on Immune Function
... decline in immunity that can lead to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV-1 is spread person-to-person by three major routes: sexual contact, motherto-child transmission, and through transmission by blood products such as shared needles and syringes. ...
... decline in immunity that can lead to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV-1 is spread person-to-person by three major routes: sexual contact, motherto-child transmission, and through transmission by blood products such as shared needles and syringes. ...
Comparison of cDNAs encoding the gibbon ape leukaemia virus
... The gibbon ape leukaemia virus (GaLV) family of type C retroviruses consists of five closely related viral isolates, GaLV SF, GaLV SEATO, GaLV Br, GaLV H and simian sarcoma-associated virus. The eDNA encoding the human receptor for GaLV SEATO had previously been isolated. We now demonstrate that all ...
... The gibbon ape leukaemia virus (GaLV) family of type C retroviruses consists of five closely related viral isolates, GaLV SF, GaLV SEATO, GaLV Br, GaLV H and simian sarcoma-associated virus. The eDNA encoding the human receptor for GaLV SEATO had previously been isolated. We now demonstrate that all ...
MUMPS IgM ELISA - Atlas Link, Inc
... This device is not intended for the determination of immune status. It is intended for the determination of a person's immune response to indicate primary infection, reinfection or virus reactivation. ...
... This device is not intended for the determination of immune status. It is intended for the determination of a person's immune response to indicate primary infection, reinfection or virus reactivation. ...
Lecture 09
... – Does not pose danger of real infection – Immuno-compromised individuals can get infection from carrier ...
... – Does not pose danger of real infection – Immuno-compromised individuals can get infection from carrier ...
1.Communicable Disease Epidemiology(Definitions). - Home
... articles of the person or on any inanimate object in the environment including water and food. ...
... articles of the person or on any inanimate object in the environment including water and food. ...
Interactions between respiratory tract infections and atopy in the
... revisited. Eur Respir J 2001; 18: 571–588. No. 2: Lambrecht BN, Prins J-B, Hoogsteden HC. Lung dendritic cells and host immunity to infection. Eur Respir J 2001; 18: 692–704. No. 3: Moore BB, Moore TA, Toews GB. Role of T- and B-lymphocytes in pulmonary host defences. Eur Respir J 2001; 18: 846–856. ...
... revisited. Eur Respir J 2001; 18: 571–588. No. 2: Lambrecht BN, Prins J-B, Hoogsteden HC. Lung dendritic cells and host immunity to infection. Eur Respir J 2001; 18: 692–704. No. 3: Moore BB, Moore TA, Toews GB. Role of T- and B-lymphocytes in pulmonary host defences. Eur Respir J 2001; 18: 846–856. ...
Ebolavirus and Marburgvirus Infections
... species. Once a virus has entered human populations, it can spread from person to person. Some epidemics have affected hundreds of people, particularly when nosocomial spread occurs from inadequate medical supplies or barrier nursing procedures, or when outbreaks are not recognized for long periods. ...
... species. Once a virus has entered human populations, it can spread from person to person. Some epidemics have affected hundreds of people, particularly when nosocomial spread occurs from inadequate medical supplies or barrier nursing procedures, or when outbreaks are not recognized for long periods. ...
Infection Control Principles to Risk Determination Table
... A surgical mask should be worn if the dental provider/examiner has symptoms of a respiratory infection (e.g., coughing, sneezing). If spray or spatter is expected, surgical masks can protect the wearer and persons in close proximity (within 6 feet) from mucous membrane exposure to droplets of potent ...
... A surgical mask should be worn if the dental provider/examiner has symptoms of a respiratory infection (e.g., coughing, sneezing). If spray or spatter is expected, surgical masks can protect the wearer and persons in close proximity (within 6 feet) from mucous membrane exposure to droplets of potent ...
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
... IBR is a highly contagious and infectious viral disease that affects cattle of all ages. Infection occurs by inhalation and requires contact between animals spreading quickly through the group. The disease is characterised by severe inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. Bovine herpes virus ...
