining their associ ...
Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Mucosal Infection by Highly
... cellular peptides generated by the proteasome from endogenous proteins that are translocated by the transporter associated with Ag processing into the ER for subsequent selection and trimming for MHC class I loading. When released from necrotic cells, gp96 functions as a danger associated molecular ...
... cellular peptides generated by the proteasome from endogenous proteins that are translocated by the transporter associated with Ag processing into the ER for subsequent selection and trimming for MHC class I loading. When released from necrotic cells, gp96 functions as a danger associated molecular ...
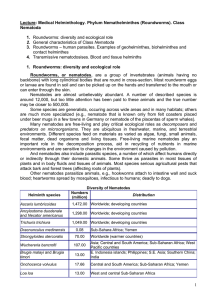
Lecture 13: “Roundworms (Nemathelminthes)
... Life cycle: Infection occurs by ingestion of larvae in poorly cooked meat, which immediately invade intestinal mucosa and sexually differentiate within 18 to 24 hours. The female, after fertilization, burrows deeply in the small intestinal mucosa, whereas the male is dislodged (intestinal stage). O ...
... Life cycle: Infection occurs by ingestion of larvae in poorly cooked meat, which immediately invade intestinal mucosa and sexually differentiate within 18 to 24 hours. The female, after fertilization, burrows deeply in the small intestinal mucosa, whereas the male is dislodged (intestinal stage). O ...
Parvovirus B19 And Pregnancy
... • Single-stranded DNA virus (Parvoviridae family, erythrovirus genus) ...
... • Single-stranded DNA virus (Parvoviridae family, erythrovirus genus) ...
Classification:
... response to the invading larvae. Various pathologies associated with filarial infection arise from immune reactions to their presence. The most pronounced of these is the damage to the lymphatic vessels, which is mediated by the immune system's response to the adult worms living in them. These immun ...
... response to the invading larvae. Various pathologies associated with filarial infection arise from immune reactions to their presence. The most pronounced of these is the damage to the lymphatic vessels, which is mediated by the immune system's response to the adult worms living in them. These immun ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-ISSN: 2278-3008, p-ISSN:2319-7676.
... also by other issues such as the activity of several drugs against the virus and development of drug-resistant HIV variants. The course of acute HIV may be modified in the presence of HBV infection, with a lower incidence of icteric illness and lower rates of spontaneous clearance of HBV. Persons wi ...
... also by other issues such as the activity of several drugs against the virus and development of drug-resistant HIV variants. The course of acute HIV may be modified in the presence of HBV infection, with a lower incidence of icteric illness and lower rates of spontaneous clearance of HBV. Persons wi ...
Mucosal Vaccines: Prevention of Caries and Periodontal Diseases
... What are the virulence factors? What is the “at risk” population? Are there easier alternatives? Who do you immunize? Most are not life-threatening ...
... What are the virulence factors? What is the “at risk” population? Are there easier alternatives? Who do you immunize? Most are not life-threatening ...
Risk of widespread outbreak of Rift Valley fever linked to
... can become infected by vector exposure or through contact with infected animals, infected fluids, or the consumption of raw milk from infected animals (LaBeaud et al., 2015). Madagascar contains a significant population of farmers, abattoir workers, butchers, and animal handlers, all of whom are at ...
... can become infected by vector exposure or through contact with infected animals, infected fluids, or the consumption of raw milk from infected animals (LaBeaud et al., 2015). Madagascar contains a significant population of farmers, abattoir workers, butchers, and animal handlers, all of whom are at ...
1 section 3: bloodborne pathogens lecture
... o Liver infection o Cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver o Liver cancer o Liver failure o Death • 30-50% of infected children become chronic carriers. • As many as 1.4 million Americans have chronic HBV. • More easily transmitted than HIV or HCV. • Vaccine preventable HCV • Can cause acute or ...
... o Liver infection o Cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver o Liver cancer o Liver failure o Death • 30-50% of infected children become chronic carriers. • As many as 1.4 million Americans have chronic HBV. • More easily transmitted than HIV or HCV. • Vaccine preventable HCV • Can cause acute or ...
Multiplication of the V4 strain of A.
... It has been demonstrated that DD facilitates the uptake of complete virions by cells in culture (Kaplan Wiktor, Maes, Campbell & Koprowski 1967; Barahona & Hanson 1968). However, the use of DD alone as one additional ingredient to the medium in this study did not induce a significant increase of mul ...
... It has been demonstrated that DD facilitates the uptake of complete virions by cells in culture (Kaplan Wiktor, Maes, Campbell & Koprowski 1967; Barahona & Hanson 1968). However, the use of DD alone as one additional ingredient to the medium in this study did not induce a significant increase of mul ...
