Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii Infection in
... or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Reprints or correspondence: Dr Jeffrey L. Jones, Mailstop F-22, Div of Parasitic Diseases, National Center for Zoonotic, Vectorborne, and Enteric Diseases, Coordinating Center for Infectious Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 4770 ...
... or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Reprints or correspondence: Dr Jeffrey L. Jones, Mailstop F-22, Div of Parasitic Diseases, National Center for Zoonotic, Vectorborne, and Enteric Diseases, Coordinating Center for Infectious Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 4770 ...
Prions - Recent
... could not be ascribed to one of the classical CJD categories i.e. sporadic (sCJD), hereditary or acquired. Hence, they were classified as variant CJD (vCJD). Later on, experimental evidence suggested that vCJD was caused by prions postulated as unique novel infectious agents and, for example, respon ...
... could not be ascribed to one of the classical CJD categories i.e. sporadic (sCJD), hereditary or acquired. Hence, they were classified as variant CJD (vCJD). Later on, experimental evidence suggested that vCJD was caused by prions postulated as unique novel infectious agents and, for example, respon ...
Facts on Zika Virus • Mosquito Species Involved
... • One of five infected with Zika will have symptoms • Symptoms usually begin 2 to 7 days after infection • Once person is infected, there is a period of 7 to 10 days for mosquito to acquire the virus from them ...
... • One of five infected with Zika will have symptoms • Symptoms usually begin 2 to 7 days after infection • Once person is infected, there is a period of 7 to 10 days for mosquito to acquire the virus from them ...
Vaccine Preventable disease (Topic 3)
... • Different sections of population affected – rotavirus more associated with infants and young children ...
... • Different sections of population affected – rotavirus more associated with infants and young children ...
Infectious Disease Control Guideline
... The National Health Policy envisions, "All Nepali citizens to have the physical, mental, social and spiritual health to lead productive and quality lives". The following strategies will be adopted in infectious disease control: a. Along with the addition of necessary immunization services, the curre ...
... The National Health Policy envisions, "All Nepali citizens to have the physical, mental, social and spiritual health to lead productive and quality lives". The following strategies will be adopted in infectious disease control: a. Along with the addition of necessary immunization services, the curre ...
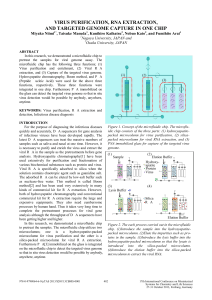
virus purification, rna extraction, and targeted genome capture in
... Viral RNA is specifically adsorbed to silica when the solution contains chaotropic agent such as guanidine salt. The adsorbed RNA can be eluted by low-salt buffer such as nuclease-free water. This method is called Boom method[2] and has been used very extensively in many kinds of commercial kit for ...
... Viral RNA is specifically adsorbed to silica when the solution contains chaotropic agent such as guanidine salt. The adsorbed RNA can be eluted by low-salt buffer such as nuclease-free water. This method is called Boom method[2] and has been used very extensively in many kinds of commercial kit for ...
quick reference guide - Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust
... Viral haemorrhagic fevers - a group of illnesses that are caused by several distinct families of viruses e.g. Ebola, Lassa fever, Crimean Congo haemorrhagic fever, Dengue fever, Yellow fever. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) - is transmitted through the bite of an infected tick, contaminatio ...
... Viral haemorrhagic fevers - a group of illnesses that are caused by several distinct families of viruses e.g. Ebola, Lassa fever, Crimean Congo haemorrhagic fever, Dengue fever, Yellow fever. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) - is transmitted through the bite of an infected tick, contaminatio ...
German Center for Infection Research
... 158 healthy adults. “The preliminary results on tolerability and safety, as well as the immune response, are promising,” explains DZIF researcher Prof Marylyn Addo, who is leading the trial at the UKE. “The data from this trial are very helpful for further clinical trials, for example on people who ...
... 158 healthy adults. “The preliminary results on tolerability and safety, as well as the immune response, are promising,” explains DZIF researcher Prof Marylyn Addo, who is leading the trial at the UKE. “The data from this trial are very helpful for further clinical trials, for example on people who ...
Lymphadenopathy in Children
... Increasing size over 2 weeks No decrease over 4-6 weeks Not return to baseline in 8-12 weeks No change despite course of antibiotic Abnormal Chest X ray Supraclavicular node Rubbery consistency Systemic symptoms: Fever/Wt.Loss/Arthralgia/Hepatosplenomegaly ...
