fvrcp - Oak Harbor Pet Haven
... Rhinotracheitis is a severe upper respiratory infection caused by a feline type 1, herpes-virus. It is most severe in young kittens and older cats, and is one of the most serious upper respiratory diseases seen in the feline species. The virus is airborne and very contagious in susceptible animals. ...
... Rhinotracheitis is a severe upper respiratory infection caused by a feline type 1, herpes-virus. It is most severe in young kittens and older cats, and is one of the most serious upper respiratory diseases seen in the feline species. The virus is airborne and very contagious in susceptible animals. ...
Zoonoses of Small Mammals
... ■ Currently, transmission of rabies from small mammal pets to humans has not been documented. ■ Interactions between infected ferrets and humans have been limited by exposure and requirements for postexposure prophylaxis only; there is no documentation of transmission to date. ■ Ferrets require annu ...
... ■ Currently, transmission of rabies from small mammal pets to humans has not been documented. ■ Interactions between infected ferrets and humans have been limited by exposure and requirements for postexposure prophylaxis only; there is no documentation of transmission to date. ■ Ferrets require annu ...
Latent TB Infection - National Center for Health in Public Housing
... close contacts and HIV- ...
... close contacts and HIV- ...
Chlamydia trachomatis infections - Leeds, Grenville and Lanark
... to 70% of sexually active females with chlamydia infection are asymptomatic. Can present as chlamydial pneumonia and conjunctivitis (Ophthalmia neonatorum) in infants. ...
... to 70% of sexually active females with chlamydia infection are asymptomatic. Can present as chlamydial pneumonia and conjunctivitis (Ophthalmia neonatorum) in infants. ...
Leptospirosis
... the urine of infected animals. Rats, Mice and Moles are important primary host. These rodents pay an important role in transmitting the disease to animals and men. Leptospirosis is an OIE Reportable Diseases in Multiple Species Disease Category. Leptospirosis is among the world's most common disease ...
... the urine of infected animals. Rats, Mice and Moles are important primary host. These rodents pay an important role in transmitting the disease to animals and men. Leptospirosis is an OIE Reportable Diseases in Multiple Species Disease Category. Leptospirosis is among the world's most common disease ...
Neospora factsheet.
... that results in abortion and stillbirth. Neospora parasites cause problems in the placenta, brain and sometimes other organs in the developing foetus. A recent survey of aborting cattle within Scotland, conducted by scientists at Moredun in collaboration with SACVS, showed that 16% of aborted foetus ...
... that results in abortion and stillbirth. Neospora parasites cause problems in the placenta, brain and sometimes other organs in the developing foetus. A recent survey of aborting cattle within Scotland, conducted by scientists at Moredun in collaboration with SACVS, showed that 16% of aborted foetus ...
Protozoan diseases
... Using the information that follows, select a disease. After you have selected your disease, your assignments is to write a report about the disease. Include a short paragraph for each of the following topics… ...
... Using the information that follows, select a disease. After you have selected your disease, your assignments is to write a report about the disease. Include a short paragraph for each of the following topics… ...
Childhood
... or blood. These diseases are dangerous and can lead to brain damage, hearing loss, blindness, paralysis, and even death. Symptoms of the disease vary depending on the part of the body infected. Common symptoms of the disease include fever, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, confusion, stiff nec ...
... or blood. These diseases are dangerous and can lead to brain damage, hearing loss, blindness, paralysis, and even death. Symptoms of the disease vary depending on the part of the body infected. Common symptoms of the disease include fever, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, confusion, stiff nec ...
4- surgical_infectio..
... Superinfection in patients in long term oral antibiotic therapy Cl. Difficile Watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever Diagnosis needs Sigmoidoscopy, stool- culture and toxin assay ...
... Superinfection in patients in long term oral antibiotic therapy Cl. Difficile Watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever Diagnosis needs Sigmoidoscopy, stool- culture and toxin assay ...
diagnostic dead ends? so what™s the next step?
... treatment. Collection of the gastric swab for either immunohistochemical staining or PCR can be done with a standard culture swab extended with sterile tubing passed in an intubated, anesthetized ferret. The stomach is gently manipulated externally to allow contact between the swab and gastric mucos ...
... treatment. Collection of the gastric swab for either immunohistochemical staining or PCR can be done with a standard culture swab extended with sterile tubing passed in an intubated, anesthetized ferret. The stomach is gently manipulated externally to allow contact between the swab and gastric mucos ...
12 L.Interventions for Clients with Infection
... proper hand washing. Artificial fingernails create poor hand hygiene. Gloves should be worn. The CDC provides guidelines for disinfection and sterilization, outlining standard precautions for all modes of transmission. ...
