Populations and Infectious Diseases: Ecology or Epidemiology?
... 'shifts' (e.g. from HI to H2, and from N1 to N2; infection by one strain confers little immunity to infection by another strain) and more frequent minor 'drifts'. Major 'shifts' facilitate virus persistence in a population with a high degree of herd immunity to earlier antigenic variants, and are of ...
... 'shifts' (e.g. from HI to H2, and from N1 to N2; infection by one strain confers little immunity to infection by another strain) and more frequent minor 'drifts'. Major 'shifts' facilitate virus persistence in a population with a high degree of herd immunity to earlier antigenic variants, and are of ...
HERPES ZOSTER Infection Control Guidelines for Long-Term Care Facilities
... varicella vaccine. Gloves and gowns should be worn at all times. Susceptible staff or visitors should not enter patient room. If unavoidable, masks should be worn. Persons immune to varicella need not wear masks. 2. Identify all exposed individuals. • “Exposure” to uncomplicated shingles is defi ...
... varicella vaccine. Gloves and gowns should be worn at all times. Susceptible staff or visitors should not enter patient room. If unavoidable, masks should be worn. Persons immune to varicella need not wear masks. 2. Identify all exposed individuals. • “Exposure” to uncomplicated shingles is defi ...
Upper respiratory tract infections
... with underlying chronic diseases or different compromises. The term opportunist indicates well this category of pathogen. Opportunistic pathogens a vary emergency in hospital are considered, they are vehicolated by paramedical staff or assistance staff ...
... with underlying chronic diseases or different compromises. The term opportunist indicates well this category of pathogen. Opportunistic pathogens a vary emergency in hospital are considered, they are vehicolated by paramedical staff or assistance staff ...
R 0 - The Chinese University of Hong Kong
... course”, in other words, to die down by itself, up to several million people will fall victim to SARS. Sufficient herd immunity that will protect the community from further epidemics will only be achieved at the expense of this magnitude of community infection; 2. An epidemic will die down only when ...
... course”, in other words, to die down by itself, up to several million people will fall victim to SARS. Sufficient herd immunity that will protect the community from further epidemics will only be achieved at the expense of this magnitude of community infection; 2. An epidemic will die down only when ...
List of emerging and re-emerging diseases
... Ebola is one of the emerging threats for the scientific community due to its high mortality rates and emerging of new stains for instance in Uganda. It has claimed many lives especially in regions around the tropical rainforest such as Congo, DR Congo, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Uganda, Nigeria, and Gam ...
... Ebola is one of the emerging threats for the scientific community due to its high mortality rates and emerging of new stains for instance in Uganda. It has claimed many lives especially in regions around the tropical rainforest such as Congo, DR Congo, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Uganda, Nigeria, and Gam ...
تحميل المحاضرة
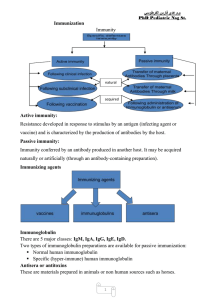
... Resistance developed in response to stimulus by an antigen (infecting agent or vaccine) and is characterized by the production of antibodies by the host. Passive immunity: Immunity conferred by an antibody produced in another host. It may be acquired naturally or artificially (through an antibody-co ...
... Resistance developed in response to stimulus by an antigen (infecting agent or vaccine) and is characterized by the production of antibodies by the host. Passive immunity: Immunity conferred by an antibody produced in another host. It may be acquired naturally or artificially (through an antibody-co ...
Infection Prevention and Control Guidelines - Speech
... environmental cleaning or practices where intermediary contaminated objects are used are generally the culprit of such transmission. Some organisms are capable of surviving on a surface for an extended period of time. Any touch surface that cannot be easily cleaned and disinfected should be discarde ...
... environmental cleaning or practices where intermediary contaminated objects are used are generally the culprit of such transmission. Some organisms are capable of surviving on a surface for an extended period of time. Any touch surface that cannot be easily cleaned and disinfected should be discarde ...
H1N1 Vaccine - McMaster University`s Faculty of Health Sciences
... Avoid contact with sick people. Wash your hands. Stay home if you are sick. Social distancing. ...
... Avoid contact with sick people. Wash your hands. Stay home if you are sick. Social distancing. ...