Rift Valley fever
... can become infected by vector exposure or through contact with infected animals, infected fluids, or the consumption of raw milk from infected animals (LaBeaud et al., 2015). Madagascar contains a significant population of farmers, abattoir workers, butchers, and animal handlers, all of whom are at ...
... can become infected by vector exposure or through contact with infected animals, infected fluids, or the consumption of raw milk from infected animals (LaBeaud et al., 2015). Madagascar contains a significant population of farmers, abattoir workers, butchers, and animal handlers, all of whom are at ...
Student Activity DOC - TI Education
... trials. In the screen at the right, there were 10 trials, so 10 was entered for Xmax. If your simulation took more than 10 trials, enter that number for Xmax. The Ymax value is the maximum number of students in the class. In this case the setting is bigger so we will be able to see the graph of all ...
... trials. In the screen at the right, there were 10 trials, so 10 was entered for Xmax. If your simulation took more than 10 trials, enter that number for Xmax. The Ymax value is the maximum number of students in the class. In this case the setting is bigger so we will be able to see the graph of all ...
Virus PowerPoint
... be transported through the endosome (i.e. envelope fusion is not necessary). Endosome? a membrane bound compartment inside eukaryotic cells. It is a compartment of the endocytic membrane transport pathway from the plasma membrane to the lysosome. ...
... be transported through the endosome (i.e. envelope fusion is not necessary). Endosome? a membrane bound compartment inside eukaryotic cells. It is a compartment of the endocytic membrane transport pathway from the plasma membrane to the lysosome. ...
Production of Safe and Uniform Infectious Bronchitis Vaccines
... science technologies Click here for a listing of Auburn’s available life science technologies Follow Auburn IAC ...
... science technologies Click here for a listing of Auburn’s available life science technologies Follow Auburn IAC ...
BSL 2 - UniMAP Portal
... - a permit is required to import etiologic agents of human disease and any materials, including live animals or insects, that may contain them. - Unsterilized specimens of human and animal tissues (such as blood, body discharges, fluids, excretions or similar material) containing an infectious or et ...
... - a permit is required to import etiologic agents of human disease and any materials, including live animals or insects, that may contain them. - Unsterilized specimens of human and animal tissues (such as blood, body discharges, fluids, excretions or similar material) containing an infectious or et ...
some key messages from the `fever` ita session
... Fever is defined as an oral temperature greater than 38º C, although some authorities do not consider a fever significant until the temperature exceeds 38.5º C ...
... Fever is defined as an oral temperature greater than 38º C, although some authorities do not consider a fever significant until the temperature exceeds 38.5º C ...
Effect of nitrogen fixation, nitrogen fertilization and viral infection on
... in a column are significantly different at p~<0.05 as assessed by Duncan's multiple range test. ...
... in a column are significantly different at p~<0.05 as assessed by Duncan's multiple range test. ...
HIV is the world`s leading infectious killer
... Structure of HIV virus • spherical enveloped virus, 90-120 nm in size • nucleocapsid has outer iscosaheral shell & inner cone shaped core, enclosing ribonucleoproteins. • genome – diploid, two identical single stranded, positive sense RNA copies. • reverse transcriptase enzyme ...
... Structure of HIV virus • spherical enveloped virus, 90-120 nm in size • nucleocapsid has outer iscosaheral shell & inner cone shaped core, enclosing ribonucleoproteins. • genome – diploid, two identical single stranded, positive sense RNA copies. • reverse transcriptase enzyme ...
Natural History of Compensated Cirrhosis in Patients with
... • Patient informs you that she and her husband would like to start a family within the year ...
... • Patient informs you that she and her husband would like to start a family within the year ...
Antigens Produced by Recombinant DNA
... detected with an anti-human IgG conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.7). A strong color reaction from a substrate cleaved by horseradish peroxidase indicates the presence of anti-H1V antibodies in the patient’s serum. The HIV diagnostic assay EnvaCor (Abbott Labs.) is configured with huma ...
... detected with an anti-human IgG conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.7). A strong color reaction from a substrate cleaved by horseradish peroxidase indicates the presence of anti-H1V antibodies in the patient’s serum. The HIV diagnostic assay EnvaCor (Abbott Labs.) is configured with huma ...
Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD) Gumboro disease
... after vaccination for chickens to develop minimal protective titers. During this "lag time," chickens are susceptible to IBD. • In addition, virulent IBD viruses are able to break through higher maternal titers than milder vaccine viruses. • Thus, if IBD field virus contamination on a broiler farm i ...
... after vaccination for chickens to develop minimal protective titers. During this "lag time," chickens are susceptible to IBD. • In addition, virulent IBD viruses are able to break through higher maternal titers than milder vaccine viruses. • Thus, if IBD field virus contamination on a broiler farm i ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.