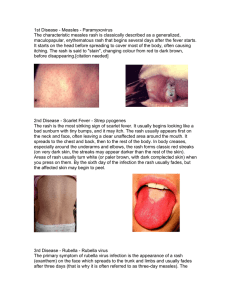
1st Disease - Measles
... comprises cardiac, cerebral, ophthalmic and auditory defects.[7] It may also cause prematurity, low birth weight, and neonatal thrombocytopenia, anaemia and hepatitis. The risk of major defects or organogenesis is highest for infection in the first trimester. CRS is the main reason a vaccine for rub ...
... comprises cardiac, cerebral, ophthalmic and auditory defects.[7] It may also cause prematurity, low birth weight, and neonatal thrombocytopenia, anaemia and hepatitis. The risk of major defects or organogenesis is highest for infection in the first trimester. CRS is the main reason a vaccine for rub ...
Infection Prevention
... Examples: tuberculosis, measles, chicken pox, smallpox and aspergillus Germs carried in this manner may be dispersed over long distances by air currents and may be inhaled by susceptible individuals who have not had face-to-face contact with the infectious individual. Blood-Borne Transmission Blood- ...
... Examples: tuberculosis, measles, chicken pox, smallpox and aspergillus Germs carried in this manner may be dispersed over long distances by air currents and may be inhaled by susceptible individuals who have not had face-to-face contact with the infectious individual. Blood-Borne Transmission Blood- ...
Pulmonary Lecture Preview
... Acute Bronchitis is generally viewed as a self limiting condition, due to upper airway infection ...
... Acute Bronchitis is generally viewed as a self limiting condition, due to upper airway infection ...
EN: Procalcitonin (PCT) Reference Ranges
... relevant bacterial infections and continue to rise with the in creasing severity of the disease. However, as an expression of individually different immune responses and different clinical situations, the same focus of infection may be associated with varying individual elevations in PCT concentrati ...
... relevant bacterial infections and continue to rise with the in creasing severity of the disease. However, as an expression of individually different immune responses and different clinical situations, the same focus of infection may be associated with varying individual elevations in PCT concentrati ...
microbes without borders: key facts on infectious diseases
... them at high risk of becoming infected, such as injecting drug users and people with multiple sex partners. Hepatitis C is the most common form of viral hepatitis in the EU. The epidemiological situation in the EU is largely unclear, due to lack of comparable national surveillance data. The disease ...
... them at high risk of becoming infected, such as injecting drug users and people with multiple sex partners. Hepatitis C is the most common form of viral hepatitis in the EU. The epidemiological situation in the EU is largely unclear, due to lack of comparable national surveillance data. The disease ...
Innate and Adaptive Immune Pathways Regulating Allergic Lung
... 2. A. niger infection induces allergic lung disease in mice through active infection. 3. A. niger induces atopy to bystander antigens, but not itself. Paul Porter, PhD ...
... 2. A. niger infection induces allergic lung disease in mice through active infection. 3. A. niger induces atopy to bystander antigens, but not itself. Paul Porter, PhD ...
Infection Prevention and Exposure Control
... Needle (sharps) Safety: Do not bend, recap, or purposely break used needles. Place used needles in a sharps disposal container. Ensure that sharps disposal containers are puncture resistant, labeled with a biohazard label, and leak-proof. Sharps Containers: Puncture resistant sharps containers are t ...
... Needle (sharps) Safety: Do not bend, recap, or purposely break used needles. Place used needles in a sharps disposal container. Ensure that sharps disposal containers are puncture resistant, labeled with a biohazard label, and leak-proof. Sharps Containers: Puncture resistant sharps containers are t ...
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
... in persons with no history or clinical evidence of syphilis; two types: ...
... in persons with no history or clinical evidence of syphilis; two types: ...
Feline Leukemia
... related, FeLV and FIV differ in many ways, including their shape: FeLV is more circular while FIV is elongated. The two viruses are also quite different genetically, and their protein consituents are dissimlar in size and composition. Although many of the diseases caused by FeLV and FIV are similar, ...
... related, FeLV and FIV differ in many ways, including their shape: FeLV is more circular while FIV is elongated. The two viruses are also quite different genetically, and their protein consituents are dissimlar in size and composition. Although many of the diseases caused by FeLV and FIV are similar, ...
chapter 26
... APSGN is an antibody-antigen disease that occurs as a result of certain strains of the Group A ß-hemolytic streptococcal infection and is most commonly seen in children between the ages of 6 and 7. The exact mechanism of the pathophysiology for APSGN is not certain. It is believed that immune comple ...