The Guillain–Barre´ syndrome: a true case of molecular - Direct-MS
... The discussion as to whether molecular mimicry is a mechanism for the induction of autoimmune disease is hampered by loose definitions of molecular mimicry and the inconsistent use of previously defined criteria for a disease to be deemed due to this mechanism. The term molecular mimicry is both use ...
... The discussion as to whether molecular mimicry is a mechanism for the induction of autoimmune disease is hampered by loose definitions of molecular mimicry and the inconsistent use of previously defined criteria for a disease to be deemed due to this mechanism. The term molecular mimicry is both use ...
cryptosporidiosis-in-young-calves
... with cryptosporidiosis at an early stage. In young live calves, it is not possible to distinguish cryptosporidiosis from the other causes of scour like rotavirus, coronavirus, Escherichia coli and Salmonella on clinical signs alone as these are non-specific tests to be carried out either by a veteri ...
... with cryptosporidiosis at an early stage. In young live calves, it is not possible to distinguish cryptosporidiosis from the other causes of scour like rotavirus, coronavirus, Escherichia coli and Salmonella on clinical signs alone as these are non-specific tests to be carried out either by a veteri ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... Molluscum Contagiosum is a common viral disease1 caused by Pox Virus (DNA Virus). The virus forms part of the normal flora in the immunocompetent people. It presents as disease in immunocompromised adults. In HIV infected patients, Molluscum Contagiosum manifests itself most commonly when the immune ...
... Molluscum Contagiosum is a common viral disease1 caused by Pox Virus (DNA Virus). The virus forms part of the normal flora in the immunocompetent people. It presents as disease in immunocompromised adults. In HIV infected patients, Molluscum Contagiosum manifests itself most commonly when the immune ...
Progresses on Studies of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1
... the viral load was much higher in HPAIV H5N1 infection, and virus clearance was delayed [50]. Pathological studies showed that HPAIV H5N1 infected both type-I and -II pneumocytes in alveolar of patients, still can infect alveolar macrophages and Dendritic Cells (DC) and other innate immune cells [46 ...
... the viral load was much higher in HPAIV H5N1 infection, and virus clearance was delayed [50]. Pathological studies showed that HPAIV H5N1 infected both type-I and -II pneumocytes in alveolar of patients, still can infect alveolar macrophages and Dendritic Cells (DC) and other innate immune cells [46 ...
PDF
... mediate lysis of these cells (Guo et al., 2011; van de Sandt et al., 2012). DCs as professional antigen presenting cells are characterized as a critical mediator between the innate and the adaptive immune system. The adaptive immune response is initiated when DCs present viral antigens to the naïve ...
... mediate lysis of these cells (Guo et al., 2011; van de Sandt et al., 2012). DCs as professional antigen presenting cells are characterized as a critical mediator between the innate and the adaptive immune system. The adaptive immune response is initiated when DCs present viral antigens to the naïve ...
Immune control of mammalian gamma- herpesviruses: lessons from
... that of I-Ab2/2 and IFN-cR2/2 mice reflects chronic lytic replication. Db2M2/2 mice also have no CD1-restricted NKT cells, reduced serum IgG concentrations and altered NK cell repertoires. dDespite an acute latency amplification deficit, chronic lytic replication is increased. §Normal B cell latency ...
... that of I-Ab2/2 and IFN-cR2/2 mice reflects chronic lytic replication. Db2M2/2 mice also have no CD1-restricted NKT cells, reduced serum IgG concentrations and altered NK cell repertoires. dDespite an acute latency amplification deficit, chronic lytic replication is increased. §Normal B cell latency ...
2.2.4 Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis
... the virus can only be isolated from tissues from the brain and is associated with abnormal fish behavior and tetany in a small proportion of the affected animals. This is referred to as “neurotropic” IHN. A third form of IHN occurs in much larger fish (~50 – 100 g) and the virus can generally be iso ...
... the virus can only be isolated from tissues from the brain and is associated with abnormal fish behavior and tetany in a small proportion of the affected animals. This is referred to as “neurotropic” IHN. A third form of IHN occurs in much larger fish (~50 – 100 g) and the virus can generally be iso ...
