Pyrexia of Unknown Origin
... A distinctive evanescent macular or M. popular rash is typically present during the course of the illness. Age ...
... A distinctive evanescent macular or M. popular rash is typically present during the course of the illness. Age ...
HIV and Aging in Canada: Physiological effects and
... and premature frailty.7 Menopause may occur at an earlier age and cause more symptoms in women living with HIV.8 HIV-positive individuals are likely to have more illnesses than HIV-negative individuals, regardless of age.9 HIVpositive individuals are also more likely to multimorbidity, defined in on ...
... and premature frailty.7 Menopause may occur at an earlier age and cause more symptoms in women living with HIV.8 HIV-positive individuals are likely to have more illnesses than HIV-negative individuals, regardless of age.9 HIVpositive individuals are also more likely to multimorbidity, defined in on ...
Nipah virus conforms to the rule of six in a minigenome replication
... genomes whose lengths are multiples of six (Hausmann et al., 1996). Genomes whose lengths deviate from ‘the rule of six’ do not replicate efficiently (Calain & Roux, 1993) and it has been proposed that the templates for transcription and replication are nucleocapsids in which each nucleoprotein subu ...
... genomes whose lengths are multiples of six (Hausmann et al., 1996). Genomes whose lengths deviate from ‘the rule of six’ do not replicate efficiently (Calain & Roux, 1993) and it has been proposed that the templates for transcription and replication are nucleocapsids in which each nucleoprotein subu ...
Institute for Microbiology, Medical Faculty of Masaryk
... CSF for the direct virus detection (PCR, tissue culture) blood for the antibody detection (IgM, 4fold titre rise): in susp. infections with TBEV, HSV 1 and 2, VZV, CMV, mumps virus Borreliosis and neurosyphilis: blood for the antibody detection Brain abscess (both acute and chronic): punctate or exc ...
... CSF for the direct virus detection (PCR, tissue culture) blood for the antibody detection (IgM, 4fold titre rise): in susp. infections with TBEV, HSV 1 and 2, VZV, CMV, mumps virus Borreliosis and neurosyphilis: blood for the antibody detection Brain abscess (both acute and chronic): punctate or exc ...
Chapter 3. Prevalence of Communicable Disease, Chronic Disease, and Mental Illness
... An estimated 35 percent (12,200) of all those in the Nation who had TB disease during 1996 served time in a correctional facility during that year. This estimate was calculated by applying a point prevalence rate for inmates (i.e., the percentage of inmates who were treated for TB disease on a given ...
... An estimated 35 percent (12,200) of all those in the Nation who had TB disease during 1996 served time in a correctional facility during that year. This estimate was calculated by applying a point prevalence rate for inmates (i.e., the percentage of inmates who were treated for TB disease on a given ...
Evolution of SIV toward RANTES resistance in - HHV
... immunosuppression in a manner similar to other human herpes viruses. Primary HHV-6 infection in adults is very rare and it is not clear whether disease manifestations are similar to those observed in children.We report the case of acute hepatitis in a 18-year-old immunocompetent woman presenting wit ...
... immunosuppression in a manner similar to other human herpes viruses. Primary HHV-6 infection in adults is very rare and it is not clear whether disease manifestations are similar to those observed in children.We report the case of acute hepatitis in a 18-year-old immunocompetent woman presenting wit ...
Age-dependency in host-vector models
... Japanese encephalitis [26], Chagas disease [5, 16, 35], West Nile virus [2, 4, 32] and Chikungunya disease [8, 25]. In some cases, partial differential equations or integro-differential equations are employed in the so-called age-dependent or agestructured models [1, 16, 27, 28], where there is an a ...
... Japanese encephalitis [26], Chagas disease [5, 16, 35], West Nile virus [2, 4, 32] and Chikungunya disease [8, 25]. In some cases, partial differential equations or integro-differential equations are employed in the so-called age-dependent or agestructured models [1, 16, 27, 28], where there is an a ...
Infectious Bursal Disease (Gumboro) in - EDIS
... and often only seen after 3 or 4 flocks. A third factor to consider in the IBD prevention and control program is vaccination of the broilers to prevent clinical IBD. Three categories of vaccines, based on their pathogenicity, have been described: 1) mild, 2) intermediate, and 3) virulent. The interm ...
... and often only seen after 3 or 4 flocks. A third factor to consider in the IBD prevention and control program is vaccination of the broilers to prevent clinical IBD. Three categories of vaccines, based on their pathogenicity, have been described: 1) mild, 2) intermediate, and 3) virulent. The interm ...
LETTERS
... Without therapy, most people infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) ultimately progress to AIDS. Rare individuals (‘elite controllers’) maintain very low levels of HIV RNA without therapy, thereby making disease progression and transmission unlikely. Certain HLA class I alleles are markedl ...
... Without therapy, most people infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) ultimately progress to AIDS. Rare individuals (‘elite controllers’) maintain very low levels of HIV RNA without therapy, thereby making disease progression and transmission unlikely. Certain HLA class I alleles are markedl ...
Genotype Analysis of Measles Viruses, 2002
... mass immunization began (1992) when measles was somewhat controlled by the intervention of vaccine and yet not fully controlled, many of them had become covert susceptible groups. ...