... APSGN is an antibody-antigen disease that occurs as a result of certain strains of the Group A ß-hemolytic streptococcal infection and is most commonly seen in children between the ages of 6 and 7. The exact mechanism of the pathophysiology for APSGN is not certain. It is believed that immune comple ...
here - Boston University Medical Campus
... diaper pin injury. Over the next few hours a rapidly progressive generalized petechial rash developed resulting in several areas of cutaneous necrosis despite appropriate antibiotic administration. Neisseria meningitidis was cultured from her spinal fluid. ...
... diaper pin injury. Over the next few hours a rapidly progressive generalized petechial rash developed resulting in several areas of cutaneous necrosis despite appropriate antibiotic administration. Neisseria meningitidis was cultured from her spinal fluid. ...
NAME OF DISEASE HEALTH ALERT
... therapy: Doxycline 100 mg IV/PO twice daily, combined with either streptomycin 1 gm IM once or twice daily for up to 2 weeks; OR rifampin 600-900 mg PO daily for 6 weeks; OR gentamicin 5 mg/kg/day IV in 2 divided doses for up to 2 weeks. This regimen, dosage-adjusted to body weight, is also first-li ...
... therapy: Doxycline 100 mg IV/PO twice daily, combined with either streptomycin 1 gm IM once or twice daily for up to 2 weeks; OR rifampin 600-900 mg PO daily for 6 weeks; OR gentamicin 5 mg/kg/day IV in 2 divided doses for up to 2 weeks. This regimen, dosage-adjusted to body weight, is also first-li ...
Understanding Avian Laboratory Tests
... malnutrition or disease conditions causing protein loss, which can sometimes occur in chronic gastrointestinal disease. Dehydration can cause an increase in the protein levels. White Blood Cell (WBC) Count White blood cells, also called leukocytes, are an important part of the body’s defense against ...
... malnutrition or disease conditions causing protein loss, which can sometimes occur in chronic gastrointestinal disease. Dehydration can cause an increase in the protein levels. White Blood Cell (WBC) Count White blood cells, also called leukocytes, are an important part of the body’s defense against ...
Overwhelming Parasitemia with Plasmodium falciparum Infection in
... and cerebral malaria seen in this patient may have been associated with her use of infliximab for management of rheumatoid arthritis. Although it may be argued that her use of methotrexate 1 month prior to her infection confounds this association, we make the following 3 points: (1) the pharmacokine ...
... and cerebral malaria seen in this patient may have been associated with her use of infliximab for management of rheumatoid arthritis. Although it may be argued that her use of methotrexate 1 month prior to her infection confounds this association, we make the following 3 points: (1) the pharmacokine ...
12-11-13 The Central Nervous System fections
... meningitidis years 25–49% of cases in children aged 5–15 years 10–35% of cases in adults Haemophilus Most common agent in patients aged 1–5 influenzae years 40–60% of cases in children aged 1–5 years 2% of cases in adults ...
... meningitidis years 25–49% of cases in children aged 5–15 years 10–35% of cases in adults Haemophilus Most common agent in patients aged 1–5 influenzae years 40–60% of cases in children aged 1–5 years 2% of cases in adults ...
Development of a Murine Model of Cerebral Aspergillosis CONCISE COMMUNICATION
... though these strains have been shown to be more susceptible to a variety of fungal infections, including CNS infection with the fungus Saccharomyces cerevisiae and pulmonary infection with A. fumigatus [3, 4]. In this model, the infection spreads to other organs, but the fungus burden in the brain r ...
... though these strains have been shown to be more susceptible to a variety of fungal infections, including CNS infection with the fungus Saccharomyces cerevisiae and pulmonary infection with A. fumigatus [3, 4]. In this model, the infection spreads to other organs, but the fungus burden in the brain r ...
General Characteristics of the Organism
... weeks. SECONDARY STAGE: It occur 6 weeks to 6 months after the chancre heals. Symptoms of this stage includes, headache and malaise, general lymphoadenopathy and a variety of skin rashes, hepatitis, meningitis, glmerulnephritis and nephritis. Nephrosis is a result of Antigen antibody complexes ...
... weeks. SECONDARY STAGE: It occur 6 weeks to 6 months after the chancre heals. Symptoms of this stage includes, headache and malaise, general lymphoadenopathy and a variety of skin rashes, hepatitis, meningitis, glmerulnephritis and nephritis. Nephrosis is a result of Antigen antibody complexes ...
Clostridium difficile Management
... Easily accessible dedicated handwashing sink Handwashing sinks need to comply with Health Building Note (HBN) 95 and Health Technical Memorandum (HTM) 64 No plugs or overflows The water jet must not flow directly into the plughole. This reduces the generation of contaminated aerosols Sink, taps and ...
... Easily accessible dedicated handwashing sink Handwashing sinks need to comply with Health Building Note (HBN) 95 and Health Technical Memorandum (HTM) 64 No plugs or overflows The water jet must not flow directly into the plughole. This reduces the generation of contaminated aerosols Sink, taps and ...