How Infections/Diseases Spread
... in children may also be symptoms without associated with some respiratory gastrointestinal symptoms (cough & symptoms such as fever) is unrelated nausea, vomiting and and not caused by diarrhea. Symptoms the influenza virus. typically last 5-7 days, cough may persist for up to 2 weeks. ...
... in children may also be symptoms without associated with some respiratory gastrointestinal symptoms (cough & symptoms such as fever) is unrelated nausea, vomiting and and not caused by diarrhea. Symptoms the influenza virus. typically last 5-7 days, cough may persist for up to 2 weeks. ...
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
... Staph is a common bacteria that lives in our body. In fact, 25-30% of people already have the bacteria in their noses. Staph can become a problem if it manages to get into the body. This can happen through a cut or big wounds. Staph first appeared in Hospitals and eventually found its way to locker ...
... Staph is a common bacteria that lives in our body. In fact, 25-30% of people already have the bacteria in their noses. Staph can become a problem if it manages to get into the body. This can happen through a cut or big wounds. Staph first appeared in Hospitals and eventually found its way to locker ...
Modelling the spread of infectious salmon anaemia among salmon
... from different infected farms. Hence, both physical distances between farms and phylogenetic relationships between ISAV isolates play prominent roles in the model. Including genetic distance between ISAV isolates in the model introduces a source of information that is independent of physical distanc ...
... from different infected farms. Hence, both physical distances between farms and phylogenetic relationships between ISAV isolates play prominent roles in the model. Including genetic distance between ISAV isolates in the model introduces a source of information that is independent of physical distanc ...
Foot and Mouth Disease Fact Sheet, March 2002
... documented. All of these persons had direct contact with infected animals. The cases experienced a mild illness with headache, fever and possibly blisters appearing on the hands or feet, or in the mouth. The virus is not spread person-to-person or via food to humans. Is it safe to eat meat or meat p ...
... documented. All of these persons had direct contact with infected animals. The cases experienced a mild illness with headache, fever and possibly blisters appearing on the hands or feet, or in the mouth. The virus is not spread person-to-person or via food to humans. Is it safe to eat meat or meat p ...
Chytrid fungus in southwestern toad populations
... and others 2005). In Canada, there has only been 1 report of Bd infection in a single Western Toad from northeastern British Columbia (Raverty and Reynolds 2001). We tested a population of breeding Western Toads from a protected area (provincial park) in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, for th ...
... and others 2005). In Canada, there has only been 1 report of Bd infection in a single Western Toad from northeastern British Columbia (Raverty and Reynolds 2001). We tested a population of breeding Western Toads from a protected area (provincial park) in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, for th ...
Assessing the risk of blood donations in metropolitan France being
... For the maximum estimate scenario (MAX), as a starting point for the estimation we used the proportion of donations which were positive for Zika RNA in blood donors screened in Martinique using individual-donation Nucleic Acid Testing (RealStar® the Zika virus RT-PCR 1.1 kit (Altona Diagnostics)) wi ...
... For the maximum estimate scenario (MAX), as a starting point for the estimation we used the proportion of donations which were positive for Zika RNA in blood donors screened in Martinique using individual-donation Nucleic Acid Testing (RealStar® the Zika virus RT-PCR 1.1 kit (Altona Diagnostics)) wi ...
Guidelines for Schools and Child Care Facilities on Communicable
... Report all outbreaks immediately to the Outbreak Reporting Line at 613-580-6744, ext 26325, Monday to Friday 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. or 3-1-1 after hours. ...
... Report all outbreaks immediately to the Outbreak Reporting Line at 613-580-6744, ext 26325, Monday to Friday 8:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. or 3-1-1 after hours. ...
EVALUATION OF VARIOUS TECHNIQUES USED FOR DIAGNOSIS
... 1982). Infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) is an economically important pathogen of chickens with world wide distribution. The clinical disease often occurs between 3 to 6 weeks of age. Severe outbreaks are characterized by sudden onset of depression in susceptible flocks. IBDV is hard nonenvelop ...
... 1982). Infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) is an economically important pathogen of chickens with world wide distribution. The clinical disease often occurs between 3 to 6 weeks of age. Severe outbreaks are characterized by sudden onset of depression in susceptible flocks. IBDV is hard nonenvelop ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.