... IBR is a highly contagious and infectious viral disease that affects cattle of all ages. Infection occurs by inhalation and requires contact between animals spreading quickly through the group. The disease is characterised by severe inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. Bovine herpes virus ...
Communicable Disease Chart - Hamilton
... into the air when a person onset of rash until 4 days sneezes, coughs etc. (Highly after onset of rash. contagious as the virus hangs in the air for 2 hours after the infected person leaves the room). Contact: Direct contact with respiratory secretions of an infected person. Indirectly (less common) ...
... into the air when a person onset of rash until 4 days sneezes, coughs etc. (Highly after onset of rash. contagious as the virus hangs in the air for 2 hours after the infected person leaves the room). Contact: Direct contact with respiratory secretions of an infected person. Indirectly (less common) ...
Preliminary Estimation of Risk Factors That Associated With
... Tuberculosis or tubercles bacillus is a common and often deadly infectious disease which is caused by various strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in humans. This bacterium usually attacks lungs, heart and other parts of the body. TB is spread through the air from one person to another (spread thro ...
... Tuberculosis or tubercles bacillus is a common and often deadly infectious disease which is caused by various strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in humans. This bacterium usually attacks lungs, heart and other parts of the body. TB is spread through the air from one person to another (spread thro ...
Foot-and-mouth disease virus epitope dominance in the antibody
... and North America. The causative agent of FMD is Footand-mouth disease virus (FMDV), the prototype member of the genus Aphthovirus in the family Picornaviridae. There are seven distinct serotypes of FMDV (O, A, C, Asia-1, SAT-1, SAT-2 and SAT-3) and multiple strains, indicating significant antigenic ...
... and North America. The causative agent of FMD is Footand-mouth disease virus (FMDV), the prototype member of the genus Aphthovirus in the family Picornaviridae. There are seven distinct serotypes of FMDV (O, A, C, Asia-1, SAT-1, SAT-2 and SAT-3) and multiple strains, indicating significant antigenic ...
13.Microbiology-MBBS
... between/mechanism of action/comment on 4x3=12 Q 4. Three short answer type questions 2x3=6 Answer to each question should be given by the candidates in a separate answer book. Only one examiner will examine all the answer scripts to the same question in that ...
... between/mechanism of action/comment on 4x3=12 Q 4. Three short answer type questions 2x3=6 Answer to each question should be given by the candidates in a separate answer book. Only one examiner will examine all the answer scripts to the same question in that ...
Blackpool Council Infection Control Policy
... • Eye protector spectacles, and disposable face mask or a full face visor may be worn if there is a risk of splashing of blood to the mouth and eyes • On rare occasions (unlikely in the council setting) it may be necessary to have a face mask that is specific to prevent the spread of airborne infect ...
... • Eye protector spectacles, and disposable face mask or a full face visor may be worn if there is a risk of splashing of blood to the mouth and eyes • On rare occasions (unlikely in the council setting) it may be necessary to have a face mask that is specific to prevent the spread of airborne infect ...
Chickenpox - Spokane Regional Health District
... Complications of chickenpox are rare but can occur. Bacterial infections, as well as pneumonia, can occur in infants, adults, pregnant women, and immune compromised persons. Diarrhea and dehydration are also a risk. Consult with a healthcare provider about medicines for controlling fever and if furt ...
... Complications of chickenpox are rare but can occur. Bacterial infections, as well as pneumonia, can occur in infants, adults, pregnant women, and immune compromised persons. Diarrhea and dehydration are also a risk. Consult with a healthcare provider about medicines for controlling fever and if furt ...
Question set no: Page no: 31 31 1. What is protozoa? How it differs
... 4. “ Schistosomia japonicum and Schistosomia mansoni resides in tributaries of portal vein but is diagnosed by detection of ova in stool ” – explain. ...
... 4. “ Schistosomia japonicum and Schistosomia mansoni resides in tributaries of portal vein but is diagnosed by detection of ova in stool ” – explain. ...