... Increasing size over 2 weeks No decrease over 4-6 weeks Not return to baseline in 8-12 weeks No change despite course of antibiotic Abnormal Chest X ray Supraclavicular node Rubbery consistency Systemic symptoms: Fever/Wt.Loss/Arthralgia/Hepatosplenomegaly ...
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical findings and
... in humans with adult respiratory distress syndrome ...
... in humans with adult respiratory distress syndrome ...
Viruses, chemicals and co-carcinogenesis
... among 115 HCC patients and 230 non-liver cancer controls. Markers of HBV infection, HBsAg and/or antibody to HBV core were found in 24% of patients, and antibodies to HCV in 23%. Multivariate analysis revealed an odds ratio for HCV infection of 15.3 (CI 4.3–54.4), HBsAg of 12.6 (2.5–63.1), heavy alc ...
... among 115 HCC patients and 230 non-liver cancer controls. Markers of HBV infection, HBsAg and/or antibody to HBV core were found in 24% of patients, and antibodies to HCV in 23%. Multivariate analysis revealed an odds ratio for HCV infection of 15.3 (CI 4.3–54.4), HBsAg of 12.6 (2.5–63.1), heavy alc ...
West Nile Virus Surveillance in Illinois, 2005
... cases rose from 49 to 132 (an increase of 269 percent) (Table 1, Figure 1). In adults ages 18 to 64 years, the number of cases rose from 13 to 37 (285%), while in adults age >65 years, the number of cases rose from 16 to 58 (363%). The number of cases in children aged <5 years also rose from 1999 to ...
... cases rose from 49 to 132 (an increase of 269 percent) (Table 1, Figure 1). In adults ages 18 to 64 years, the number of cases rose from 13 to 37 (285%), while in adults age >65 years, the number of cases rose from 16 to 58 (363%). The number of cases in children aged <5 years also rose from 1999 to ...
Full Text
... Synthesis. A number of studies have established that vertical transmission of viruses is an important phenomenon affecting a wide range of viruses, especially as a result of breeding programs. Nevertheless, the presence of virus in a seed, does not always lead to seedling infection. In grapevine, se ...
... Synthesis. A number of studies have established that vertical transmission of viruses is an important phenomenon affecting a wide range of viruses, especially as a result of breeding programs. Nevertheless, the presence of virus in a seed, does not always lead to seedling infection. In grapevine, se ...
Zika Virus in the Americas — Yet Another Arbovirus Threat
... as dengue and West Nile. The most historically important of these is yellow fever virus, the first recognized viral cause of deadly epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Zika, which was discovered incidentally in Uganda in 1947 in the course of mosquito and primate surveillance,1 had until now remained an obs ...
... as dengue and West Nile. The most historically important of these is yellow fever virus, the first recognized viral cause of deadly epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Zika, which was discovered incidentally in Uganda in 1947 in the course of mosquito and primate surveillance,1 had until now remained an obs ...
Infection Control Measures
... Infections progress through distinct stages Incubation stage 2. Prodromal stage 3. Acute stage 4. Convalescent stage and , 5. Resolution stage (Table 22-1). The characteristics and length of each stage may differ depending on the infectious agent. For example, the incubation period for the common ...
... Infections progress through distinct stages Incubation stage 2. Prodromal stage 3. Acute stage 4. Convalescent stage and , 5. Resolution stage (Table 22-1). The characteristics and length of each stage may differ depending on the infectious agent. For example, the incubation period for the common ...
Perioperative Services Policy Manual
... • Avoiding placing hands or arms in the laundry or rinse water to keep items submerged; • Using the highest drying setting possible that is safe for the material of attire construction and • Promptly removing attire when dry to avoid desiccation of materials. Laundered surgical attire should be prot ...
... • Avoiding placing hands or arms in the laundry or rinse water to keep items submerged; • Using the highest drying setting possible that is safe for the material of attire construction and • Promptly removing attire when dry to avoid desiccation of materials. Laundered surgical attire should be prot ...
infectious disease as aetiological factor in the
... become a target of T-helper lymphocytes. Superantigens are proteins that are expressed endogenously in the organism or that are derived exogenously by bacteria.51 Numerous infectious agents have been proposed as possible triggering factors in SSc but very few infections are as rare as SSc. Therefore ...
... become a target of T-helper lymphocytes. Superantigens are proteins that are expressed endogenously in the organism or that are derived exogenously by bacteria.51 Numerous infectious agents have been proposed as possible triggering factors in SSc but very few infections are as rare as SSc. Therefore ...