... proper hand washing. Artificial fingernails create poor hand hygiene. Gloves should be worn. The CDC provides guidelines for disinfection and sterilization, outlining standard precautions for all modes of transmission. ...
Ch.13 Part II
... • A live animal (other than human) that transmits an infectious agent from one host to another is called a vector • Majority of vectors are arthropods – fleas, mosquitoes, flies, and ticks • Some larger animals can also spread infection – mammals, birds, lower vertebrates • Biological vectors – acti ...
... • A live animal (other than human) that transmits an infectious agent from one host to another is called a vector • Majority of vectors are arthropods – fleas, mosquitoes, flies, and ticks • Some larger animals can also spread infection – mammals, birds, lower vertebrates • Biological vectors – acti ...
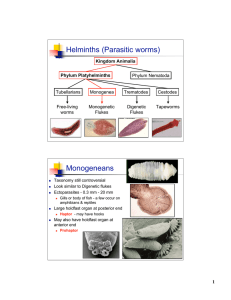
Helminths (Parasitic worms) Monogeneans
... About 2.4 million humans worldwide are infected. Transmission to D.H.: Ingestion of metacercaria. Human infections usually come from ingestion in water or on water cress. Location in Definitive Host: Liver, particularly bile duct. ...
... About 2.4 million humans worldwide are infected. Transmission to D.H.: Ingestion of metacercaria. Human infections usually come from ingestion in water or on water cress. Location in Definitive Host: Liver, particularly bile duct. ...
16.9 Infective agents 2 - fungi, protozoa and larger parasites
... cause the hair to fall out, are called ringworm (it’s not a worm, it’s a fungus!) and an itchy infection in the groin is called dhobi’s itch. Tinea or similar fungi are responsible for all these conditions. Tinea is highly infectious (easily passed from one person to another) but can be avoided by g ...
... cause the hair to fall out, are called ringworm (it’s not a worm, it’s a fungus!) and an itchy infection in the groin is called dhobi’s itch. Tinea or similar fungi are responsible for all these conditions. Tinea is highly infectious (easily passed from one person to another) but can be avoided by g ...
What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis
... drugs that kill TB germs. But TB germs are strong. It takes at least six to nine months of medication to wipe them all out. It is very important that you take all your medication. • If you stop taking medication too soon, it is a big problem. The TB germs that are still alive ...
... drugs that kill TB germs. But TB germs are strong. It takes at least six to nine months of medication to wipe them all out. It is very important that you take all your medication. • If you stop taking medication too soon, it is a big problem. The TB germs that are still alive ...
Trichinosis

Trichinosis, trichinellosis or trichiniasis is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the genus Trichinella. Several subspecies cause human disease, but T. spiralis is the most known. Infection may occur without symptoms, while intestinal invasion can cause diarrhea, abdominal pain or vomiting. Larval migration into muscle tissue (one week after being infected) can cause edema of the face or around the eyes, conjunctivitis, fever, muscle pains, splinter hemorrhages, rashes, and peripheral eosinophilia. Life-threatening cases can result in myocarditis, central nervous system involvement, and pneumonitis. Larval encystment in the muscles causes pain and weakness, followed by slow progression of symptoms.Trichinosis is mainly caused by eating undercooked meat containing encysted larval Trichinella. In the stomach the larvae are exposed to stomach acid and pepsin which releases them from their cysts. They then start invading wall of the small intestine, where they develop into adult worms. Females are 2.2 mm in length; males 1.2 mm. The life span in the small intestine is about four weeks. After 1 week, the females release more larvae that migrate to voluntarily controlled muscles where they encyst. Diagnosis is usually made based on symptoms, and is confirmed by serology or by finding encysted or non-encysted larvae in biopsy or autopsy samples.The best way to prevent trichinellosis is to cook meat to safe temperatures. Using food thermometers can make sure the temperature inside the meat is high enough to kill the parasites. The meat should not be tasted until it is completely cooked. Once infection has been verified treatment with antiparasitic drugs such as albendazole or mebendazole should be started at once. A fast response may help kill adult worms and thereby stop further release of larvae. Once the larvae have established in muscle cells, usually by 3 to 4 weeks after infection, treatment may not completely get rid of the infection or symptoms. Both drugs are considered safe but have been associated with side effects such as bone marrow suppression. Patients on longer courses should be monitored though regular blood counts to detect adverse effects quickly and then discontinue treatment. Both medicines should be treated with caution during pregnancy or children under the age of 2 years, but the WHO weighs the benefits of treatment higher than the risks. In addition to antiparasitic medication, treatment with steroids is sometimes required in severe cases.Trichinosis can be acquired by eating both domestic and wild animals, but is not soil-transmitted.