Reoviruses - KSU Faculty Member websites
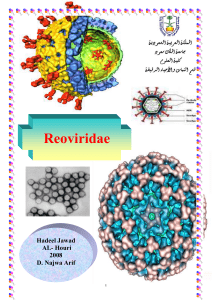
... in diameter. When the outer layer is absent, they measure about 55 nm. Within the inner capsid is the 37-nm core, which contains the RNA genome. The term rotavirus is derived from the Latin word "rota," meaning wheel, and was suggested because the sharply defined circular outline of the outer capsid ...
... in diameter. When the outer layer is absent, they measure about 55 nm. Within the inner capsid is the 37-nm core, which contains the RNA genome. The term rotavirus is derived from the Latin word "rota," meaning wheel, and was suggested because the sharply defined circular outline of the outer capsid ...
Document
... restriction factor of HIV-1. It has been shown that A3G blocks HIV-1 replication or transmission when its expression is up-regulated. Streptococcus Cristatus CC5A is a non-pathogenic oral bacterial. We found that a small molecule of Streptococcus cristatus CC5A (S. cristatus CC5A) was able to upregu ...
... restriction factor of HIV-1. It has been shown that A3G blocks HIV-1 replication or transmission when its expression is up-regulated. Streptococcus Cristatus CC5A is a non-pathogenic oral bacterial. We found that a small molecule of Streptococcus cristatus CC5A (S. cristatus CC5A) was able to upregu ...
Reoviruses - KSU Faculty Member websites
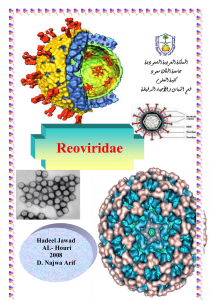
... in diameter. When the outer layer is absent, they measure about 55 nm. Within the inner capsid is the 37-nm core, which contains the RNA genome. The term rotavirus is derived from the Latin word "rota," meaning wheel, and was suggested because the sharply defined circular outline of the outer capsid ...
... in diameter. When the outer layer is absent, they measure about 55 nm. Within the inner capsid is the 37-nm core, which contains the RNA genome. The term rotavirus is derived from the Latin word "rota," meaning wheel, and was suggested because the sharply defined circular outline of the outer capsid ...
Underlying Systemic Conditions for Anterior Uveitis
... antibodies directed against a person's own proteins – Cell nuclei most commonly attacked • these are most commonly anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA), which are found in nearly all cases of Lupus. ...
... antibodies directed against a person's own proteins – Cell nuclei most commonly attacked • these are most commonly anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA), which are found in nearly all cases of Lupus. ...
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
... The tumours were all of infective origin, namely bacterial, parasitic, fungal and viral aetiology. The two bacterial tumours were each a tuberculous and rhinoscleroma granulomas. Thirty tumours were caused by parasites (onchocerciasis and leishmaniasis) while fifteen were of fungal aetiology, namely ...
... The tumours were all of infective origin, namely bacterial, parasitic, fungal and viral aetiology. The two bacterial tumours were each a tuberculous and rhinoscleroma granulomas. Thirty tumours were caused by parasites (onchocerciasis and leishmaniasis) while fifteen were of fungal aetiology, namely ...
An Introduction to Biosafety
... than Hazard Group 2 - unless evidence that they are not pathogenic • if there is any uncertainty then the higher of the two possible ...
... than Hazard Group 2 - unless evidence that they are not pathogenic • if there is any uncertainty then the higher of the two possible ...
Infectious Diseases and Human Population History
... that were typical of human social structure for most of humankind's ...
... that were typical of human social structure for most of humankind's ...
Bubonic Plague
... originated in ancient Egypt, not in Asia as originally thought. The disease, termed "Black Death" also may have begun in North Africa. In a new study reported in the Journal of Biogeography, Eva Panagiotakopulu, an archaeologist and fossil-insect expert at the University of Sheffield reports that ar ...
... originated in ancient Egypt, not in Asia as originally thought. The disease, termed "Black Death" also may have begun in North Africa. In a new study reported in the Journal of Biogeography, Eva Panagiotakopulu, an archaeologist and fossil-insect expert at the University of Sheffield reports that ar ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.