Zika Virus as a Cause of Neurologic Disorders
... risks demand decisive, immediate action to protect public health. The WHO recommends applying key interventions such as intensive mosquito control; personal protection against mosquito bites; provision of appropriate clinical care for all patients with Guillain–Barré syndrome and for women before, d ...
... risks demand decisive, immediate action to protect public health. The WHO recommends applying key interventions such as intensive mosquito control; personal protection against mosquito bites; provision of appropriate clinical care for all patients with Guillain–Barré syndrome and for women before, d ...
Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure EMPLOYEE
... the right to be informed about the risks from a bloodborne or body fluid pathogen exposure and the recommended prophylaxis (retroviral drug) treatment. _____ I have been informed that there are certain side effects which are associated with retroviral drugs. They can include at minimum nausea, vomit ...
... the right to be informed about the risks from a bloodborne or body fluid pathogen exposure and the recommended prophylaxis (retroviral drug) treatment. _____ I have been informed that there are certain side effects which are associated with retroviral drugs. They can include at minimum nausea, vomit ...
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pregnant women in some
... Primary infection with T.gondii in pregnancy is usually asymptomatic, nevertheless infection may be transmitted to the fetus (Morris and Croxson, 2004), and can cause severe damage such as microcephaly, retinochoroditis and cerebral calcification (Falavigna et al., 2007) especially if a women get i ...
... Primary infection with T.gondii in pregnancy is usually asymptomatic, nevertheless infection may be transmitted to the fetus (Morris and Croxson, 2004), and can cause severe damage such as microcephaly, retinochoroditis and cerebral calcification (Falavigna et al., 2007) especially if a women get i ...
Presentation
... Pandemic H1N1: Disease burden estimates • In United States, as of 3/13/2010: – 59.98 million cases – 270, 435 hospitalizations – 12, 271 deaths • Mean age of deaths 37 years – Source: CDC website ...
... Pandemic H1N1: Disease burden estimates • In United States, as of 3/13/2010: – 59.98 million cases – 270, 435 hospitalizations – 12, 271 deaths • Mean age of deaths 37 years – Source: CDC website ...
Word version - kudos concepts
... humans. All species can be affected. Our colony has been free of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for greater than 15 years but we remain vigilant due to the severity of disease following transmission of the bacteria from humans to animals. Tuberculosis causes severe weight loss, lethargy and coughing and ...
... humans. All species can be affected. Our colony has been free of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for greater than 15 years but we remain vigilant due to the severity of disease following transmission of the bacteria from humans to animals. Tuberculosis causes severe weight loss, lethargy and coughing and ...
Cell-to-cell spread of HIV permits ongoing replication
... HIV in the presence of the drug tenofovir. We then examine the drug sensitivity of cell-to-cell spread of HIV4–7, a mode of HIV transmission that can lead to multiple infection events per target cell8–10. Infections originating from cell-free virus decrease strongly in the presence of antiretroviral ...
... HIV in the presence of the drug tenofovir. We then examine the drug sensitivity of cell-to-cell spread of HIV4–7, a mode of HIV transmission that can lead to multiple infection events per target cell8–10. Infections originating from cell-free virus decrease strongly in the presence of antiretroviral ...
Infectious Disease - Medical Association of Atlanta
... about 50 percent of cases, gaining the appropriate nickname of “breakbone” fevers. Incubation period ranges from 3-14 days, but typically occurs 4-7 days after exposure. Gastrointestinal symptoms are common as well. The most severe presentations are dengue hemorrhagic syndrome and dengue shock syndr ...
... about 50 percent of cases, gaining the appropriate nickname of “breakbone” fevers. Incubation period ranges from 3-14 days, but typically occurs 4-7 days after exposure. Gastrointestinal symptoms are common as well. The most severe presentations are dengue hemorrhagic syndrome and dengue shock syndr ...
Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will go on to develop liver failure, liver cancer, or life-threatening esophageal and gastric varices.HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with intravenous drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, and transfusions. An estimated 150–200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. The existence of hepatitis C – originally identifiable only as a type of non-A non-B hepatitis – was suggested in the 1970s and proven in 1989. Hepatitis C infects only humans and chimpanzees. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The virus persists in the liver in about 85% of those infected. This chronic infection can be treated with medication: the standard therapy is a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin, with either boceprevir or telaprevir added in some cases. Overall, 50–80% of people treated are cured. Those who develop cirrhosis or liver cancer may require a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is the leading reason for liver transplantation, though the virus usually recurs after transplantation. No vaccine against hepatitis C is available. About 343,000 deaths due to liver cancer from hepatitis C occurred in 2013, up from 198,000 in 1990. An additional 358,000 in 2013 occurred due to cirrhosis.