Antibiotics: Potential Harms - Canadian Pharmacists Association
... Hyperkalemia with cotrimoxazole: in older adults taking medications which can raise potassium (such as ACEIs, ARBs, spironolactone, or NSAIDs), cotrimoxazole was associated with sudden death (NNH ≈ 300).19,20 Contraceptive failure/drug interaction? Although this is thought to be unlikely, there ...
... Hyperkalemia with cotrimoxazole: in older adults taking medications which can raise potassium (such as ACEIs, ARBs, spironolactone, or NSAIDs), cotrimoxazole was associated with sudden death (NNH ≈ 300).19,20 Contraceptive failure/drug interaction? Although this is thought to be unlikely, there ...
Running head: SEVERE ACUTE RESPIRATORY SYNDROME
... Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome or SARS is a newly emerging infection that was first seen in China in late 2002 (Rhinehart, Jackson, & Chiarello, 2007). The viral respiratory illness quickly spread to more than two dozen countries including North America, South America, Europe, and throughout Asia ...
... Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome or SARS is a newly emerging infection that was first seen in China in late 2002 (Rhinehart, Jackson, & Chiarello, 2007). The viral respiratory illness quickly spread to more than two dozen countries including North America, South America, Europe, and throughout Asia ...
Antibiotics: Potential Harms
... Hyperkalemia with cotrimoxazole: in older adults taking medications which can raise potassium (such as ACEIs, ARBs, spironolactone, or NSAIDs), cotrimoxazole was associated with sudden death (NNH ≈ 300).19,20 Contraceptive failure/drug interaction? Although this is thought to be unlikely, there ...
... Hyperkalemia with cotrimoxazole: in older adults taking medications which can raise potassium (such as ACEIs, ARBs, spironolactone, or NSAIDs), cotrimoxazole was associated with sudden death (NNH ≈ 300).19,20 Contraceptive failure/drug interaction? Although this is thought to be unlikely, there ...
54 year old male with fever, altered mental status
... reaction against the drug or metabolite One suggested mechanism is hypersensitivity to the drug as a hapten with an CSF-protein which would explain the limitation of the inflammation to only the central nervous system. Some patients have idiosyncratic reactions to only one NSAID while others have be ...
... reaction against the drug or metabolite One suggested mechanism is hypersensitivity to the drug as a hapten with an CSF-protein which would explain the limitation of the inflammation to only the central nervous system. Some patients have idiosyncratic reactions to only one NSAID while others have be ...
West Nile Virus
... Flaviviruses are found in arthropods like mosquitoes and ticks which then infect the human. These viruses cause encephalitis and other hemorrhagic diseases. VIrulence factors specific to WNV: -Capsid Protein binds and protects viral RNA -Premembrane helps fold the envelope protein into correct shape ...
... Flaviviruses are found in arthropods like mosquitoes and ticks which then infect the human. These viruses cause encephalitis and other hemorrhagic diseases. VIrulence factors specific to WNV: -Capsid Protein binds and protects viral RNA -Premembrane helps fold the envelope protein into correct shape ...
The Removal of Metalwork in Children
... Patterns of skeletal fractures in child abuse: systematic review. BMJ 337: a1518. ...
... Patterns of skeletal fractures in child abuse: systematic review. BMJ 337: a1518. ...
Epidemiological studies
... Childhood leukemia and infectious diseases in the first year of life: a registerbased case-control study. Am J Epidemiol, 1986. 124(4): p. 590-4. Grossarth-Maticek, R., et al., Reported herpes-virus-infection, fever and cancer incidence in a prospective study. J Chronic Dis, 1987. 40(10): p. 96776. ...
... Childhood leukemia and infectious diseases in the first year of life: a registerbased case-control study. Am J Epidemiol, 1986. 124(4): p. 590-4. Grossarth-Maticek, R., et al., Reported herpes-virus-infection, fever and cancer incidence in a prospective study. J Chronic Dis, 1987. 40(10): p. 96776. ...
Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will go on to develop liver failure, liver cancer, or life-threatening esophageal and gastric varices.HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with intravenous drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, and transfusions. An estimated 150–200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. The existence of hepatitis C – originally identifiable only as a type of non-A non-B hepatitis – was suggested in the 1970s and proven in 1989. Hepatitis C infects only humans and chimpanzees. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The virus persists in the liver in about 85% of those infected. This chronic infection can be treated with medication: the standard therapy is a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin, with either boceprevir or telaprevir added in some cases. Overall, 50–80% of people treated are cured. Those who develop cirrhosis or liver cancer may require a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is the leading reason for liver transplantation, though the virus usually recurs after transplantation. No vaccine against hepatitis C is available. About 343,000 deaths due to liver cancer from hepatitis C occurred in 2013, up from 198,000 in 1990. An additional 358,000 in 2013 occurred due to cirrhosis.