... mass immunization began (1992) when measles was somewhat controlled by the intervention of vaccine and yet not fully controlled, many of them had become covert susceptible groups. ...
Bloodborne Pathogens 1 - Alabama Retail Association
... • Hepatitis B can cause serious health problems • The virus survives well outside the body • Symptoms include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, pain, vomiting, and jaundice • An effective vaccination is available ...
... • Hepatitis B can cause serious health problems • The virus survives well outside the body • Symptoms include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, pain, vomiting, and jaundice • An effective vaccination is available ...
Chapter 3 (Biology and Diseases of Mice)
... PVM causes natural infections of ___, _____, _____, and possibly other rodents and may be infectious for ___________. ...
... PVM causes natural infections of ___, _____, _____, and possibly other rodents and may be infectious for ___________. ...
“Dryland Distemper” C. psedotuberculosis Infections in Horses
... swelling improves, and then therapy with orally administered antimicrobials such as trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole or rifampin are continued to prevent relapse. The time to resolution reported in one study was approximately 35 days.12 Physical therapy, including hydrotherapy, hand walking, and wraps, ...
... swelling improves, and then therapy with orally administered antimicrobials such as trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole or rifampin are continued to prevent relapse. The time to resolution reported in one study was approximately 35 days.12 Physical therapy, including hydrotherapy, hand walking, and wraps, ...
An Overview of Infectious Bronchitis Virus in Chickens Abbreviated t
... been isolated from various non-respiratory tissues including kidneys and different parts of the ...
... been isolated from various non-respiratory tissues including kidneys and different parts of the ...
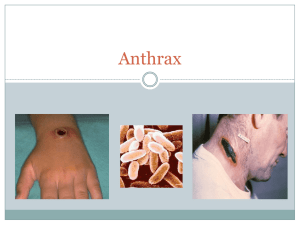
Anthrax
... but humans who come into contact with infected animals can get sick from anthrax too. In the past, the people who were most at risk for anthrax included farm workers, veterinarians, and tannery and wool workers. ...
... but humans who come into contact with infected animals can get sick from anthrax too. In the past, the people who were most at risk for anthrax included farm workers, veterinarians, and tannery and wool workers. ...
Vaccination of healthcare workers
... screening and vaccination programs for all VPDs. For prospective workers, roles are categorised based on risk of exposure to infectious material and risk of acquisition or transmission of specified VPDs to patients. Refer to the Definitions of terms for definitions of existing and prospective worker ...
... screening and vaccination programs for all VPDs. For prospective workers, roles are categorised based on risk of exposure to infectious material and risk of acquisition or transmission of specified VPDs to patients. Refer to the Definitions of terms for definitions of existing and prospective worker ...
Neurologic Manifestations and Outcome of West Nile Virus Infection BRIEF REPORT
... manifest as a mild febrile illness, but a small proportion of patients (⬍1%) develop acute neurologic illness.1-4 Although recent WNV outbreaks have been associated with severe neurologic disease,1-5 retrospective studies have failed to identify clinical features that distinguish WNV from other vira ...
... manifest as a mild febrile illness, but a small proportion of patients (⬍1%) develop acute neurologic illness.1-4 Although recent WNV outbreaks have been associated with severe neurologic disease,1-5 retrospective studies have failed to identify clinical features that distinguish WNV from other vira ...
Virus evolution within patients increases pathogenicity
... PnÞ is larger than before the invasion, and hence Y ¼ i¼1 bi yi should increase. Fig. 1 illustrates the situation where two strains (strains 1 and 3) exist in the initial population, and then strain 2 invades it (a1 =b1 oa2 =b2 oa3 =b3 ). The broken curve in Fig. 1 is for the population before the i ...
... PnÞ is larger than before the invasion, and hence Y ¼ i¼1 bi yi should increase. Fig. 1 illustrates the situation where two strains (strains 1 and 3) exist in the initial population, and then strain 2 invades it (a1 =b1 oa2 =b2 oa3 =b3 ). The broken curve in Fig. 1 is for the population before the i ...
Serological monitoring and interpretation of ELISA results
... l Monitor maternal antibody levels, to time vaccinations. l Prior to vaccinations or at the onset of clinical signs (acute sample). l 2-4 weeks post-vaccination or post-onset of clinical signs (convalescent sample). ...
... l Monitor maternal antibody levels, to time vaccinations. l Prior to vaccinations or at the onset of clinical signs (acute sample). l 2-4 weeks post-vaccination or post-onset of clinical signs (convalescent sample). ...
Epidemic Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis in La Guajira, Colombia
... 1993. No other month in these 3 years had as many as 40 abortions. Because most of the women lived in rural areas (rancherias) without known addresses, only 10 were located for serologic testing. One had a positive result, a similar proportion as the general population. Epidemiologic field investiga ...
... 1993. No other month in these 3 years had as many as 40 abortions. Because most of the women lived in rural areas (rancherias) without known addresses, only 10 were located for serologic testing. One had a positive result, a similar proportion as the general population. Epidemiologic field investiga ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.